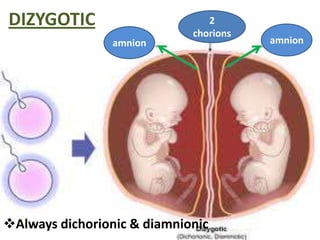
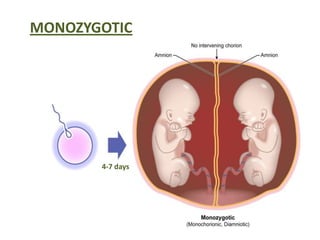
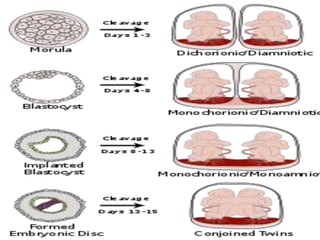
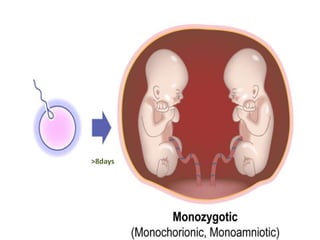
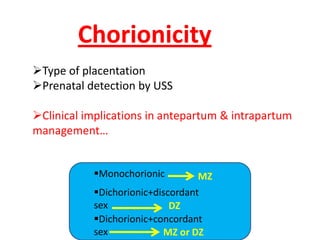
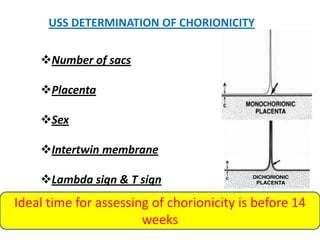
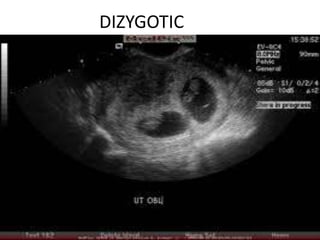
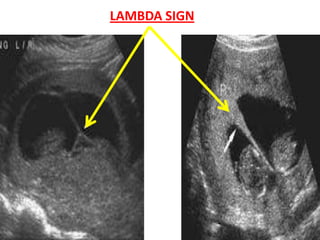
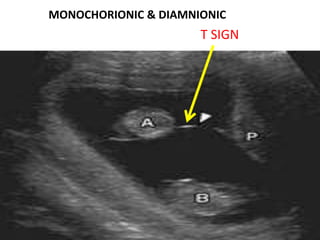
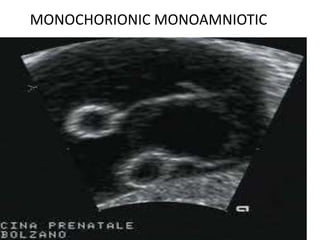
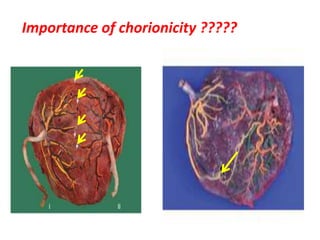
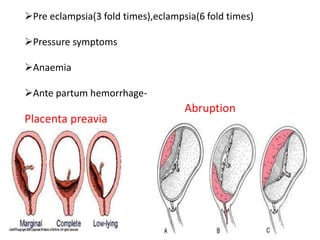
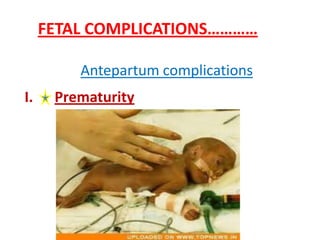
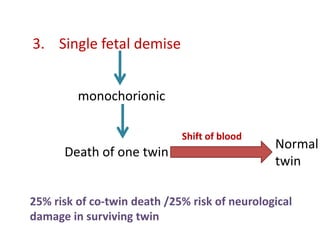
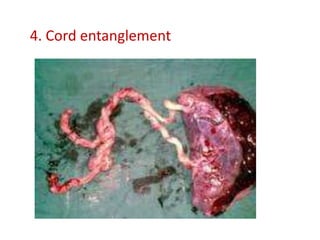
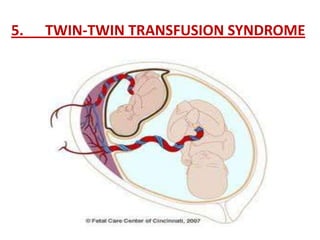
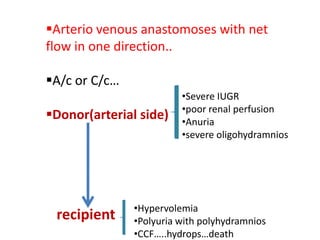
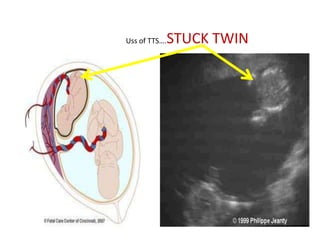
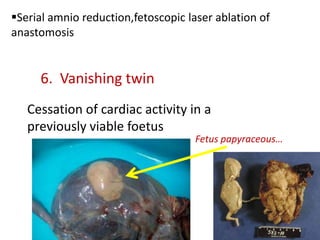
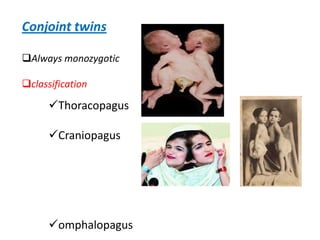
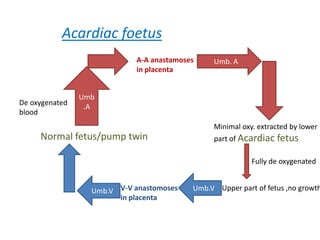
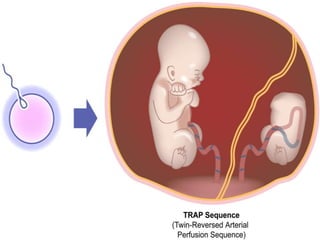
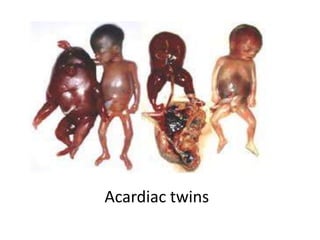
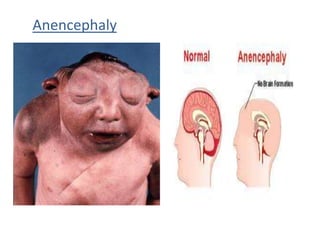
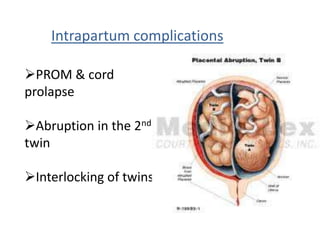
This document discusses multiple pregnancy, specifically twins. It begins by outlining Hellin's Rule which describes the statistical likelihood of having multiples based on maternal factors. It then differentiates between dizygotic and monozygotic twins and describes the key differences. Factors that can increase the chances of dizygotic twins are also outlined. The rest of the document details various maternal and fetal complications that can arise in twin pregnancies such as preeclampsia and preterm birth. Specific complications of monozygotic twins like twin-twin transfusion syndrome are also explained.