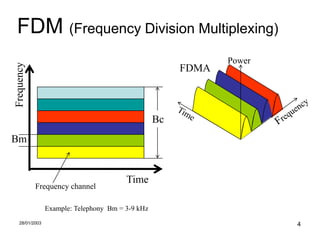
There are three basic forms of multiplexing: frequency-division multiplexing (FDM), time-division multiplexing (TDM), and code-division multiplexing (CDM). FDM involves assigning separate portions of the available frequency spectrum to individual channels to allow simultaneous transmission. Frequency reuse is possible if channels are sufficiently separated in frequency or distance to avoid interference. Higher frequency reuse allows more channels but with smaller separation between cells.





![• Some simple calculations will show that the
output of the system Y, in addition to the linearly
transposed input signals, contains the following
spectral components:
• 1st order
Multiplied version of the input signal
a1[ A(t ) cos( 1t ) B(t ) cos( 2 t ) C (t ) cos( 3t )]
28/01/2003 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g-multiplexing-111206040705-phpapp01/85/Multiplexing-10-320.jpg)




















![DS SS: transmitter
Modulator X Antenna
[A(t), (t)] [g1(t)]
Information
Carrier Modulated signal Spread signal
cos( 0t) S1(t) = A(t) cos( 0t + (t)) g1(t)S1(t)
band Bm Hz band Bc Hz
Bc >> Bm
gi(t): pseudo-random noise (PN) spreading functions that spreads the energy of S1(t) over a bandwidth
considerably wider than that of S1(t): ideally gi(t) gj(t) = 1 if i = j and gi(t) gj(t) = 0 if i j
28/01/2003 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g-multiplexing-111206040705-phpapp01/85/Multiplexing-31-320.jpg)
![DS SS-receiver
To demodulator
Correlator
&
antenna X bandpass
filter
Linear
combination g1(t) g1(t)S1(t)
g1(t)S1(t) Spreading g (t) g (t)S (t)
1 2 2
g2(t)S2(t) function ……. S1(t)
……. [g1(t)] g (t) g (t)S (t)
1 n n
gn(t)Sn(t) g1(t) N(t)
N(t) (noise) g1(t) S’(t)
S’(t)
28/01/2003 41](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g-multiplexing-111206040705-phpapp01/85/Multiplexing-32-320.jpg)
![SS-receiver’s Input
W/Hz Unwanted signals
SS s.: g2(t)S2(t); …;
gn(t)Sn(t)
Other s. : S’(t)
Wanted (spread) signal: g1(t)S1(t) Noise: N(t)
Hz
Bc
Signal-to-interference ratio (S/ I)in = S/ [I( )*Bc]
Bc = Input correlator bandwidth
I( ) = Average spectral power density of unwanted signals in Bc
S= Power of the wanted signal
28/01/2003 42](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g-multiplexing-111206040705-phpapp01/85/Multiplexing-33-320.jpg)
![SS-correlator/ filter output
Wanted (correlated) signal: de-spread to its original bandwidth
as g1(t) g1(t)S1(t) = S1(t) with g1(t) g1(t) = 1
Bm Uncorrelated (unwanted) signals
spread & rejected by correlator + noise
g1(t) S’(t); g1(t) N(t); g1(t) gj(t)Sj(t) = 0
as gi(t) gj(t) = 0 for i j
Signal-to-interference ratio
(S/ I)out = S/ [I( )*Bm]
Bc = Input correlator bandwidth
Bm = Output filter bandwidth
I( ) = Average spectral power density of unwanted signals & noise in Bm
Bc S = power of the wanted signal at the correlator output
Spreading = reducing spectral power density
28/01/2003 43](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g-multiplexing-111206040705-phpapp01/85/Multiplexing-34-320.jpg)
![SS Processing Gain =
= [(S/ I)in/ (S/ I)out ] = ~Bc/ Bm
Example: GPS signal
RF bandwidth Bc ~ 2MHz Filter bandwidth Bm ~ 100 Hz
Processing gain ~20’000 (+43 dB)
Input S/N = -20 dB (signal power = 1% of noise power)
Output S/N = +23 dB (signal power = 200 x noise power)
(GPS = Global Positioning System)
28/01/2003 44](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/g-multiplexing-111206040705-phpapp01/85/Multiplexing-35-320.jpg)









