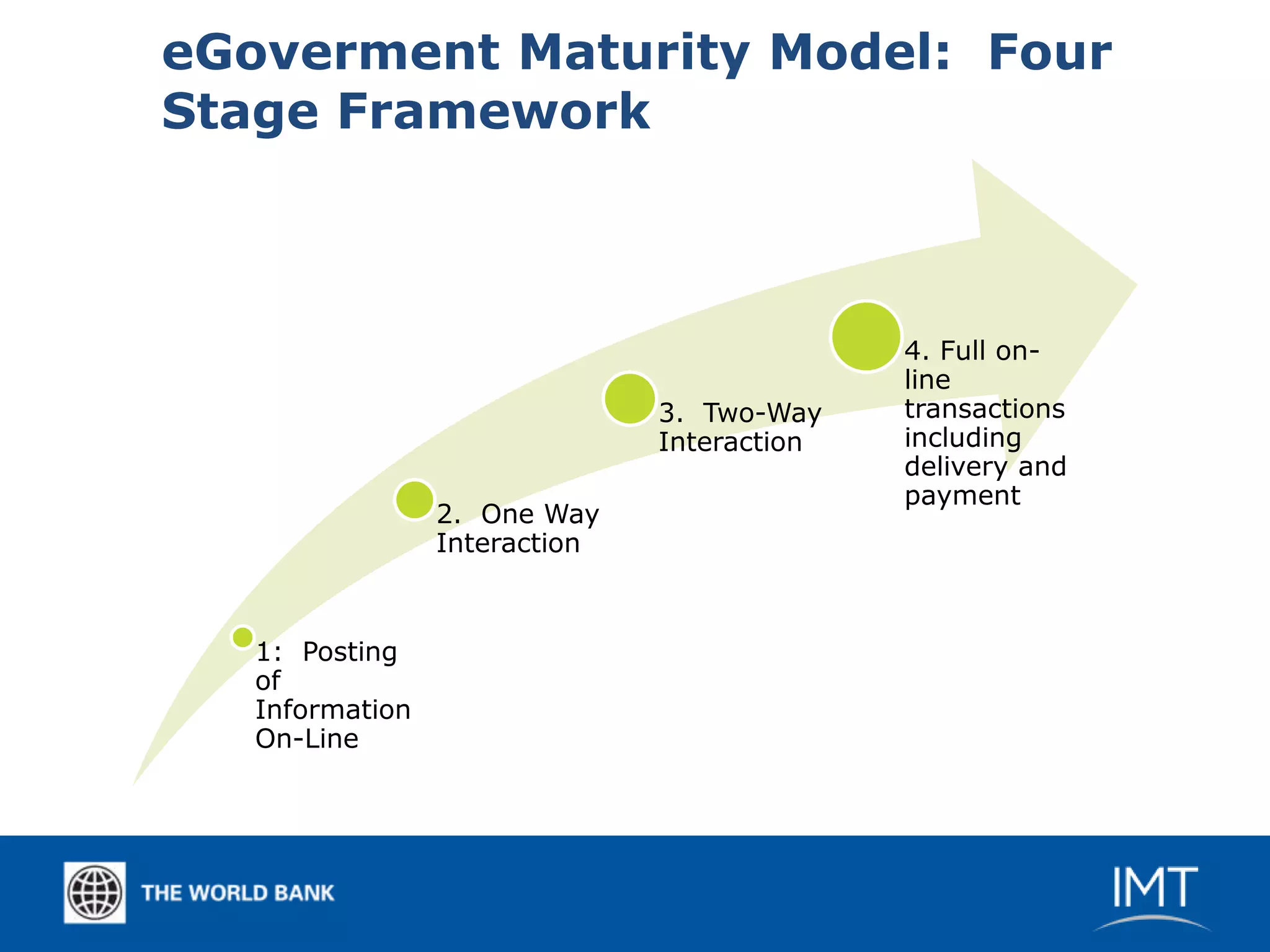
Government innovation through cloud computing provides several advantages for developing countries according to the document. Key benefits include lower upfront costs than maintaining own data centers, easy scalability with increased usage, and eliminating hardware refreshes and infrastructure planning. The document discusses how cloud computing can enable efficient eGovernment services, mobility initiatives, document management, and email/collaboration for governments. However, it notes some legal issues around data sovereignty and jurisdiction need to be considered when using public clouds.