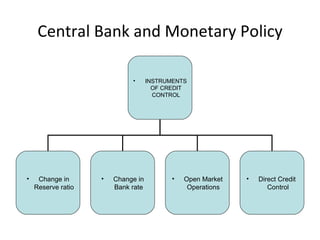
Central banks play a key role in regulating the monetary system and promoting financial stability. They have several functions including issuing currency, acting as a banker to the government and commercial banks, regulating money supply and credit through various instruments of credit control. Some of the main instruments of credit control used by central banks are cash reserve ratio, statutory liquidity ratio, open market operations, and changing the bank rate. These tools allow central banks to increase or decrease money supply in the economy as needed to influence monetary policy.