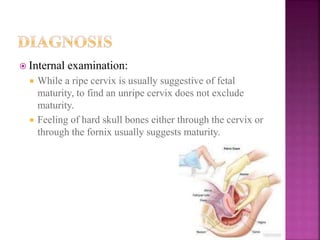
This document discusses post-term or prolonged pregnancy, which is defined as continuing past 294 days or 42 completed weeks of gestation. The risk of stillbirth increases significantly past this point. Signs of post-term pregnancy include slowing or stopping of weight gain, decreasing abdominal girth, and fetal skull bones that feel hard on examination. Risks to the fetus include hypoxia, meconium aspiration, and complications during labor from being large in size. Maternal risks are mainly from potential difficulties in delivery. Close monitoring of the fetus is important to detect any signs of distress.