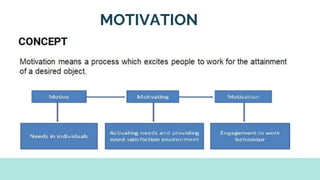
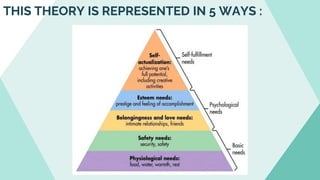
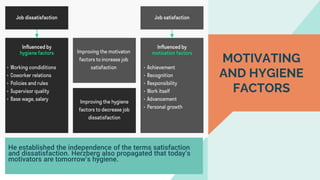
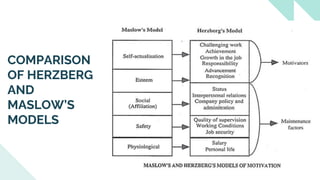
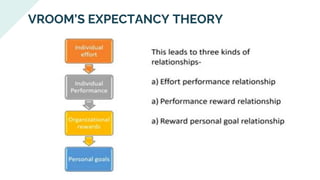
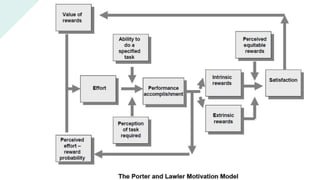
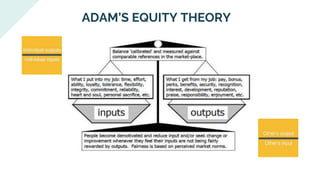
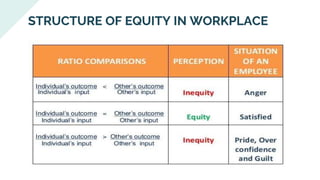
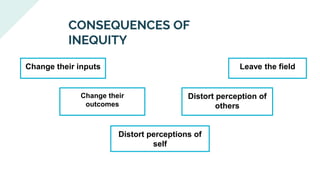
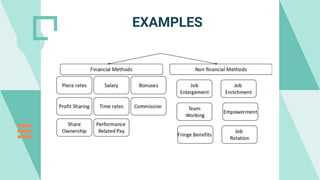
The document explores various motivation theories, including Maslow's hierarchy of needs and Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene model, addressing intrinsic and extrinsic rewards. It also discusses equity theory, emphasizing fairness in workplace motivation, and concludes with a case study of Kellogg’s, highlighting their motivational strategies and employee incentives. Key initiatives at Kellogg's include flexible working arrangements, health programs, and creating a supportive workplace culture.