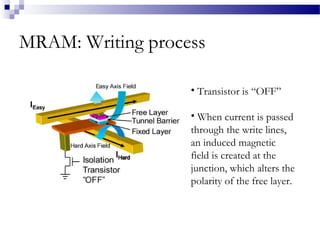
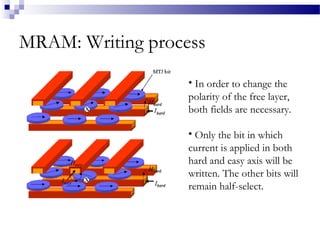
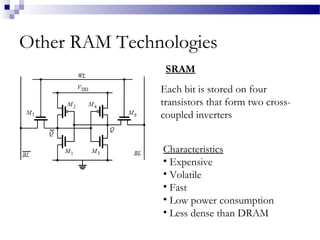
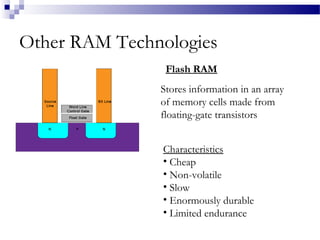
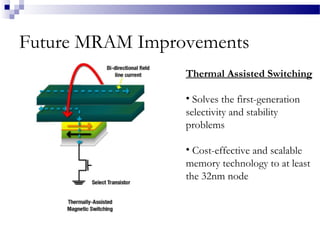
MRAM is a type of non-volatile memory that uses magnetism instead of electricity to store data. It has the potential for unlimited read/write endurance, high speed performance, and lower power consumption compared to other RAM technologies. MRAM uses magnetic tunnel junctions consisting of two ferromagnetic plates separated by an insulator, where one plate's magnetization represents a 1 and the other a 0. Over time, MRAM development has improved switching speed and density, with multi-Mbit demonstration chips produced in the 2000s and research continuing on thermal assisted switching and spin torque transfer to enable smaller geometries.