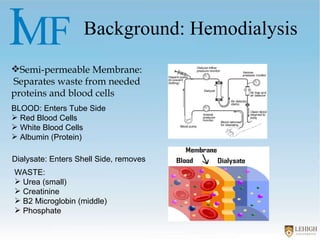
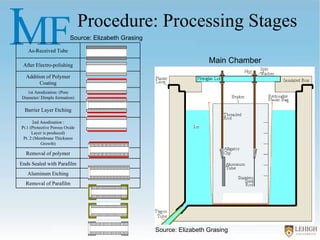
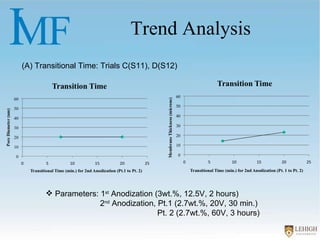
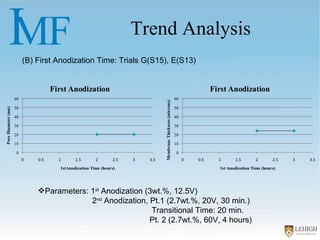
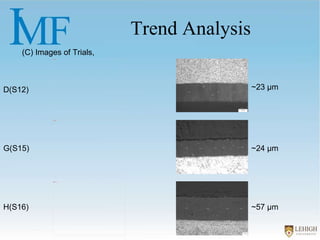
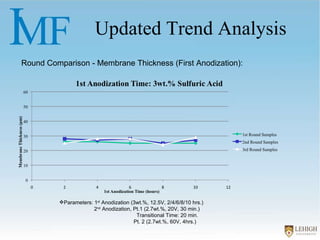
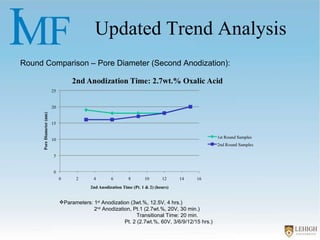
The document describes experiments to create a tapered porous structure in anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) tubular membranes for use in hemodialysis. It outlines procedures for a two-step anodization process using different electrolyte solutions and voltage parameters at each step. Analysis of results from initial experiments showed that membrane thickness increased with voltage and time during second anodization. Future work proposed repeating experiments while systematically varying time parameters to optimize pore size around 20nm and thickness near 60μm.