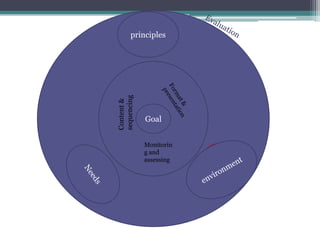
This document discusses various types of monitoring and assessment used in language teaching. It describes placement assessment, which determines a learner's starting level, and observation of learning, which provides feedback on teaching activities without directly assessing learners. Short-term achievement assessment evaluates weekly progress, while diagnostic assessment identifies gaps to address. Achievement tests measure learning over time and proficiency tests assess language skills independent of any particular course. All assessment should consider reliability, validity, and practicality to ensure they serve their intended purpose.