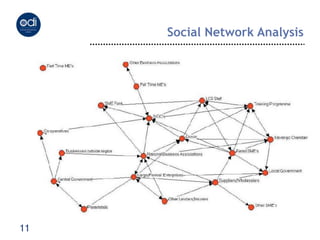
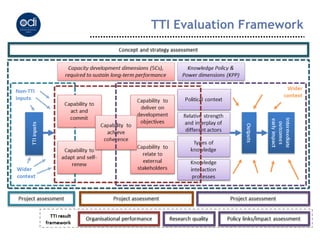
The document outlines the complexities of measuring policy influence, emphasizing various methodologies such as outcome mapping and social network analysis. It discusses the importance of monitoring and evaluation (M&E) for learning, accountability, and improving policy processes. Key themes include the role of knowledge intermediaries, a focus on behavior change, and the need for structured approaches to assess impacts and effectiveness in policy formulation and implementation.