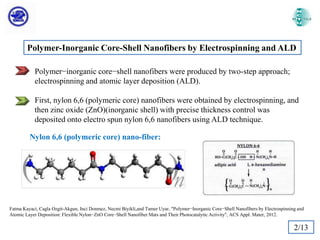
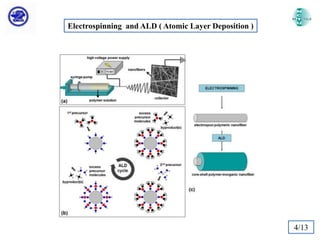
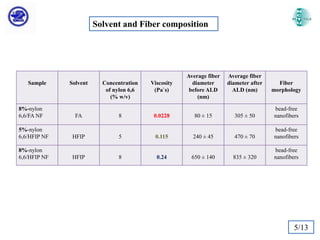
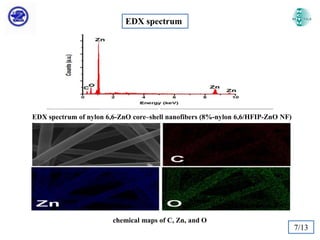
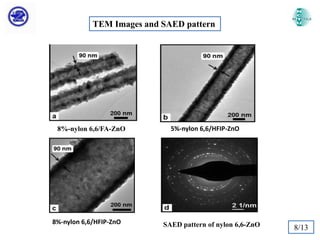
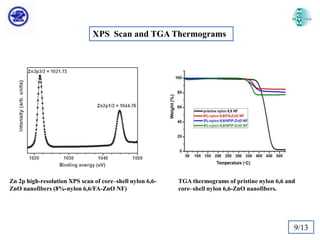
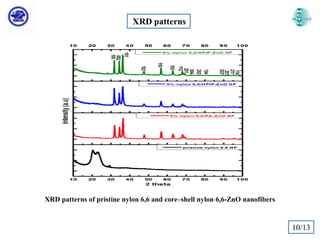
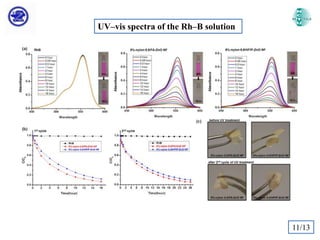
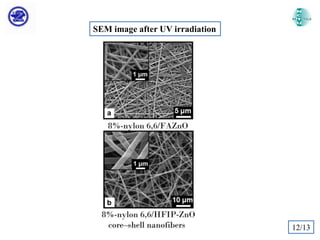
The document discusses Atomic Layer Deposition (ALD) and its application in creating polymer-inorganic core-shell nanofibers. Specifically, it summarizes a study where nylon 6,6 nanofibers produced by electrospinning were coated with zinc oxide using ALD to create flexible nylon-ZnO core-shell nanofiber mats. Characterization techniques like SEM, TEM, EDX, XPS and XRD were used to analyze the core-shell structure and properties. The nanofiber mats exhibited photocatalytic activity and could potentially be used as filter materials for water purification or organic waste treatment.