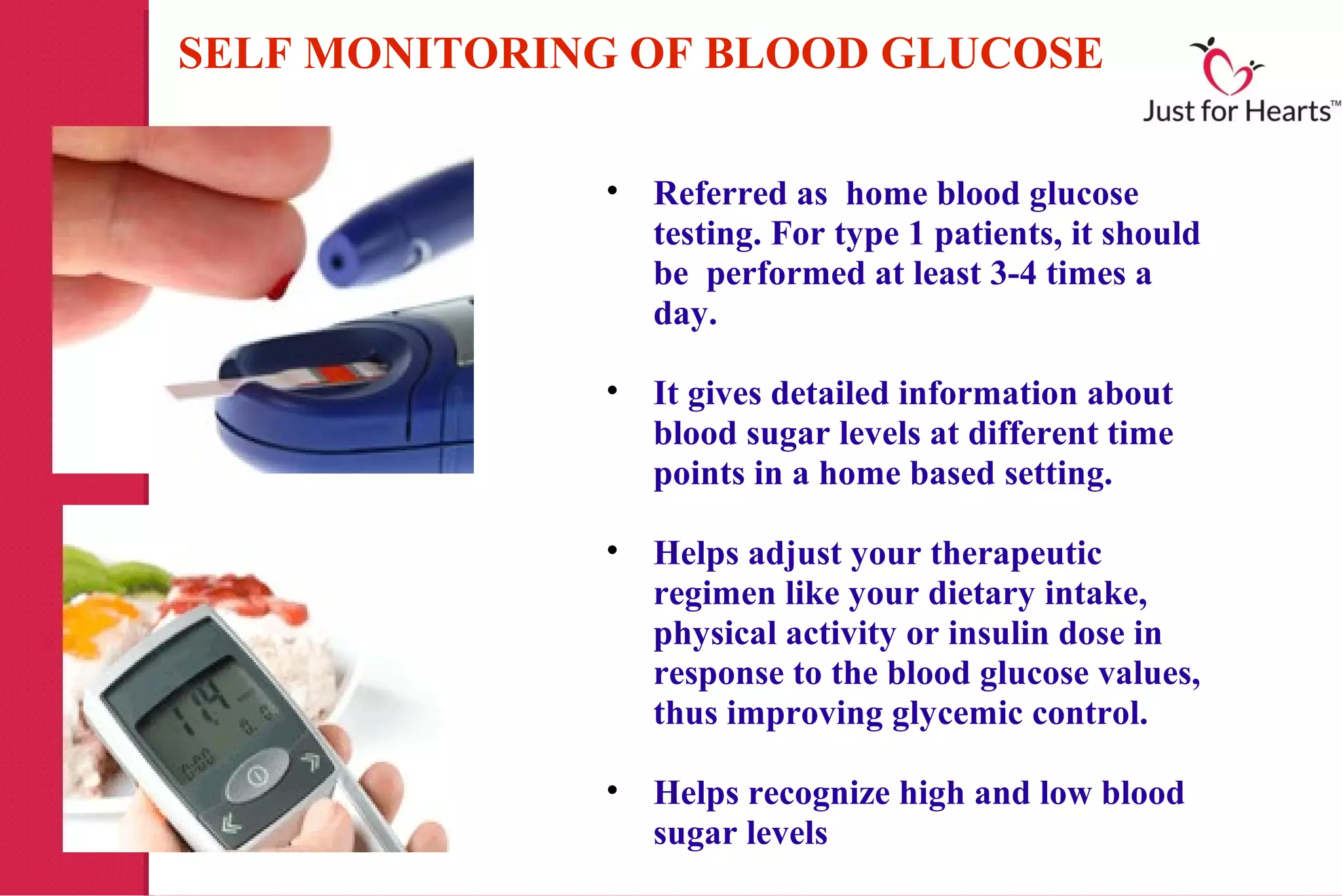
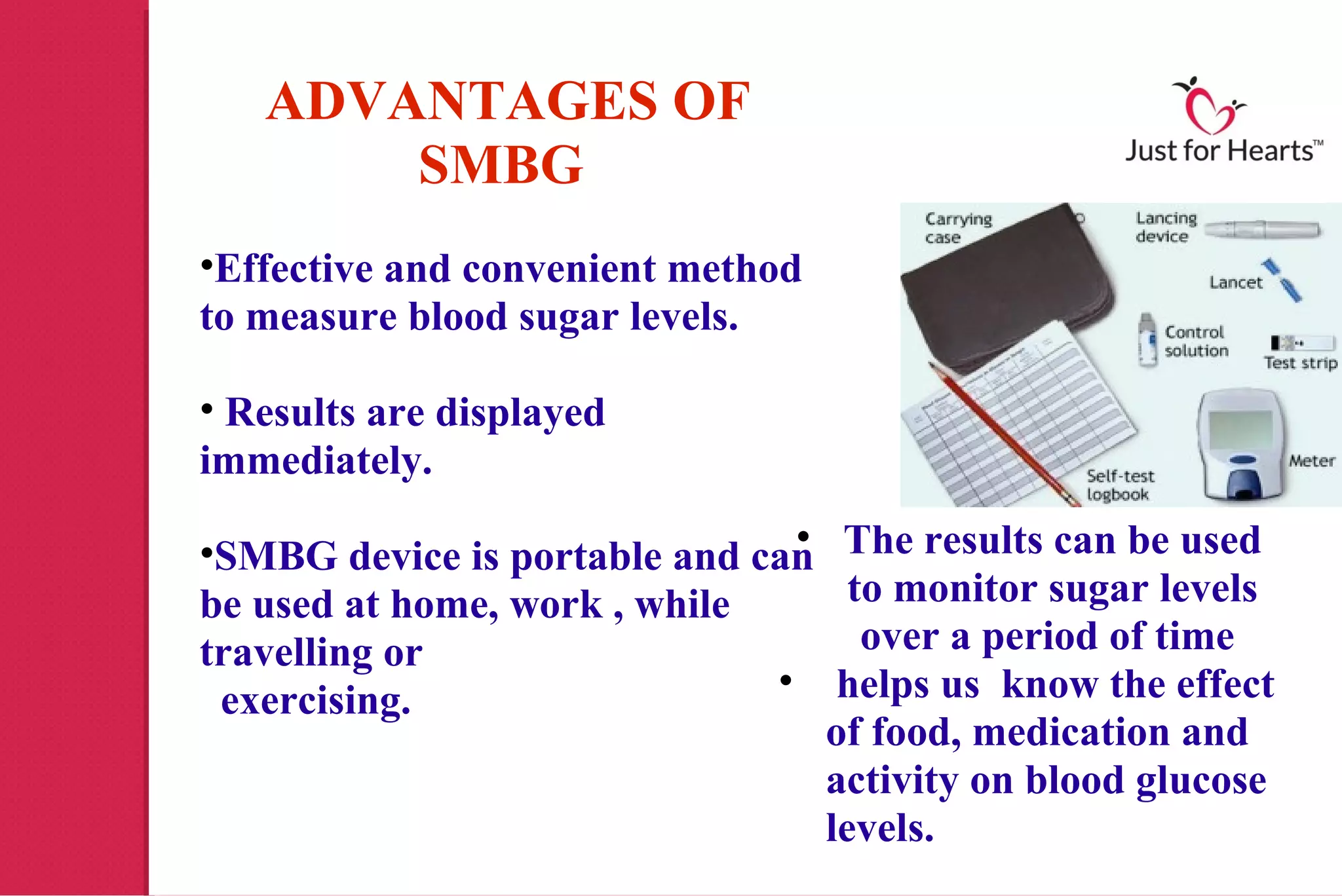
Type 1 diabetes mellitus, primarily affecting children and young adults, results from the body's inability to produce insulin, requiring regular blood sugar monitoring to manage levels. Various methods for monitoring include laboratory tests, self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG), continuous glucose monitoring systems (CGMS), and insulin pumps, each with their own advantages and disadvantages. Effective monitoring is crucial for adjusting treatment and reducing the risk of diabetic complications.