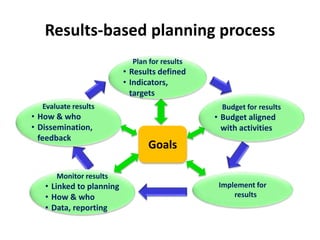
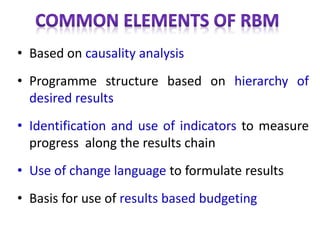
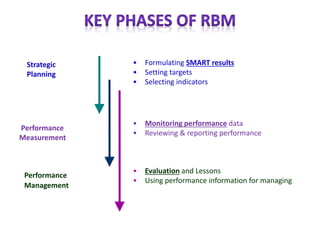
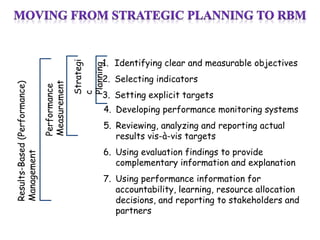
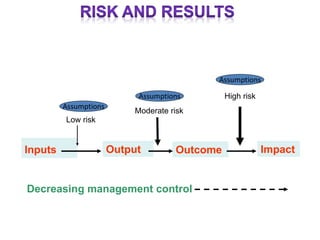
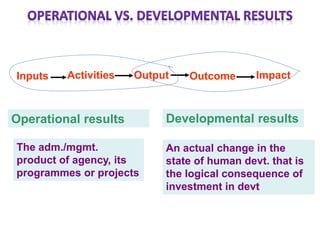
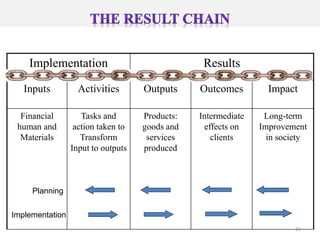
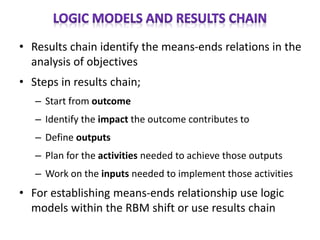
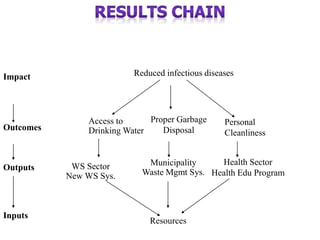
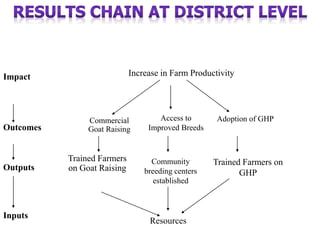
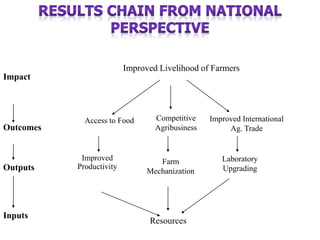
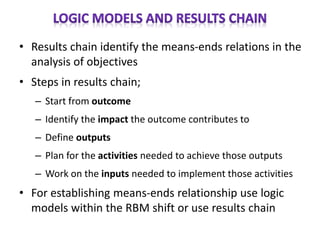
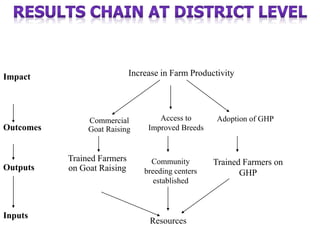
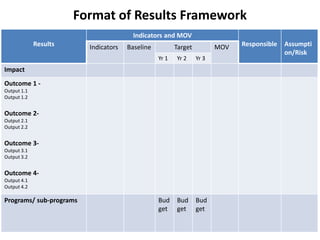
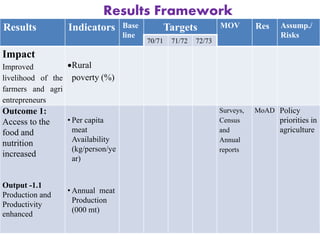
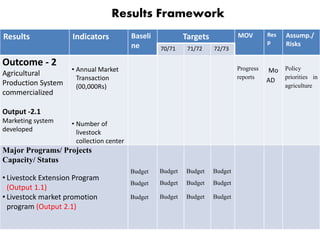
The document outlines the framework and processes of result-based planning (RBP) and management (RBM), emphasizing their importance in achieving effective and accountable governance through strategic planning focused on outcomes and impacts. It discusses the need for clear objectives, use of indicators, monitoring systems, and stakeholder involvement to ensure that public planning meets societal needs. Key components include understanding socio-economic contexts, setting long-term goals, and aligning resources with prioritized objectives to enhance development effectiveness.