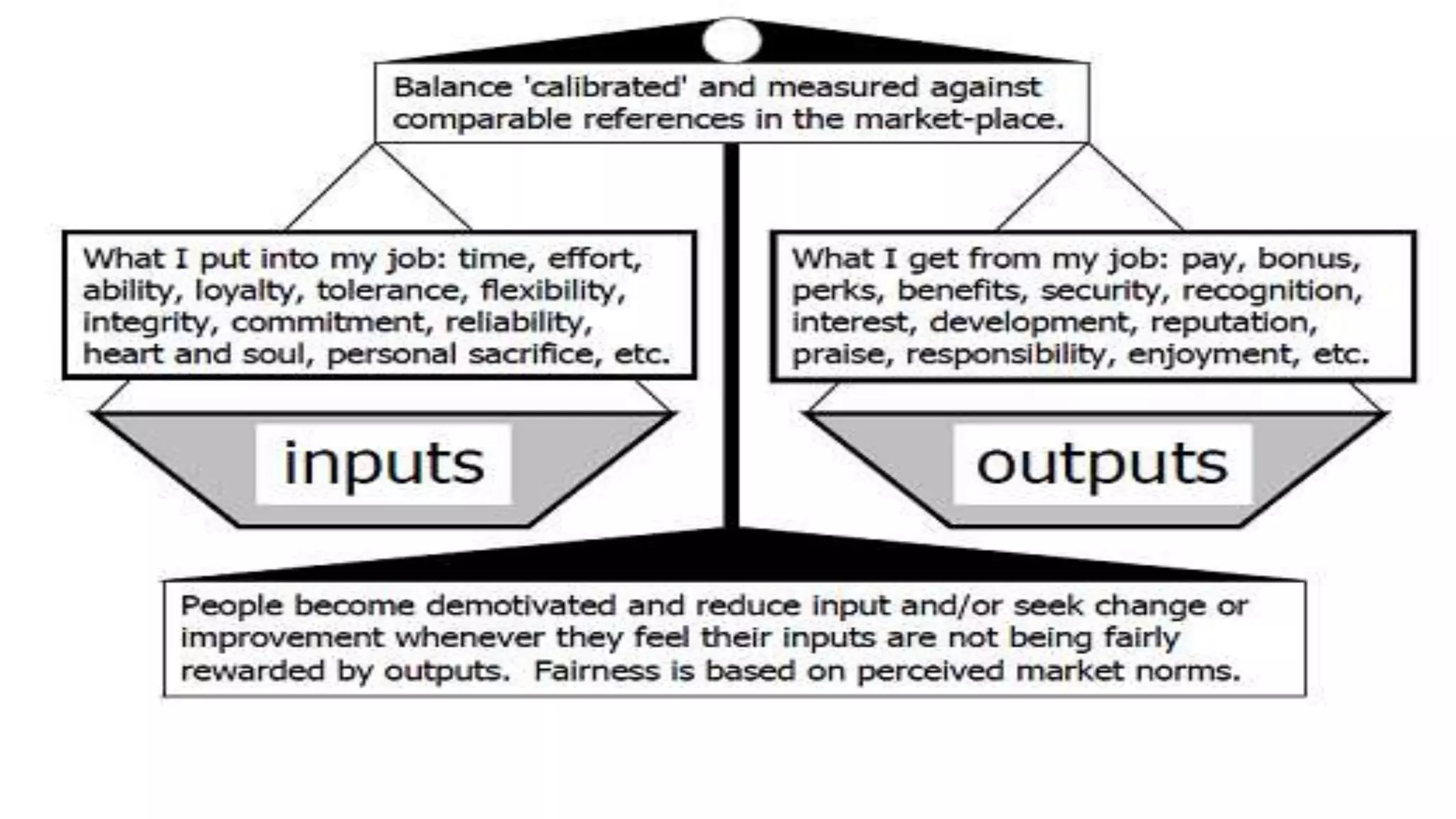
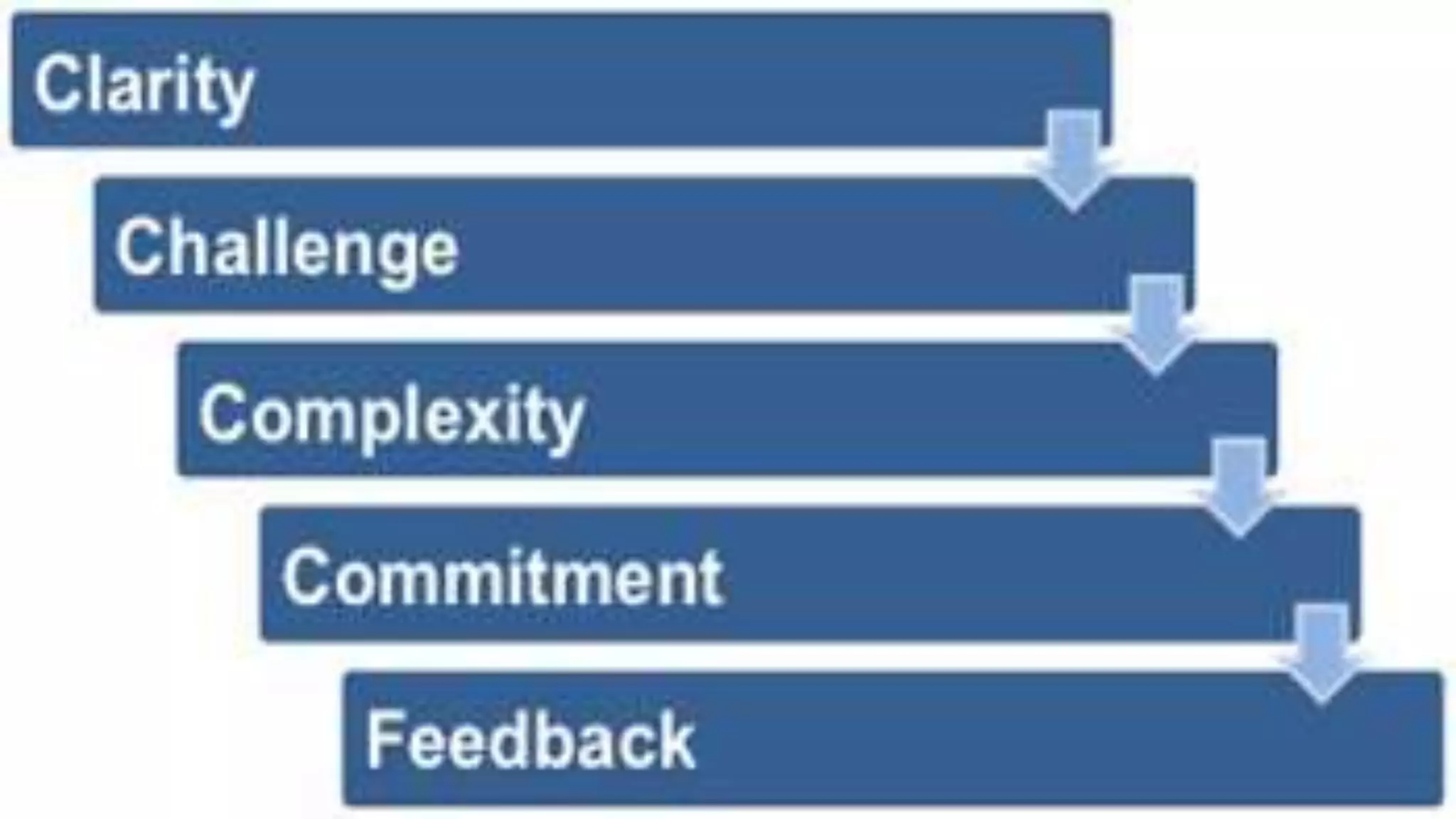
This document discusses morale and motivation in the workplace. It defines morale as the mental attitude and satisfaction that determines an individual's willingness to work. High morale is characterized by enthusiasm, satisfaction, team spirit and pride. Motivation refers to factors that encourage employees to achieve goals and objectives. It discusses theories of motivation from McGregor, Maslow, Herzberg, Adams and Locke. The document also covers factors that influence morale like management practices, and signs of low employee morale such as absenteeism and turnover.