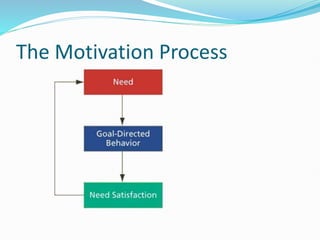
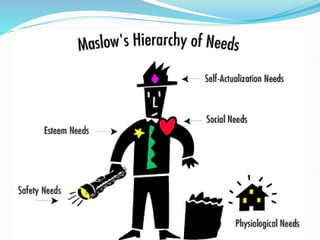
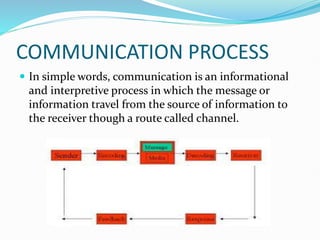
This document discusses the concept of directing, which is the third function of management aimed at achieving organizational goals. Directing involves activities like issuing orders, training subordinates, motivating staff, maintaining discipline, and rewarding good performance. It is a complex process that encourages effective and efficient work. Key elements of directing include supervision, motivation, leadership, communication, and order giving. The document also discusses theories of motivation like Maslow's hierarchy of needs and McClelland's need theory, which aim to explain what motivates employees.