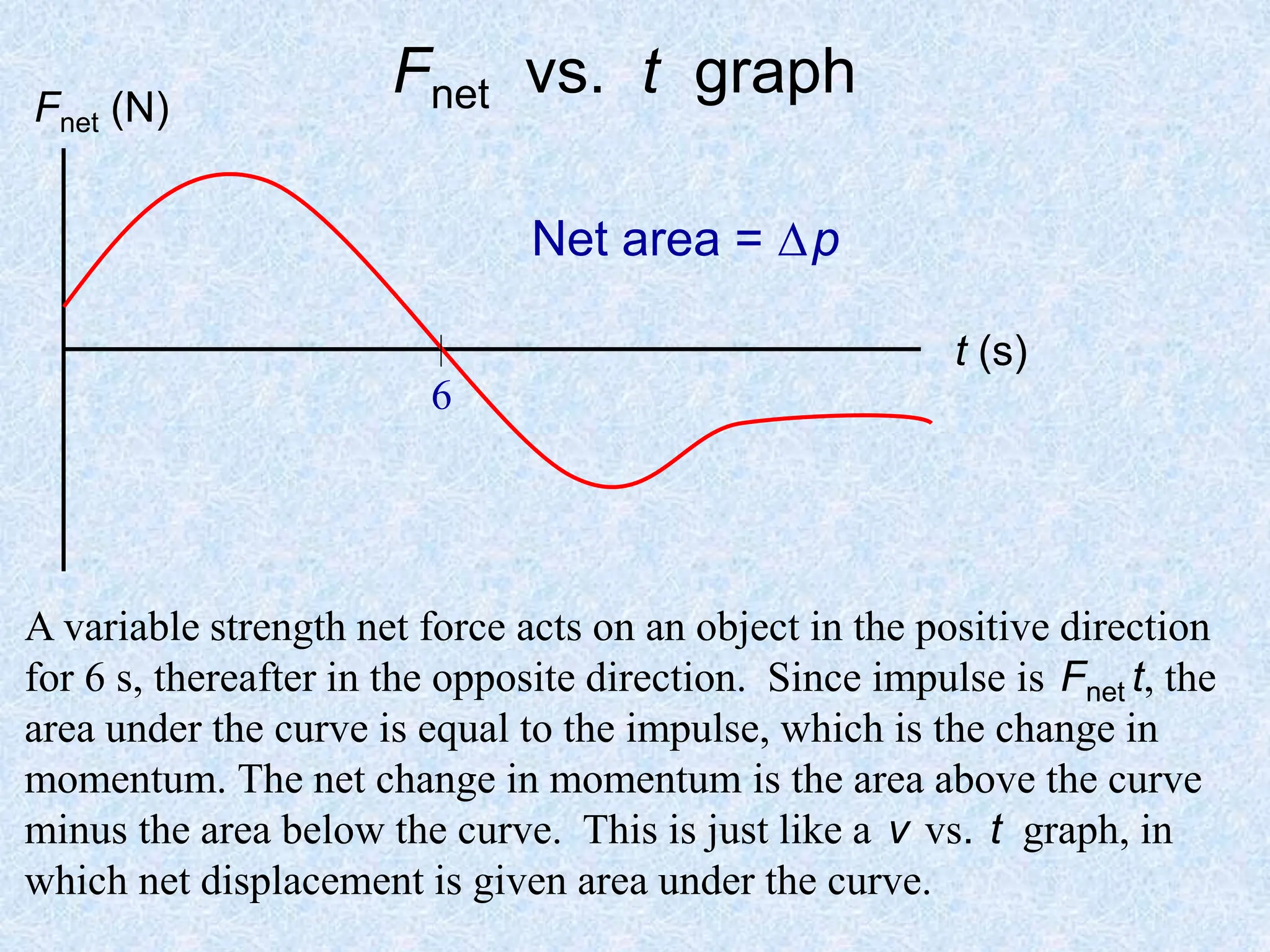
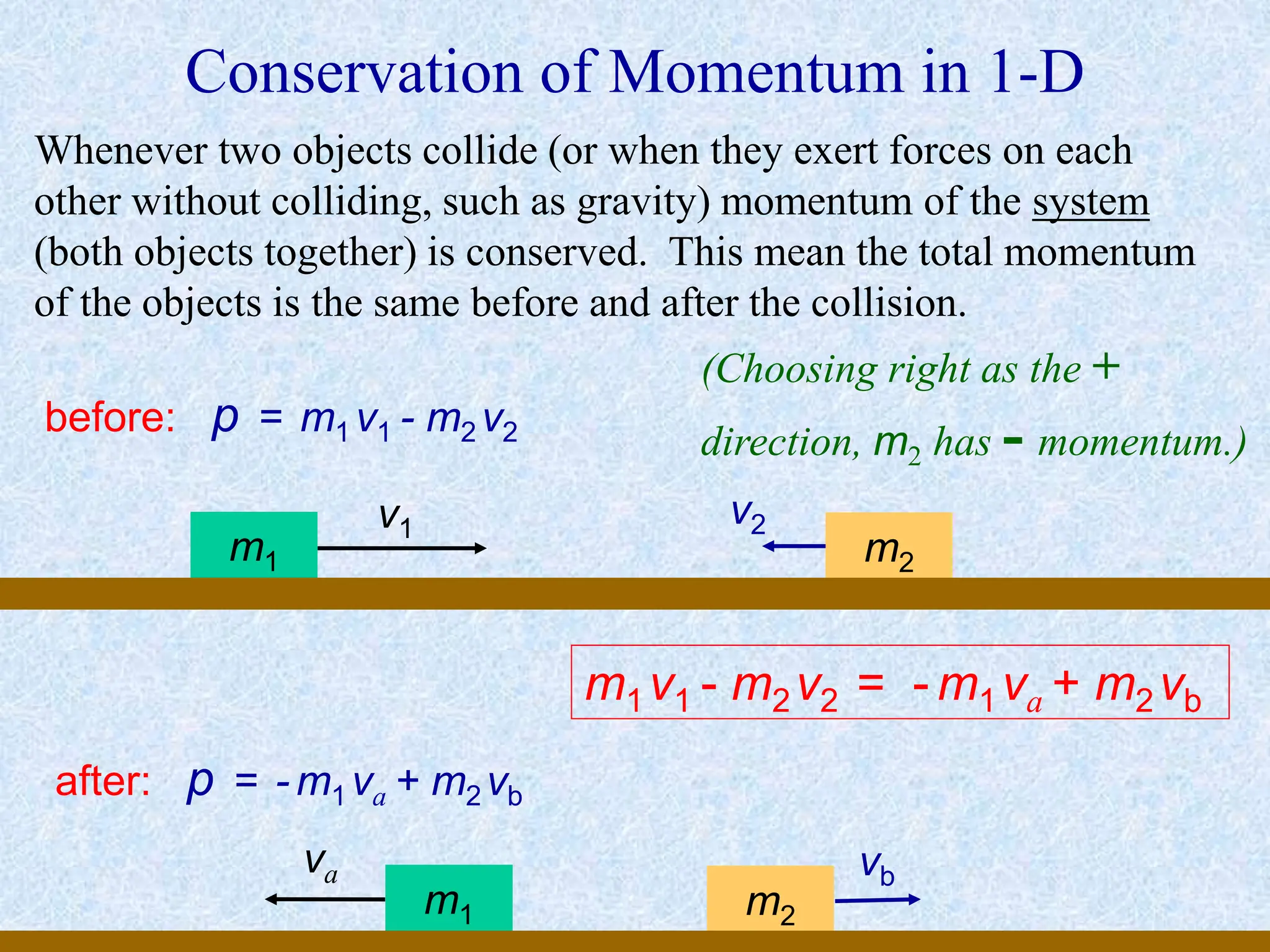
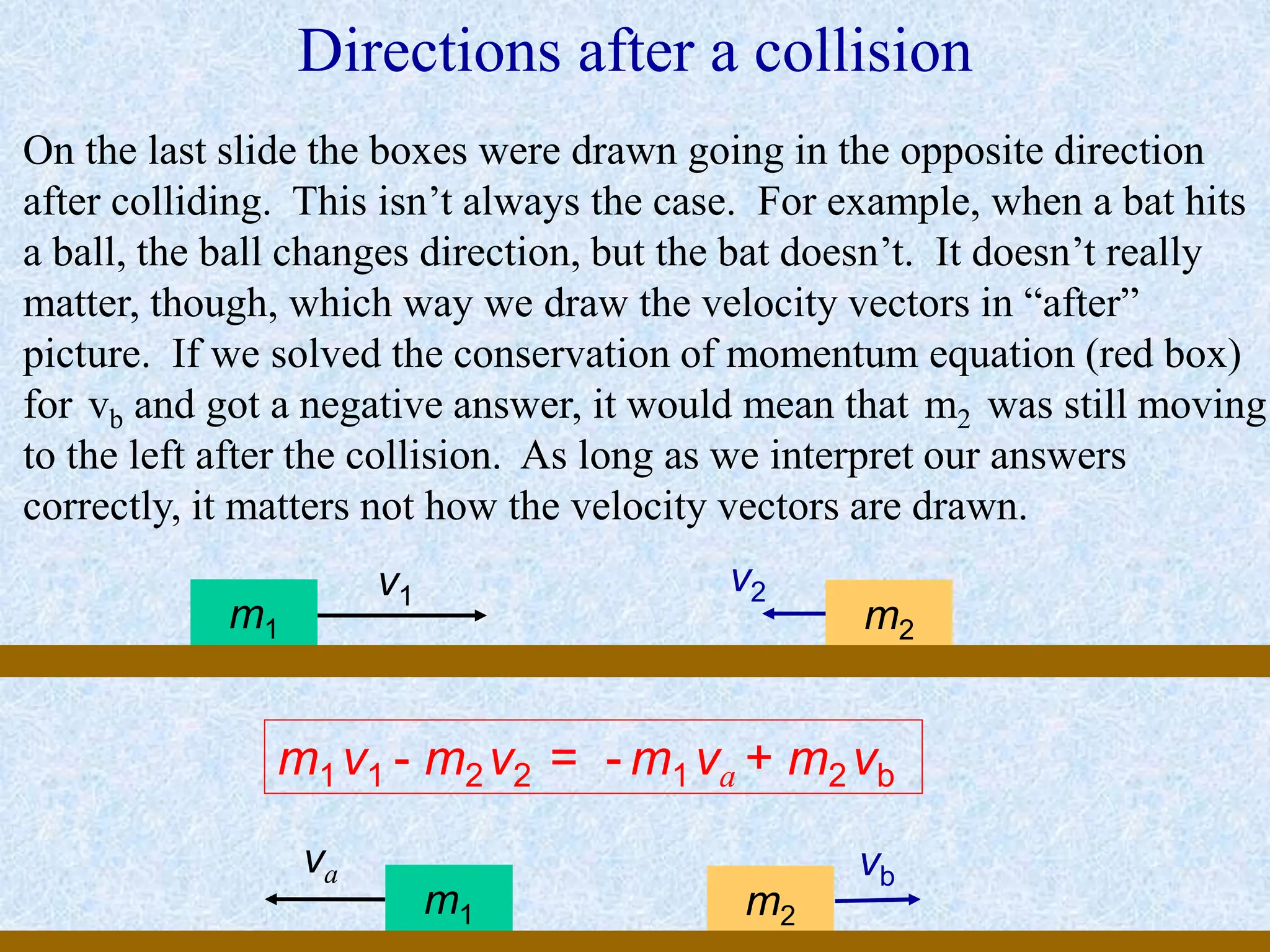
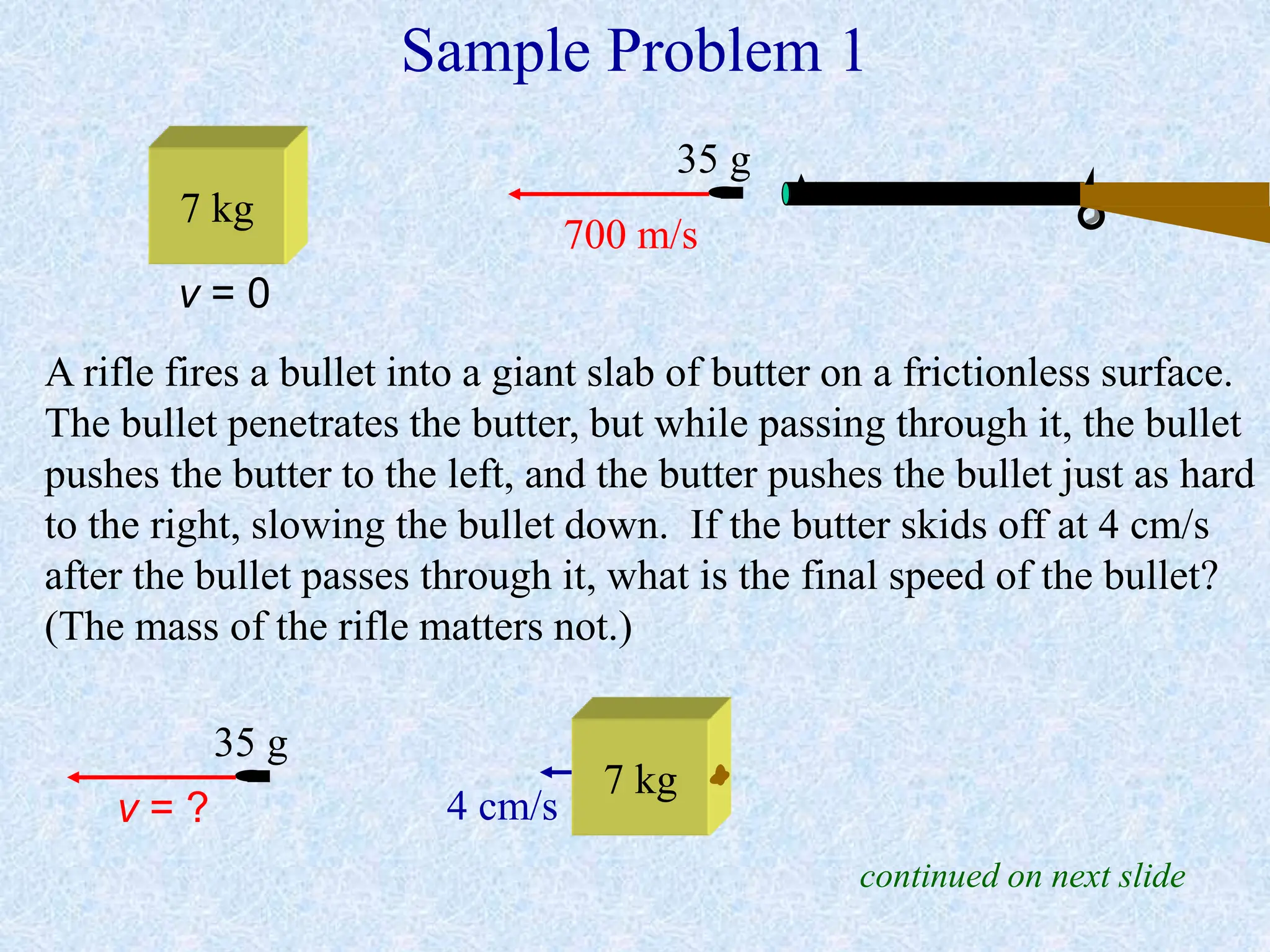
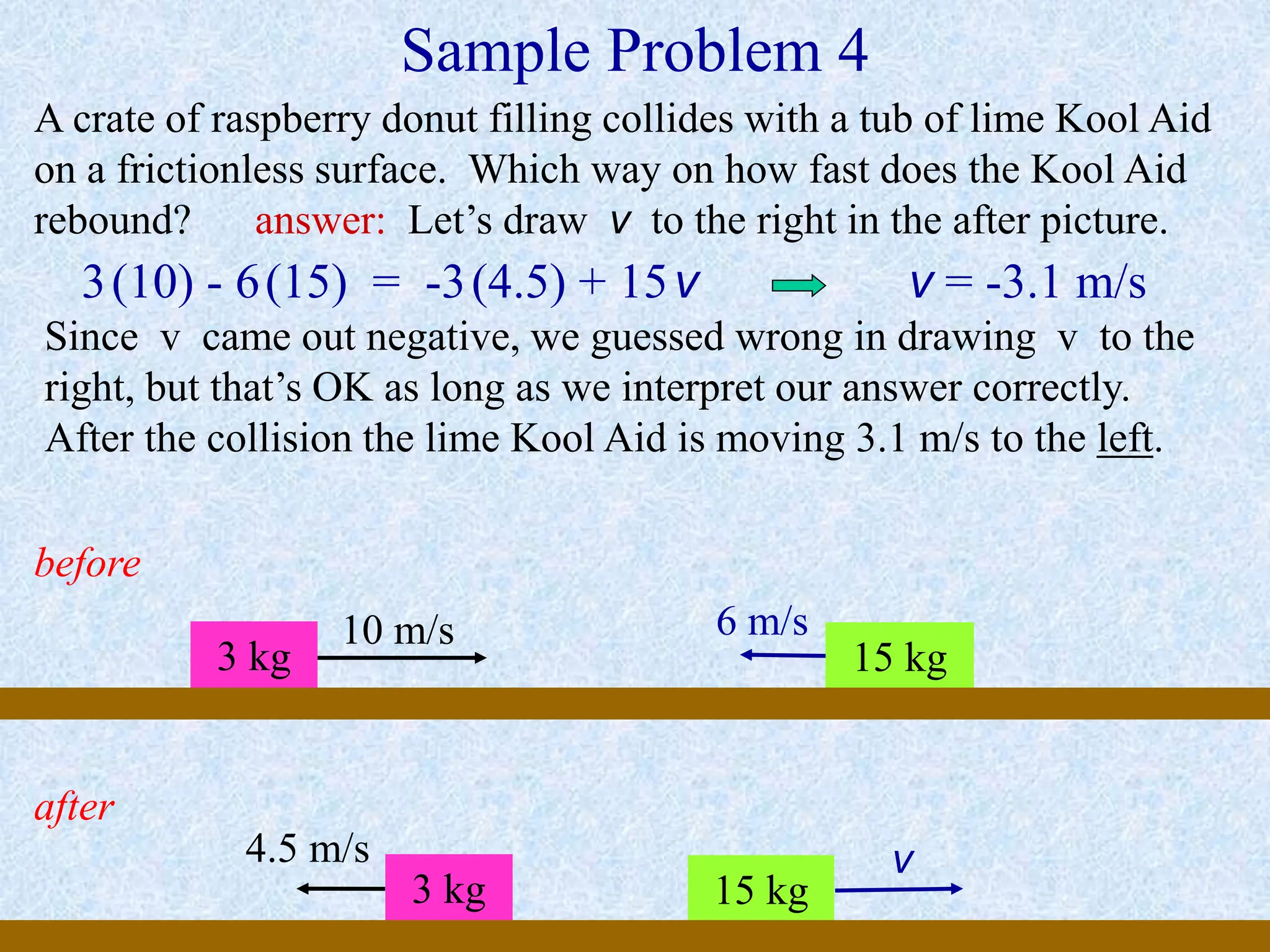
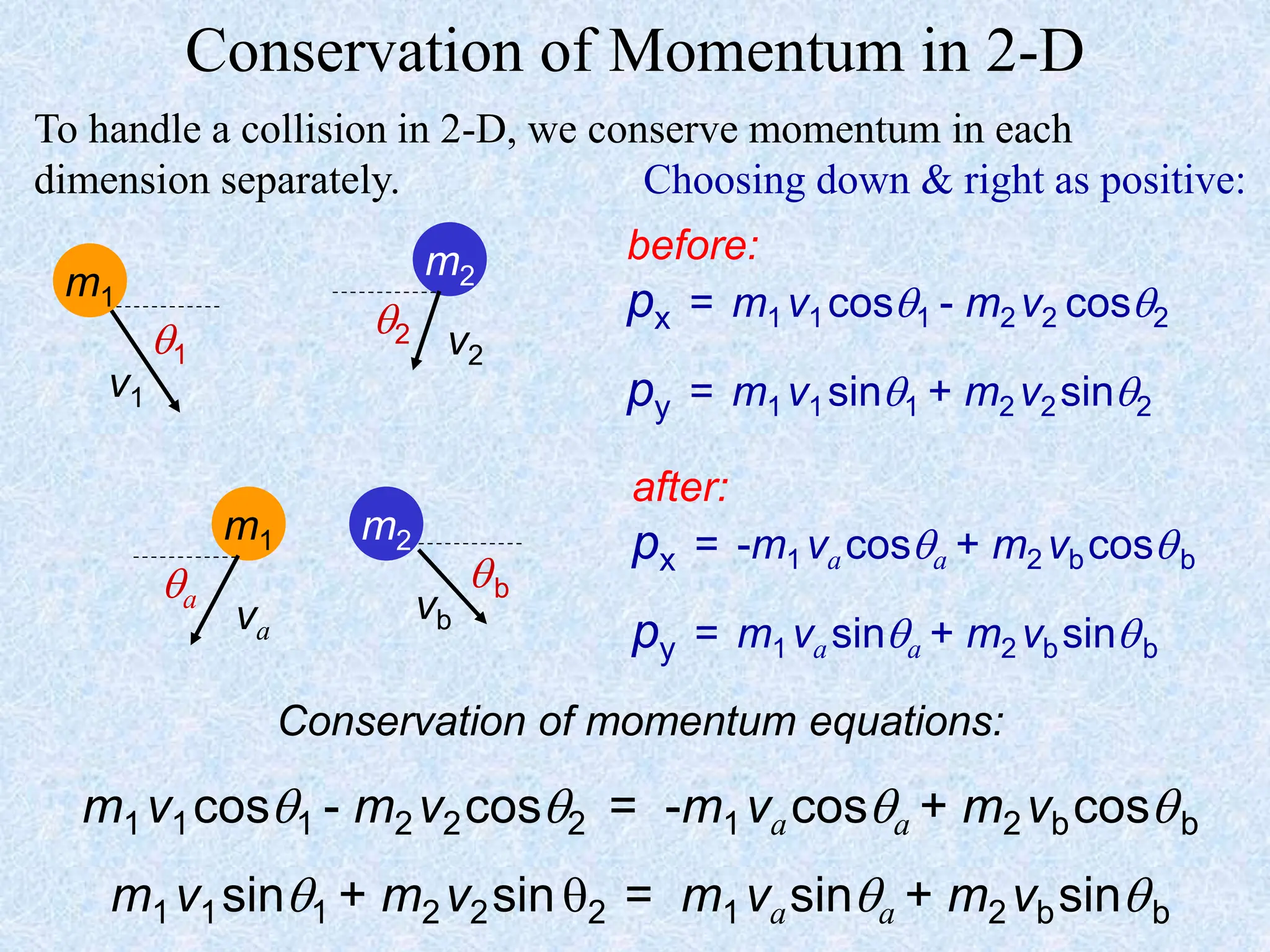
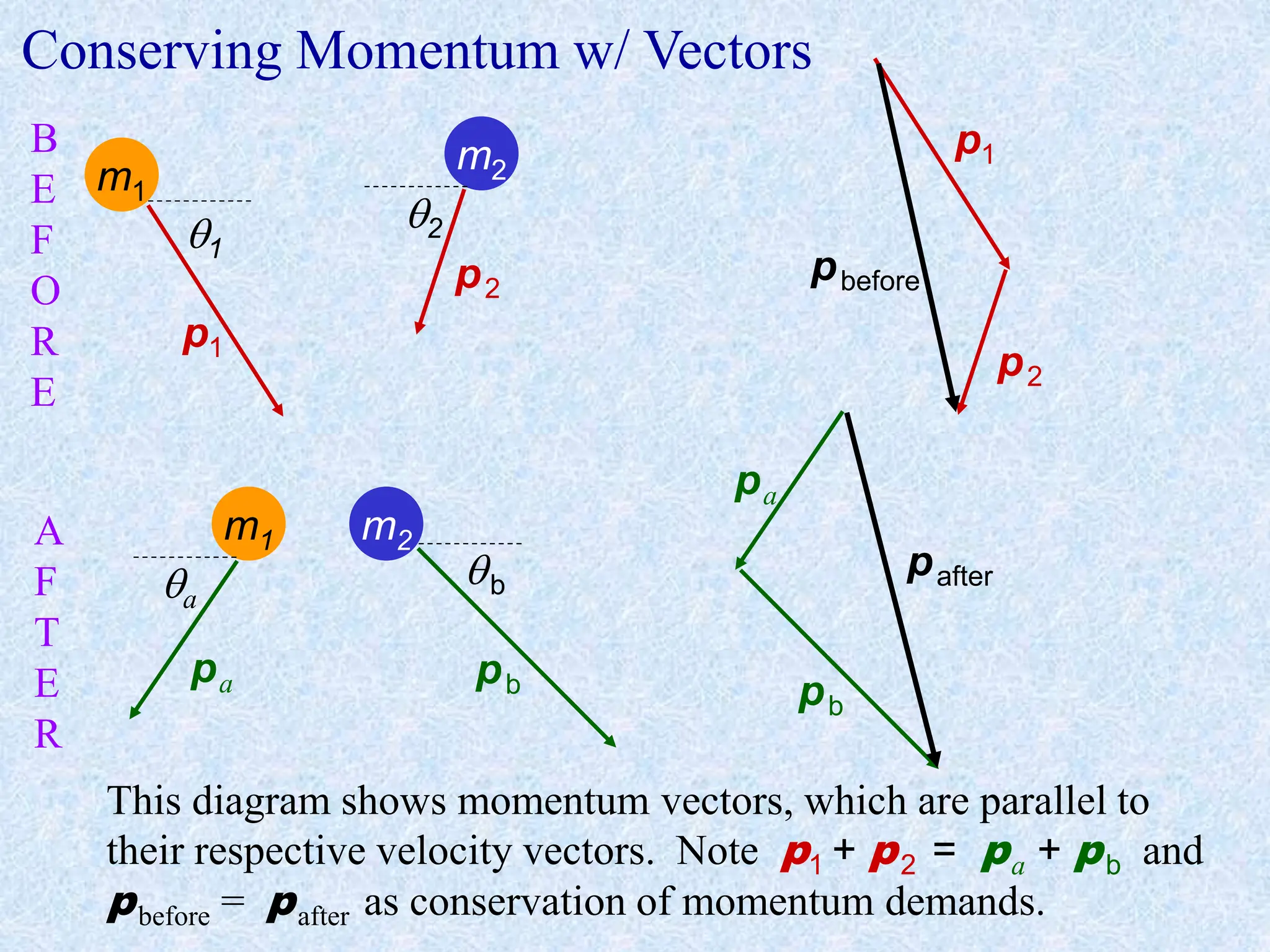
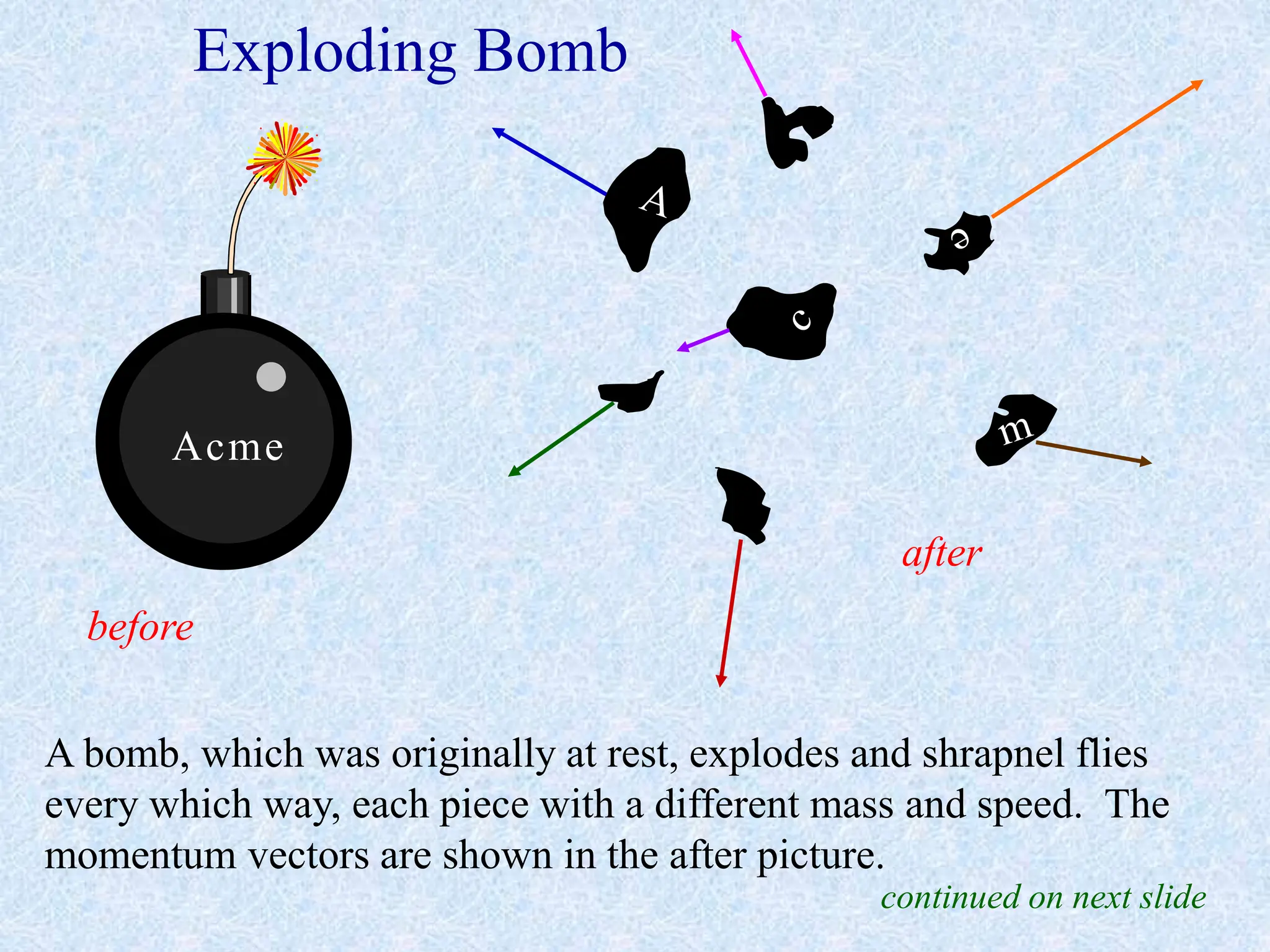
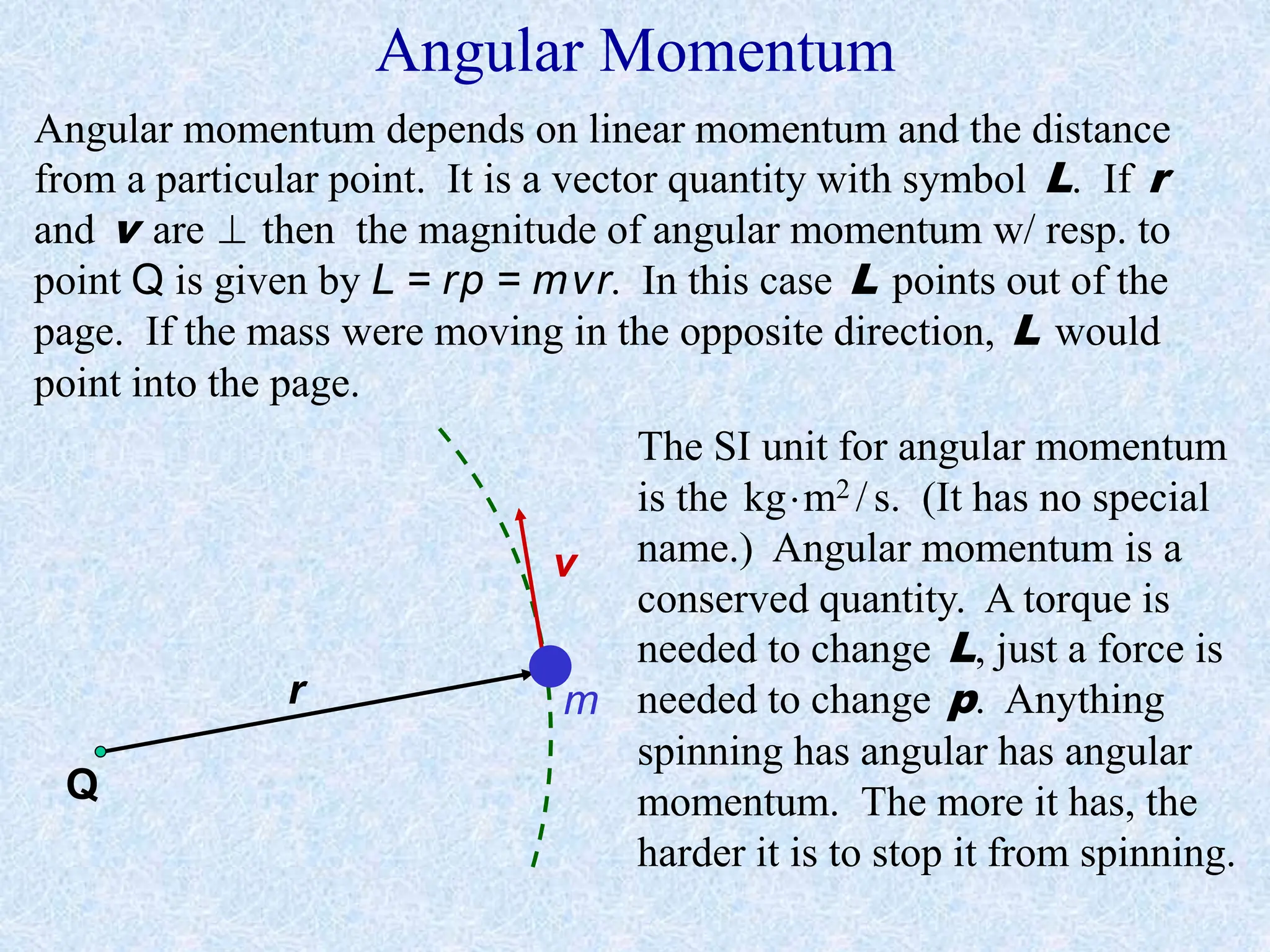
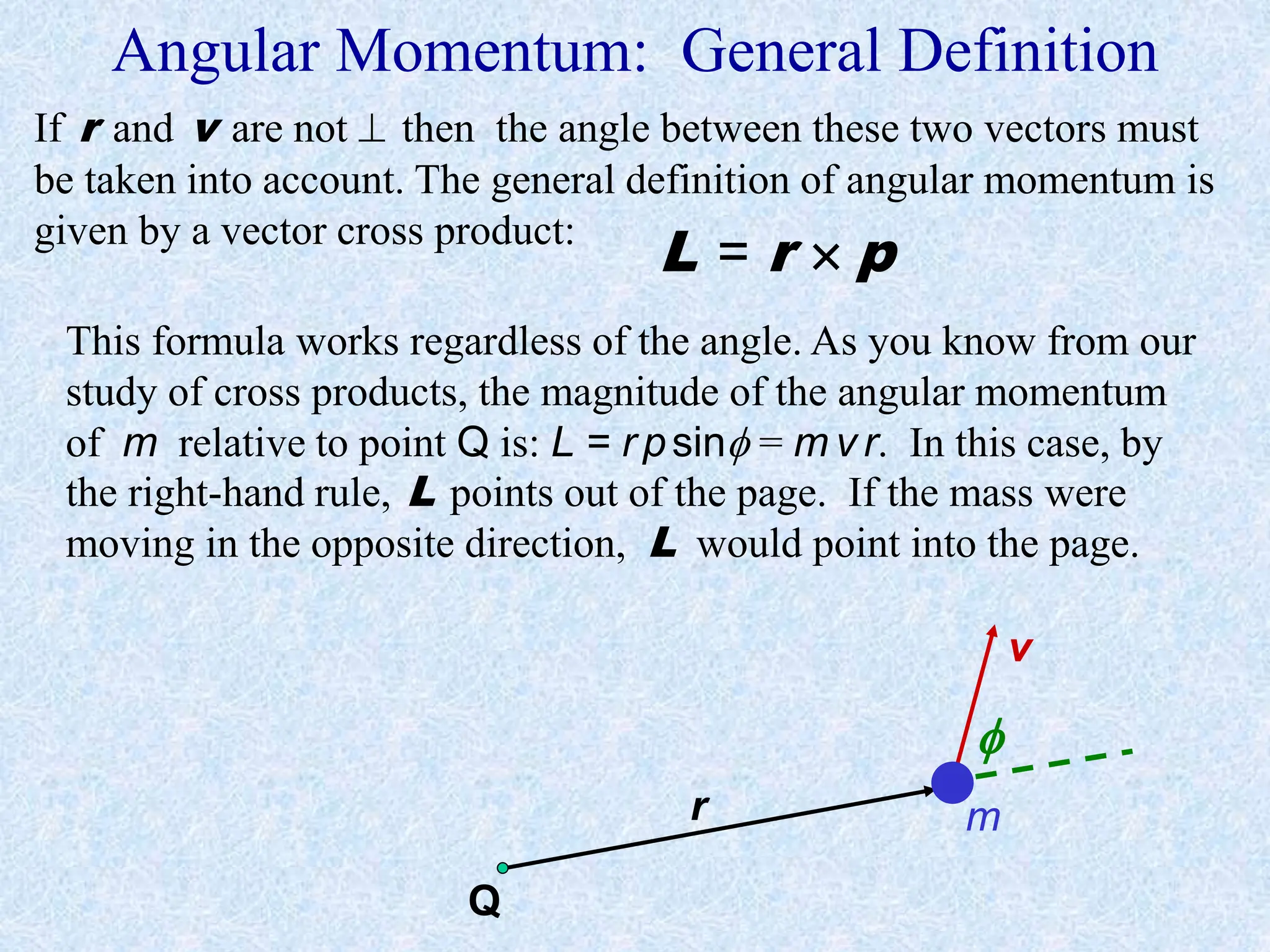
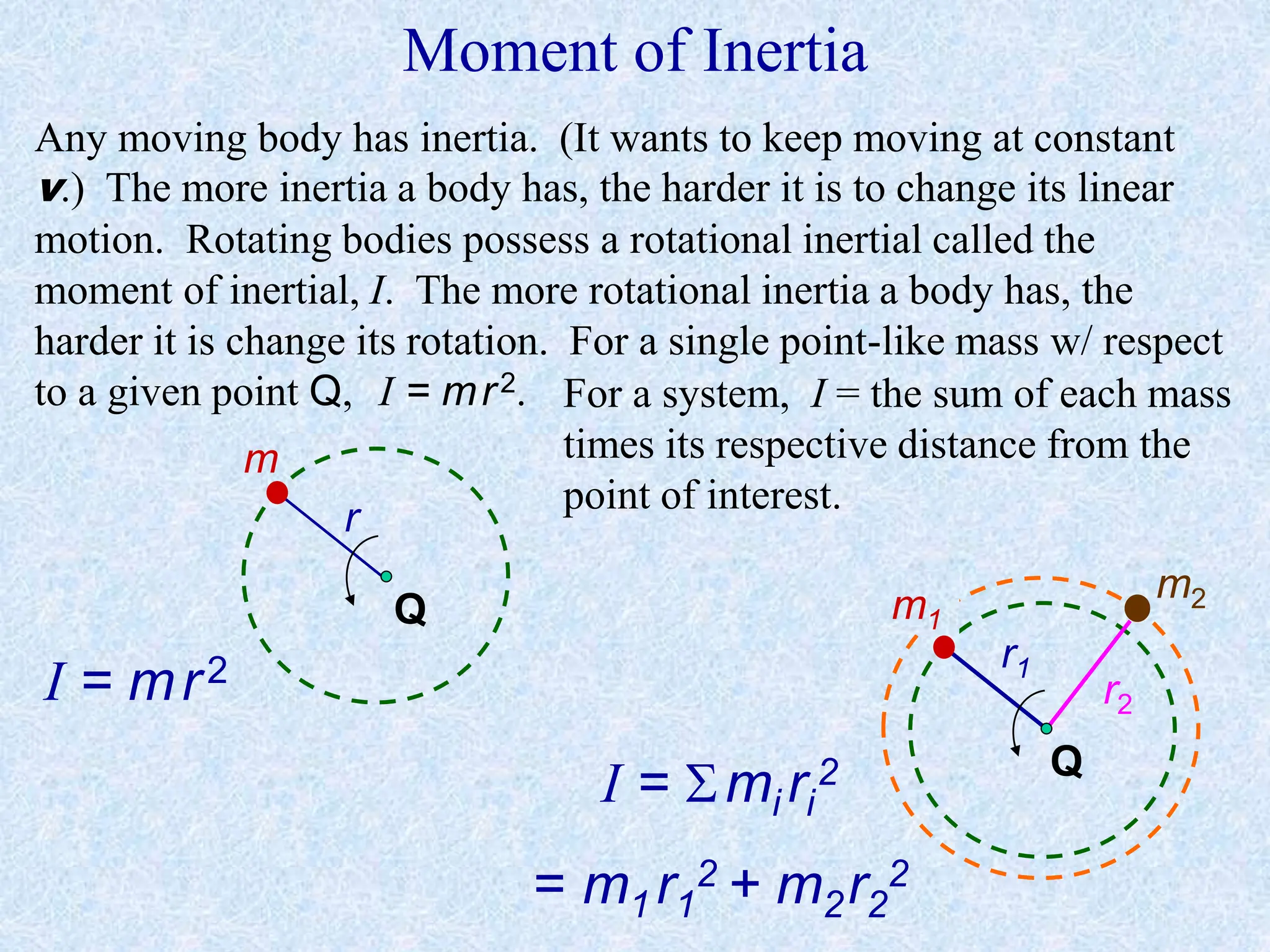
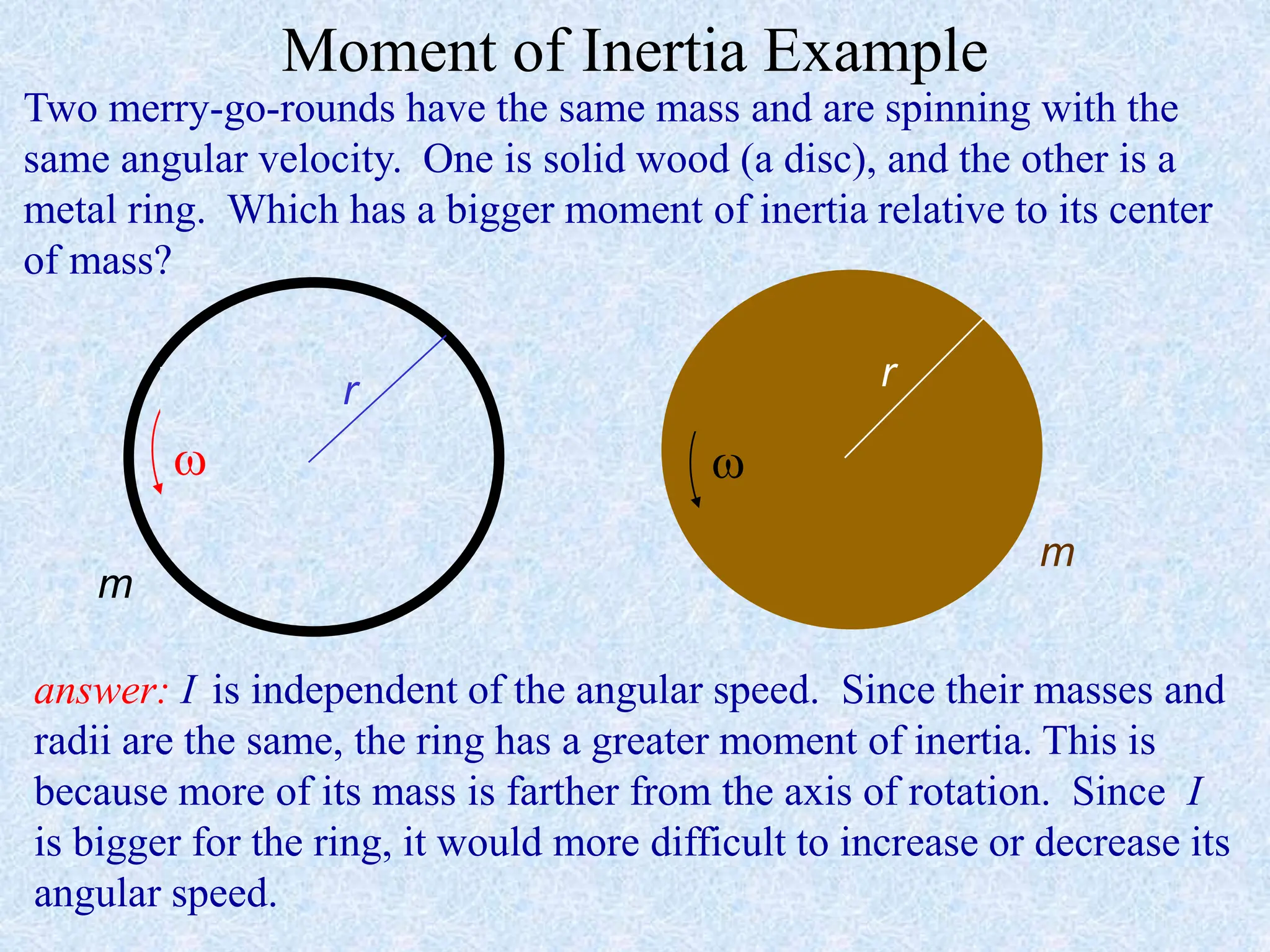
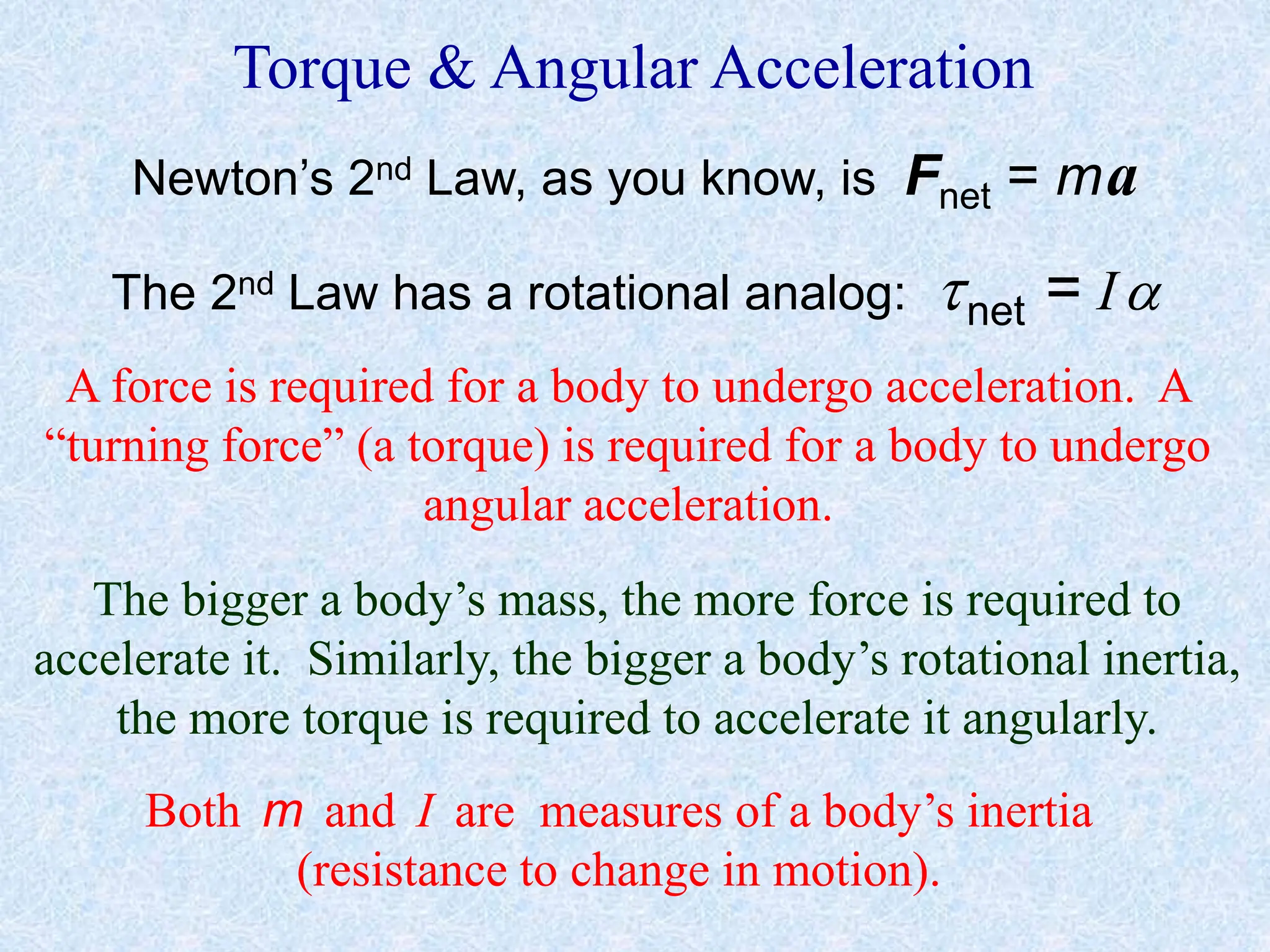
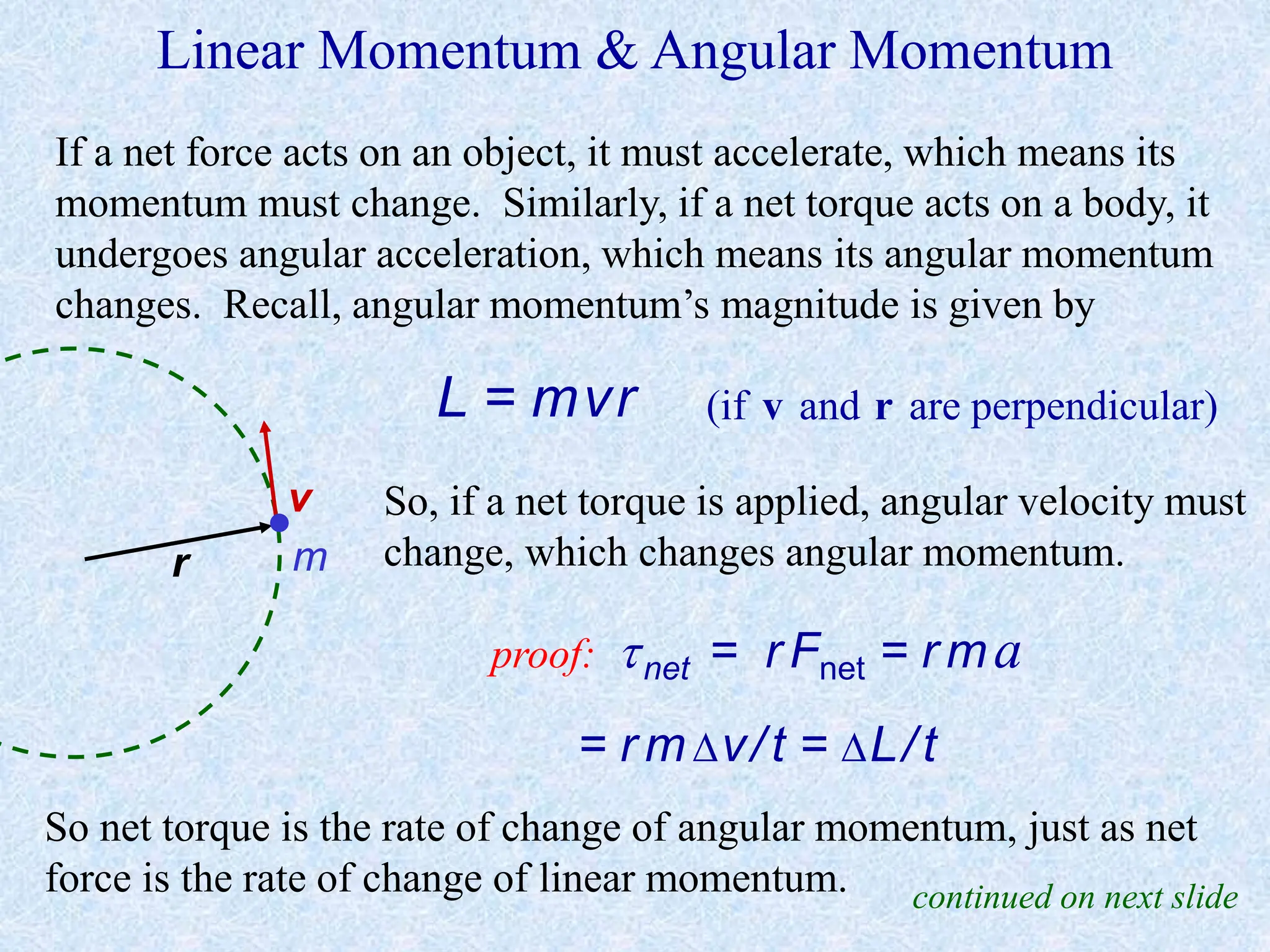
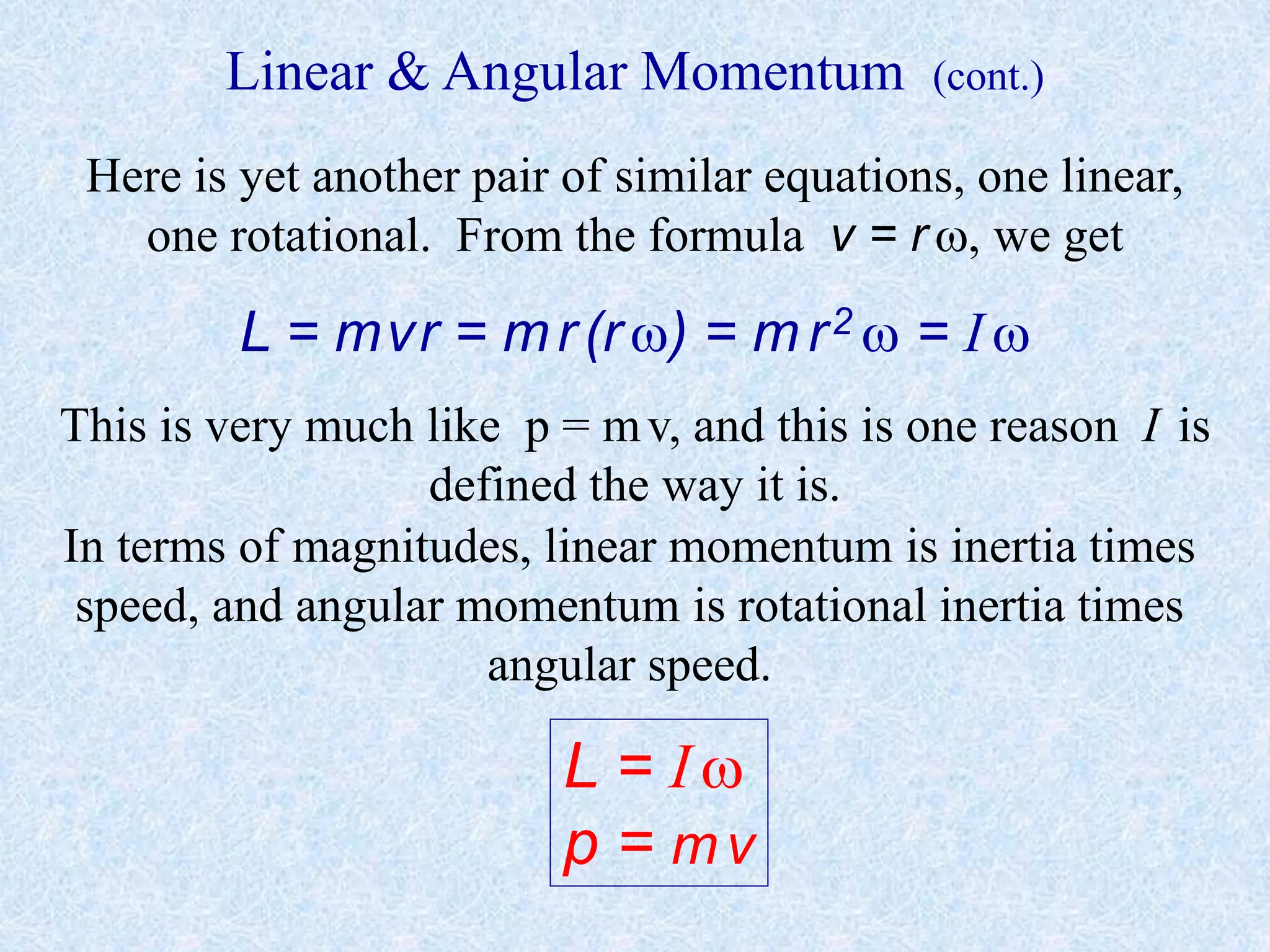
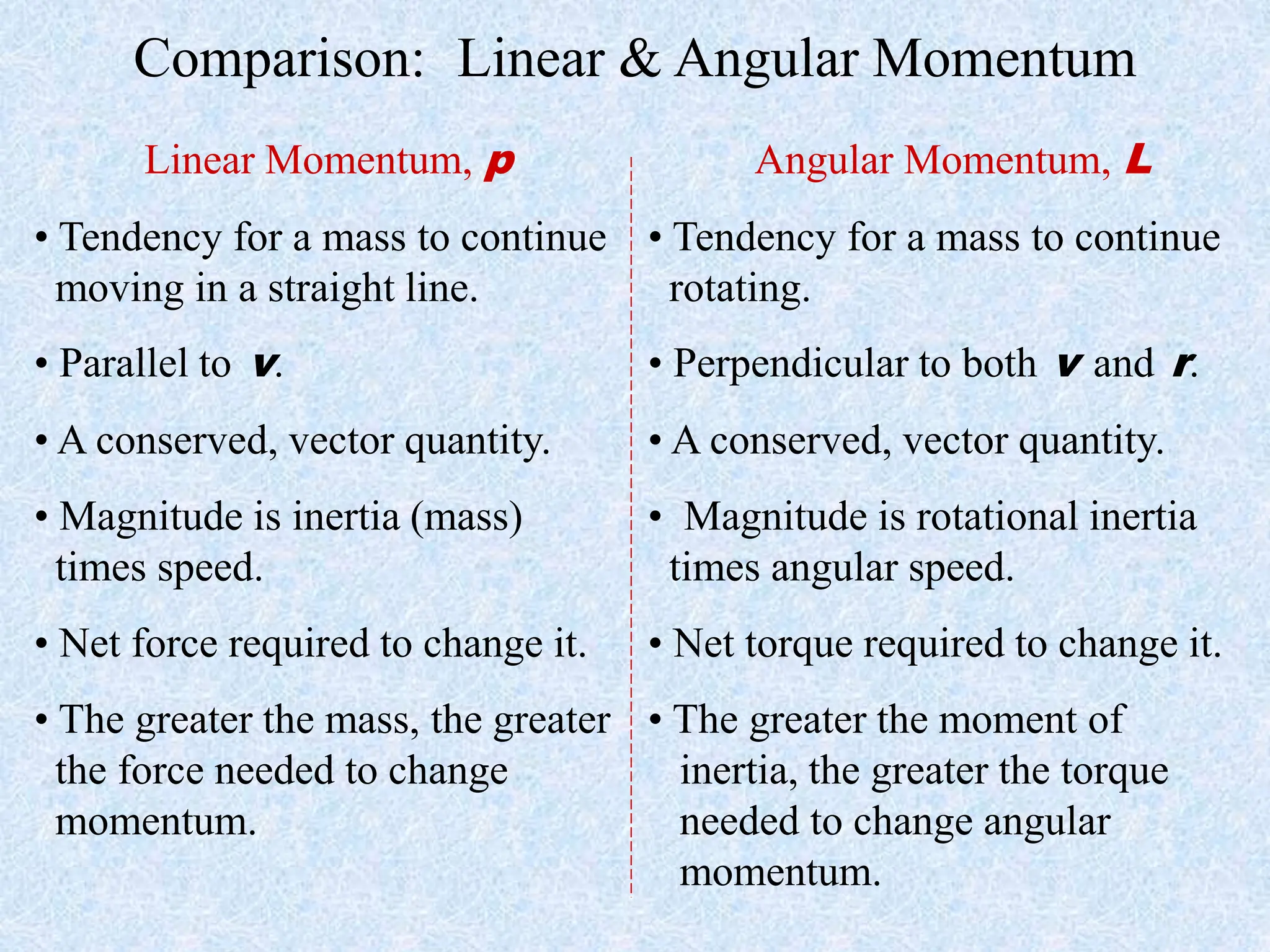
This document provides information about momentum, including its definition, units, examples, and applications of the principle of conservation of momentum. Some key points covered include:
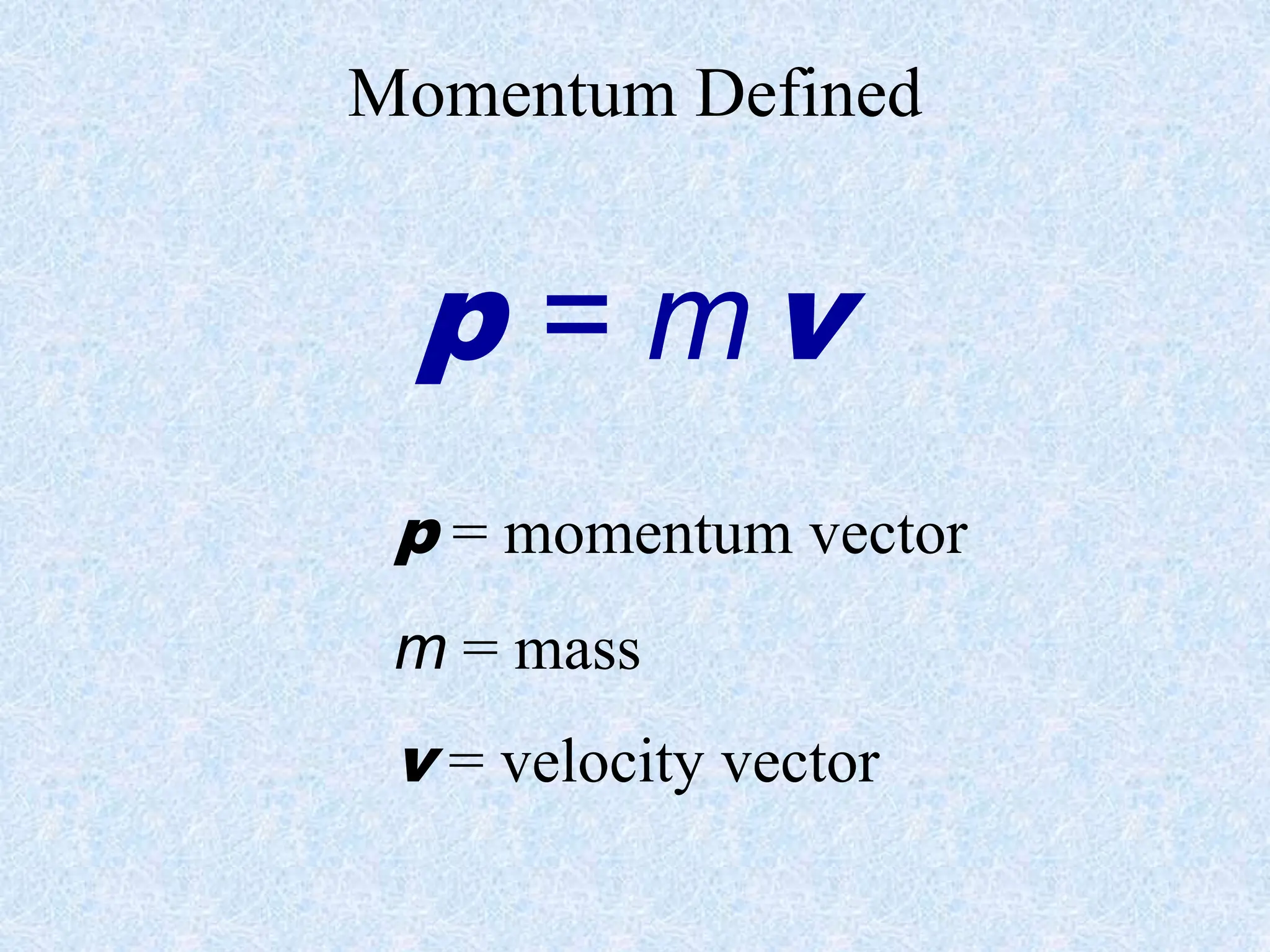
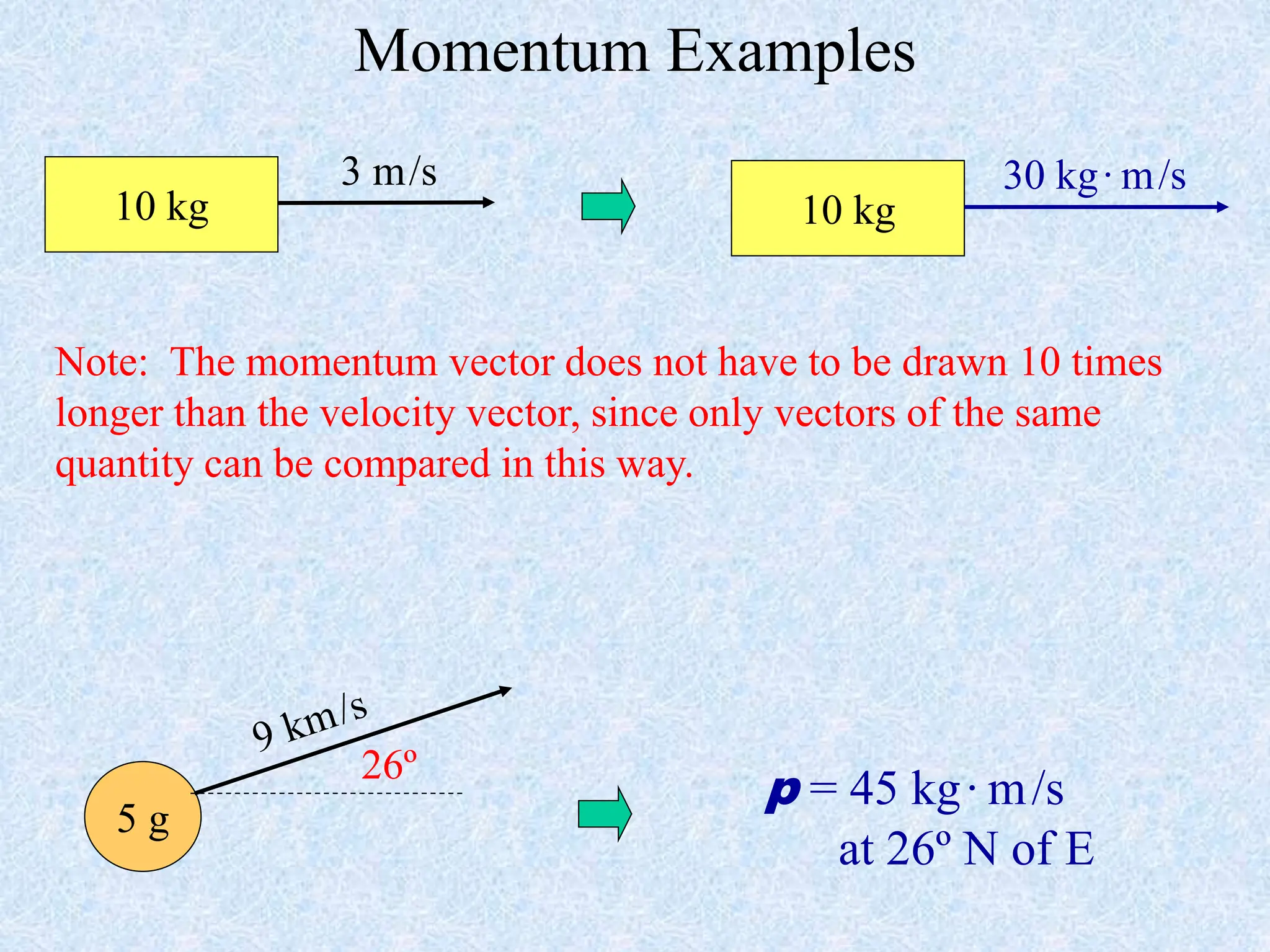
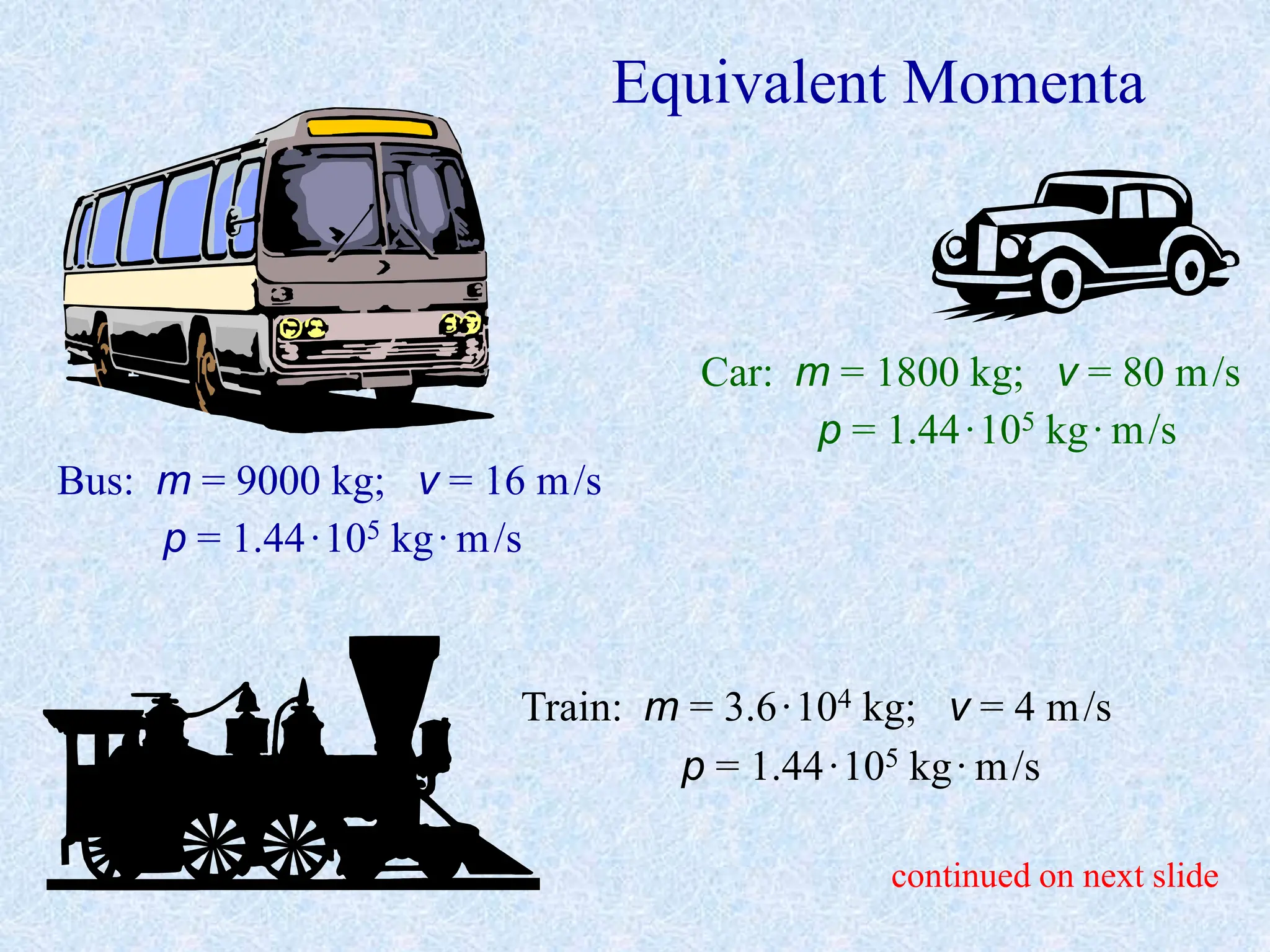
- Momentum is defined as the product of an object's mass and velocity (p=mv). It is a vector quantity.
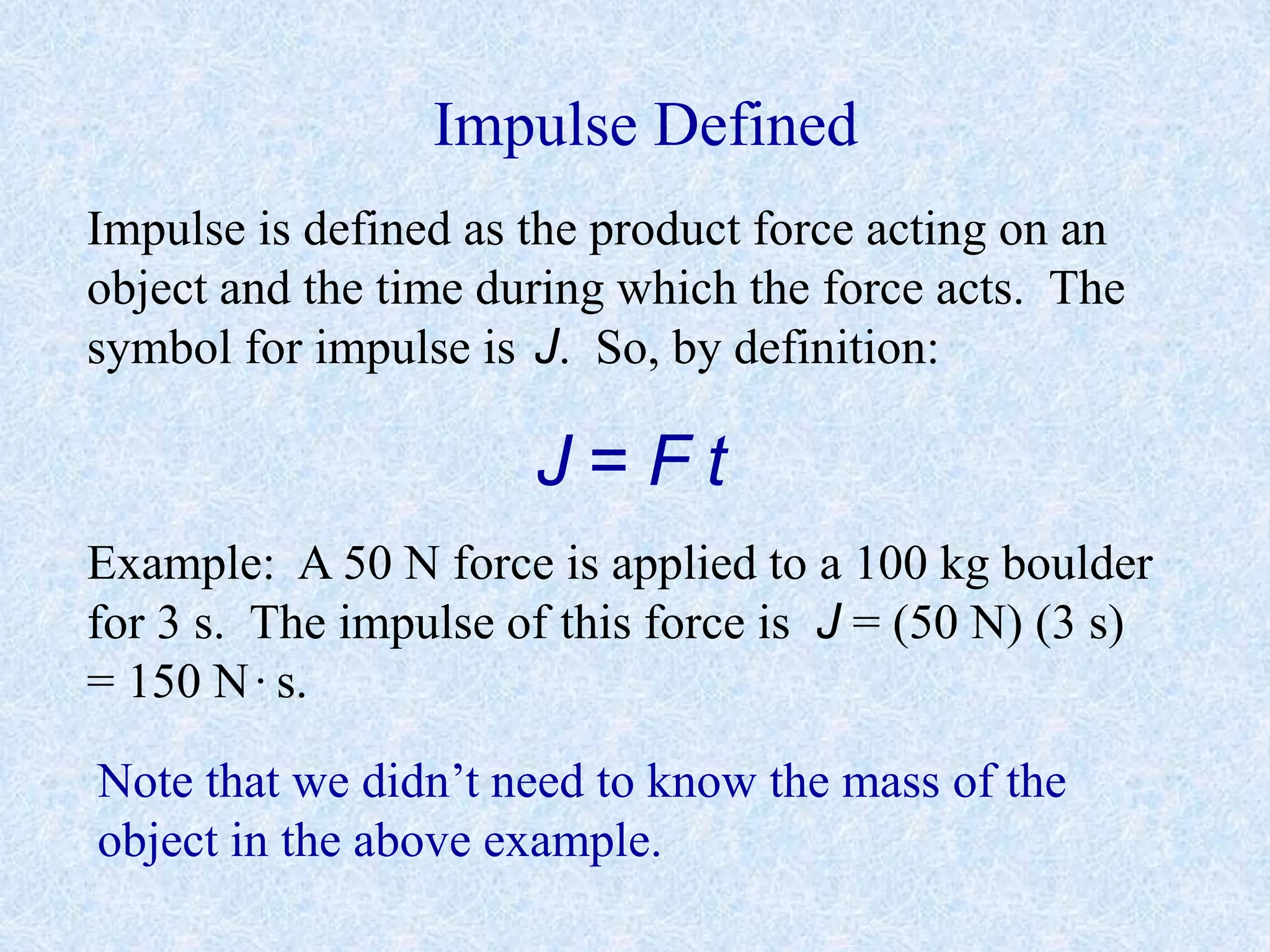
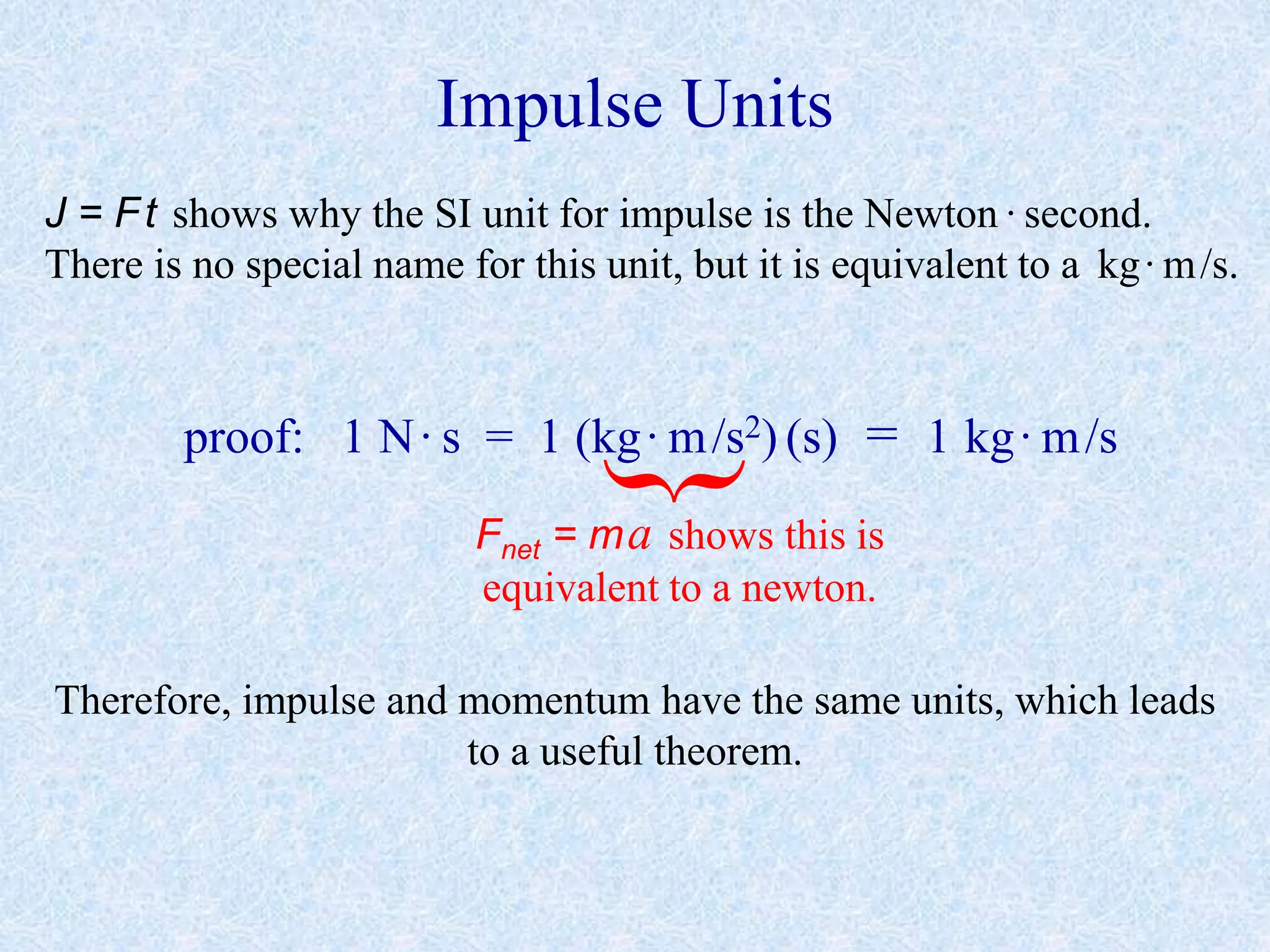
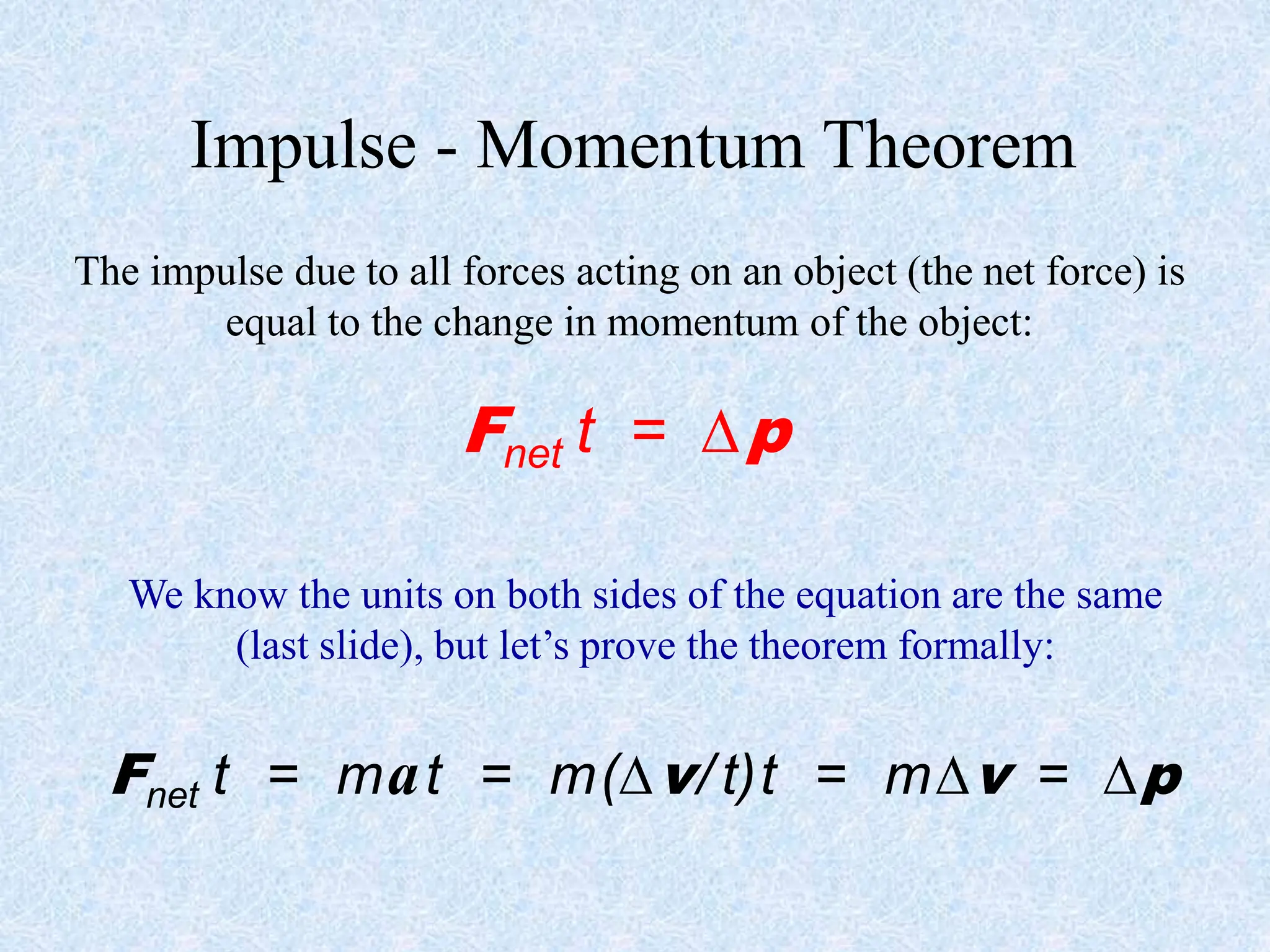
- Impulse is the product of force and time (J=Ft). Impulse and momentum have the same units.
- For collisions or interactions between objects, the total momentum of the system is conserved according to the law of conservation of momentum.
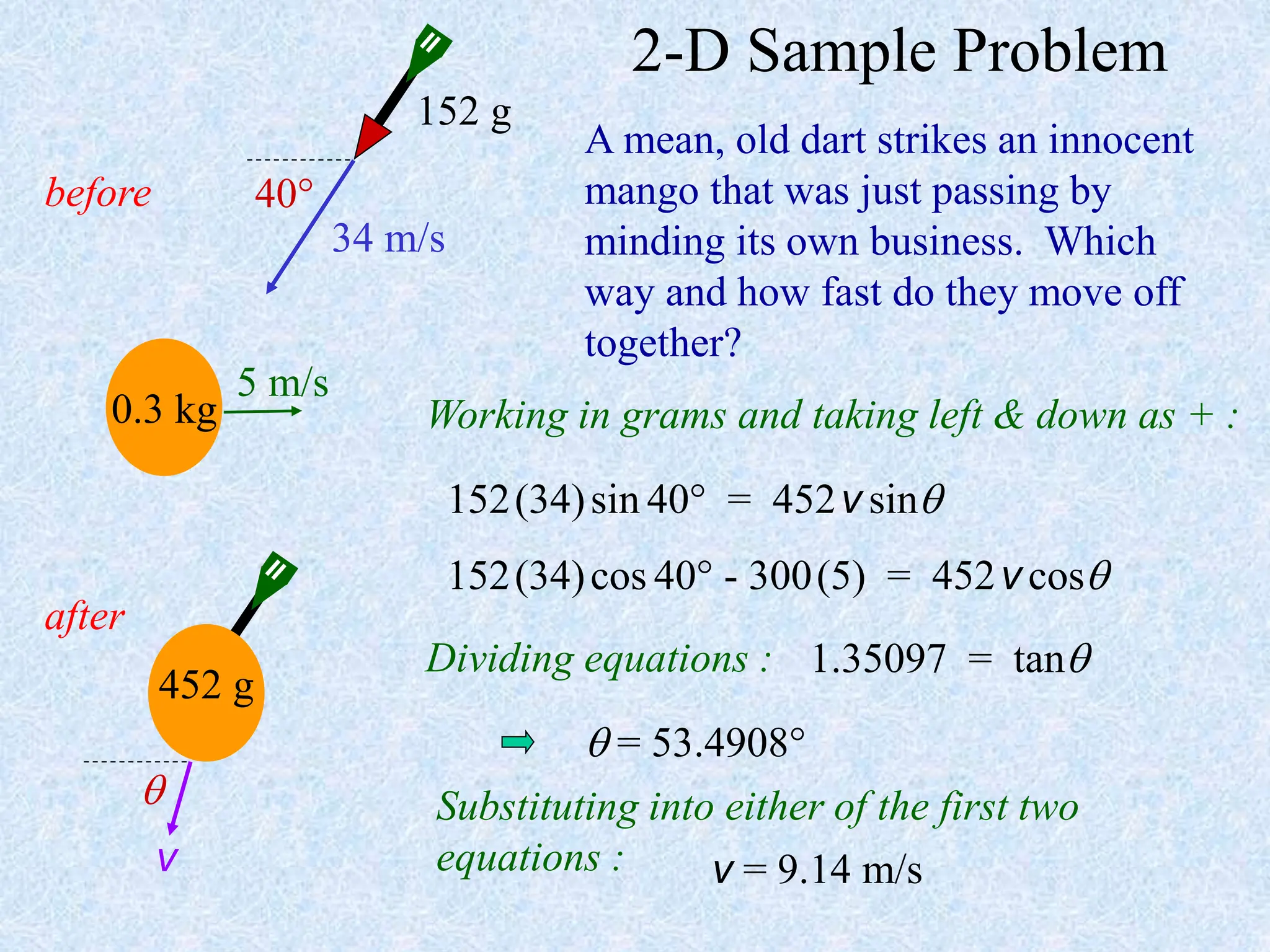
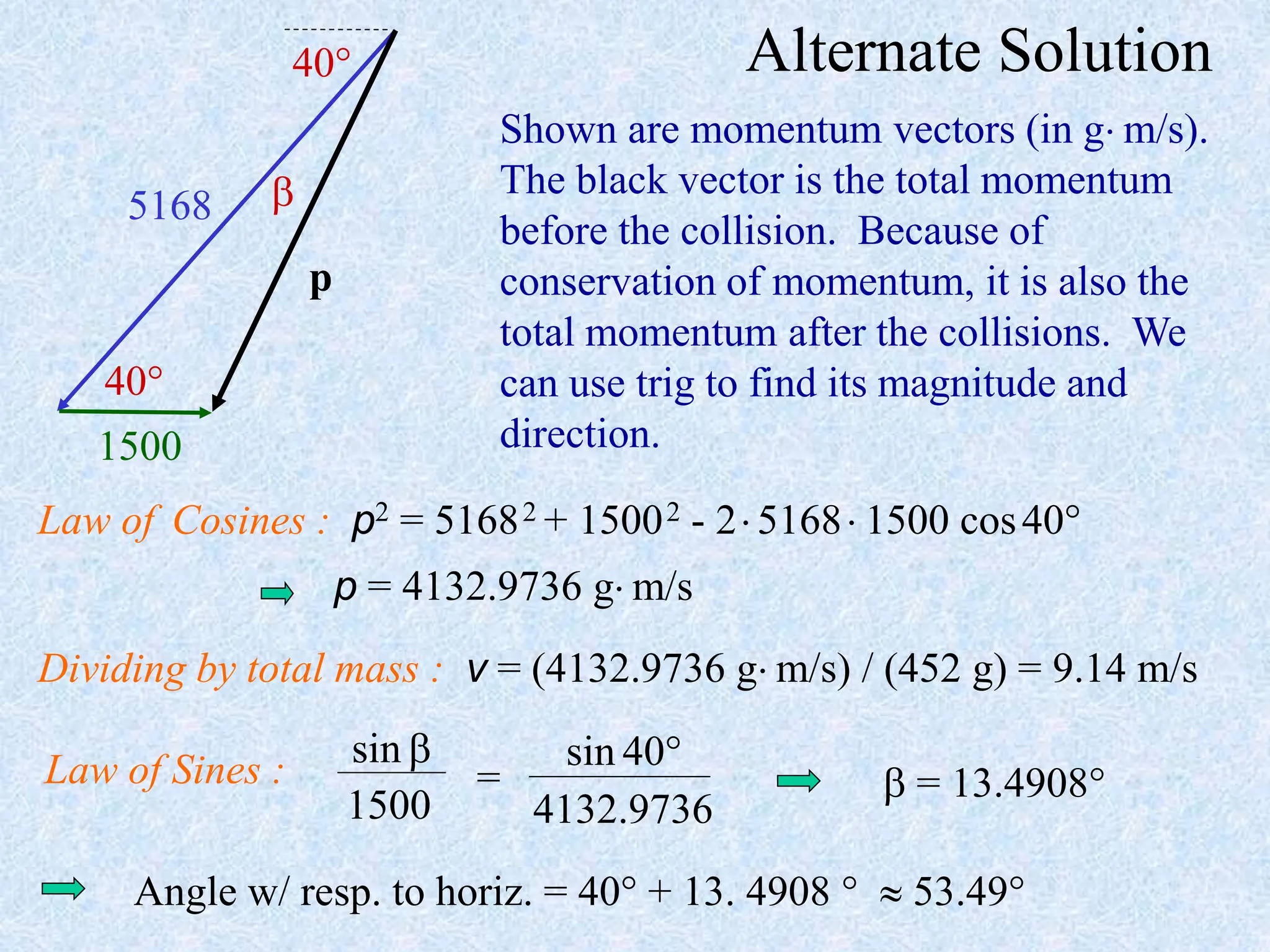
- Conservation of momentum can be applied to analyze one-dimensional and two-dimensional collisions or interactions between objects. Vector diagrams and component analysis are used for two-




![Impulse - Momentum Example
A 1.3 kg ball is coming straight at a 75 kg soccer player at 13 m/s who
kicks it in the exact opposite direction at 22 m/s with an average force
of 1200 N. How long are his foot and the ball in contact?
answer: We’ll use Fnet t = p. Since the ball
changes direction, p = mv = m(vf - v0)
= 1.3 [22 - (-13)] = (1.3 kg) (35 m/s)
= 45.5 kg·m/s. Thus, t = 45.5 / 1200
= 0.0379 s, which is just under 40 ms.
During this contact time the ball compresses substantially and then
decompresses. This happens too quickly for us to see, though. This
compression occurs in many cases, such as hitting a baseball or golf
ball.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/7-momentum-240402014301-91896a76/75/Power-point-slides-for-momentum-Impullse-conservation-of-memntum-11-2048.jpg)