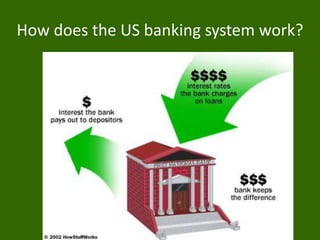
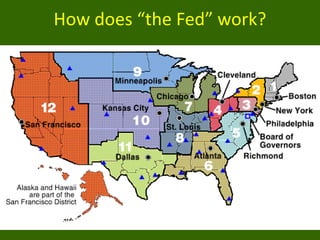
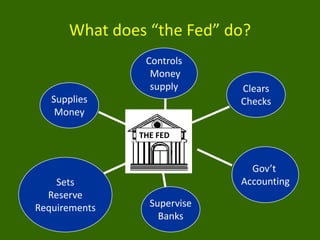
The document discusses key aspects of the US banking system including:
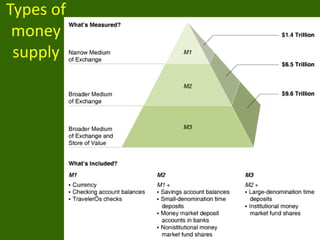
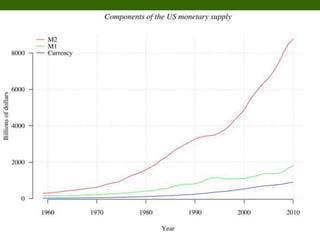
1) Types of money like demand deposits that depositors can access through checks and the central bank that controls monetary policy.
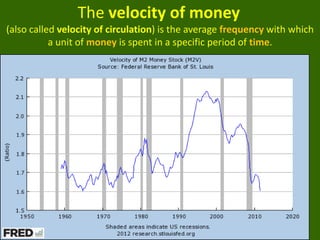
2) How the Federal Reserve ("the Fed") regulates banks and implements monetary policy through tools like open market operations and adjusting reserve requirements.
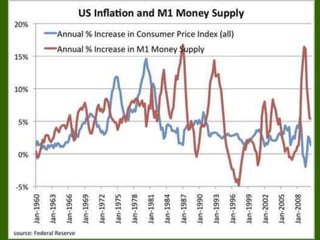
3) Why the Chairman of the Fed is powerful as monetary policy changes can increase or decrease the money supply and reserve rates.