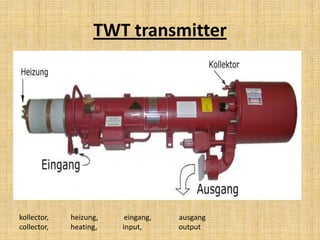
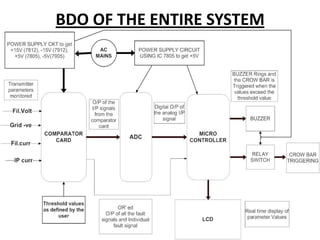
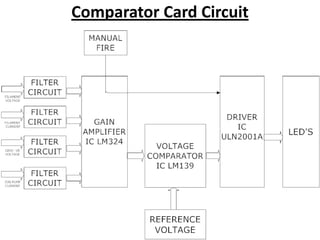
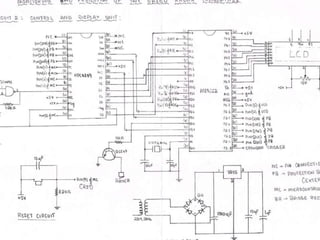
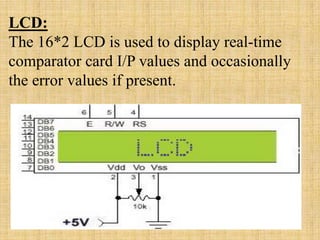
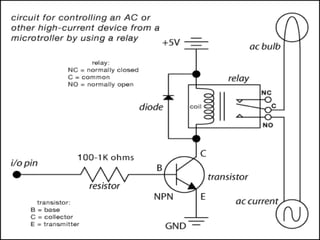
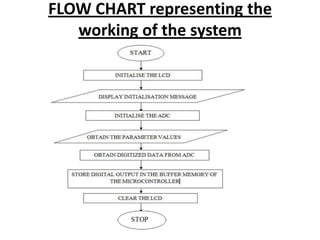
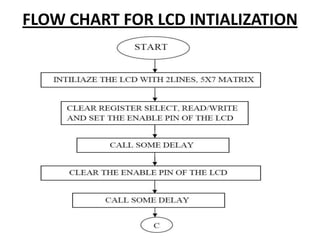
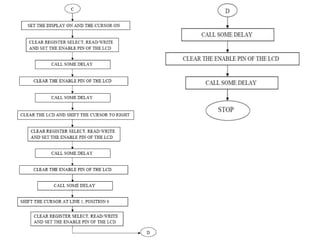
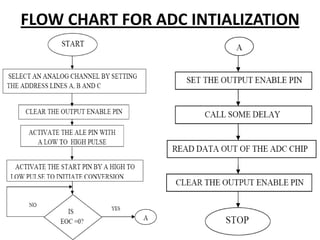
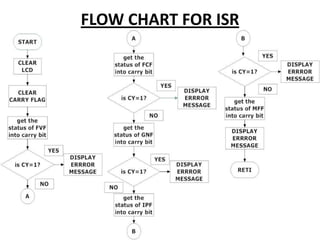
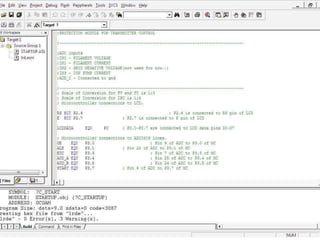
This document describes a monitoring, protection, and control module for a radar transmitter. The module monitors key transmitter parameters, protects the system by triggering faults if parameters exceed thresholds, and controls the transmitter's on/off sequencing. It uses comparators to detect parameter faults, a microcontroller for control and interfacing, an ADC to convert analog signals, and an LCD for output display. The design aims to safely monitor and protect the expensive transmitter components.