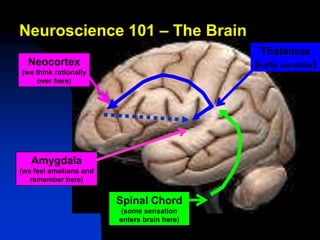
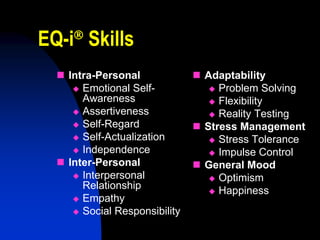
The document discusses the integration of emotional intelligence (EQ) into mentoring programs, highlighting its importance in enhancing both mentor and mentee relationships. It defines EQ, outlines the necessary skills for effective mentoring, and emphasizes the assessment of EQ before matching mentors and mentees. Strategies to develop emotional self-awareness and interpersonal relationships are also presented to foster a more productive mentoring environment.