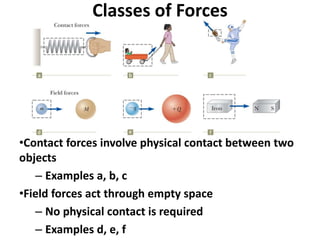
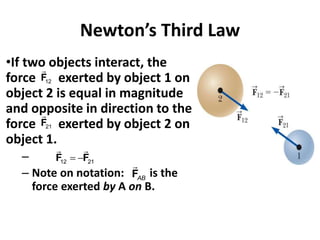
1) Newton's laws of motion describe and quantify the relationship between the forces acting on an object and its motion. The laws were formulated by Sir Isaac Newton and include Newton's first, second, and third laws.
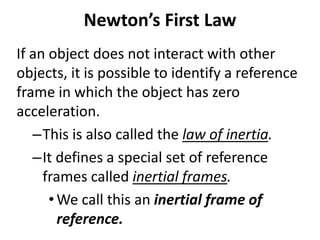
2) Newton's first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force.
3) Newton's second law states that the acceleration of an object as produced by a net force is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the object's mass.
4) Newton's third law states that