Embed presentation
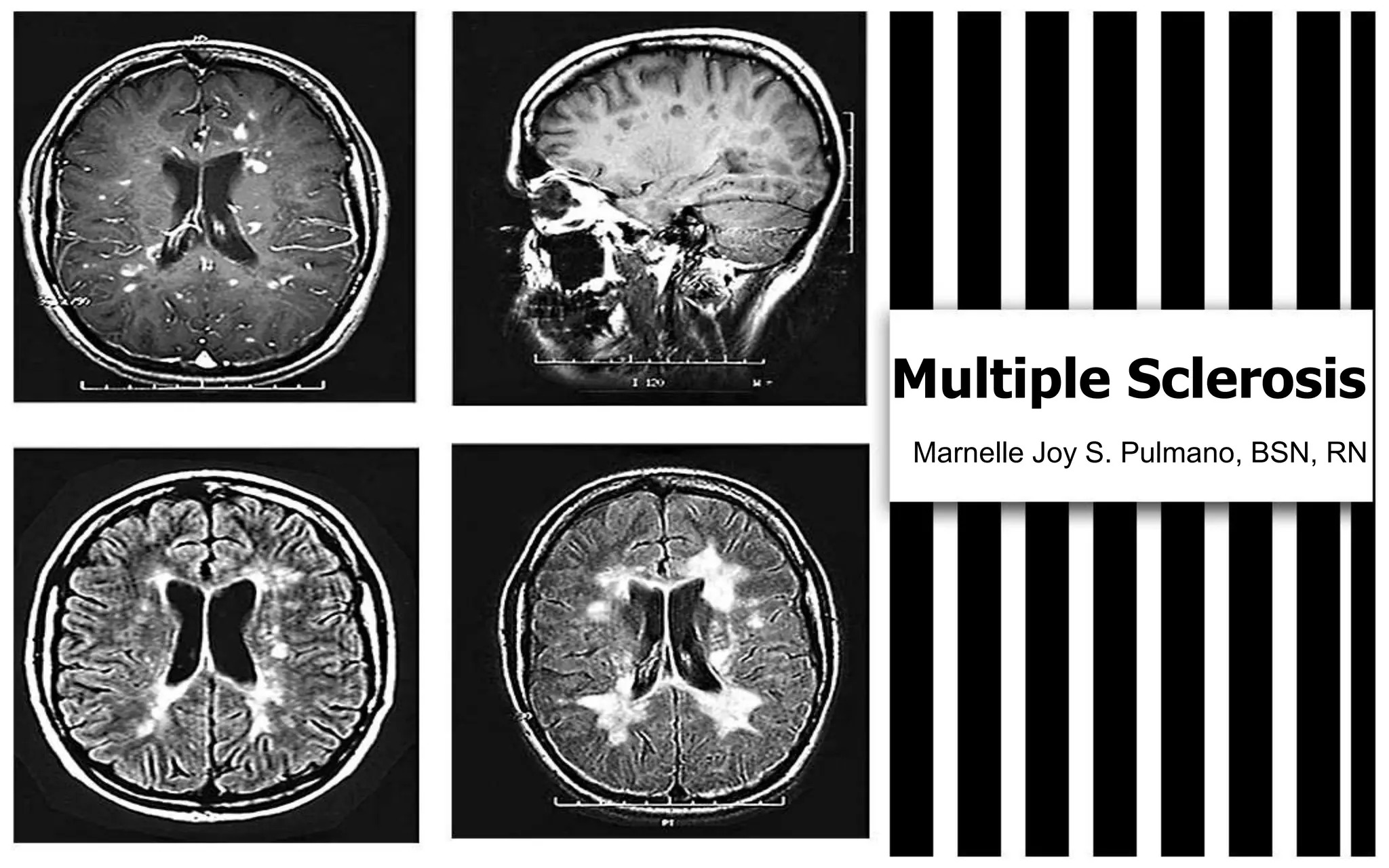















Multiple Sclerosis is a chronic and progressive disorder that affects the brain and spinal cord. It is caused by damage to the myelin sheath, which leads to scarring and decreased nerve conduction. It most commonly occurs in people between 20-40 years old, affects 1 in 1000 people, and is possibly an autoimmune disorder or viral exposure. Symptoms include weakness, impaired vision, fatigue, and loss of coordination. Treatment focuses on controlling symptoms, preserving function, and maximizing quality of life through exercise, nutrition, medication management, and therapy.















