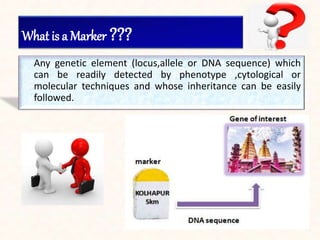
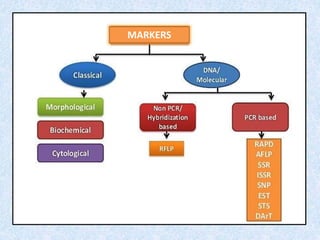
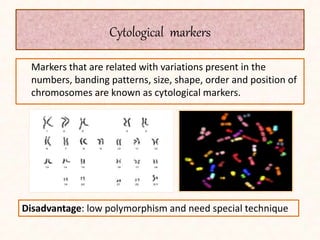
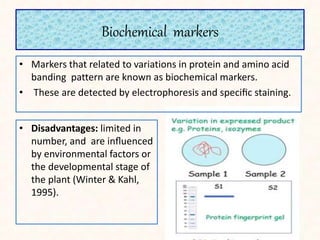
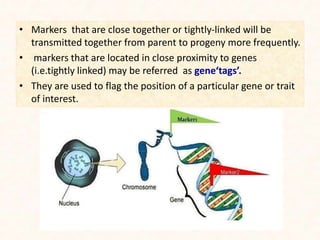
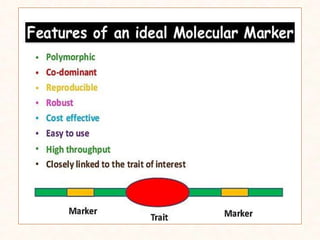
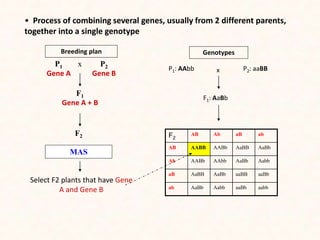
1. The document discusses a seminar on applying molecular markers in plant breeding. It defines different types of markers including morphological, cytological, biochemical, and DNA/molecular markers.
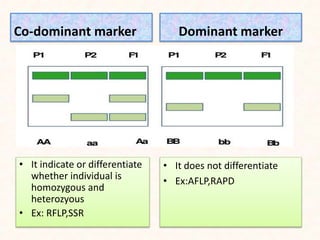
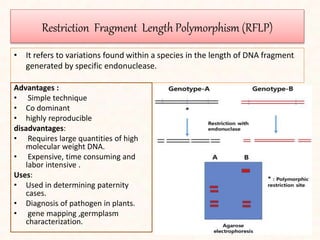
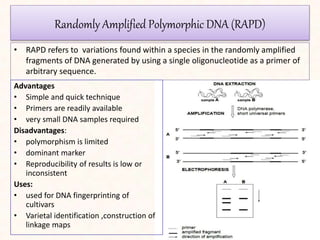
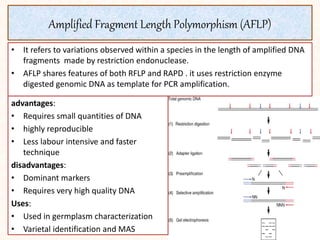
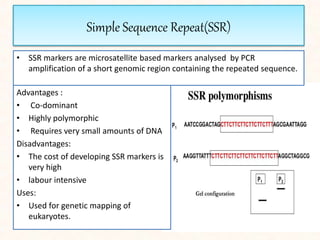
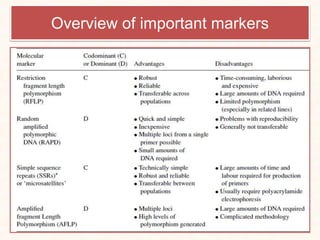
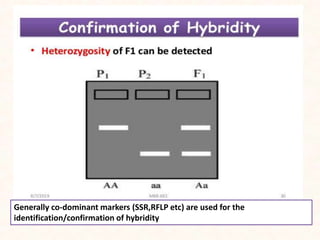
2. It describes various molecular marker techniques like RFLP, RAPD, AFLP, and SSR. The techniques differ in characteristics like being dominant or co-dominant.
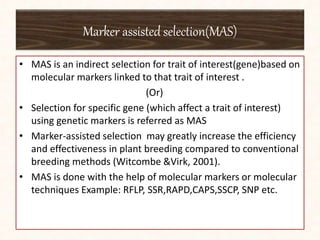
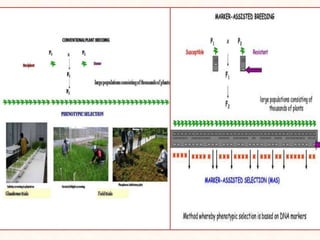
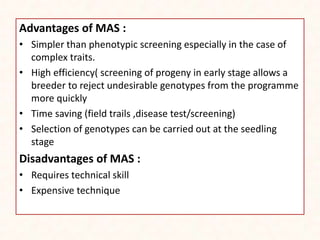
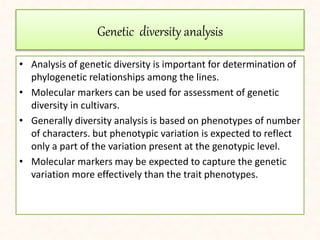
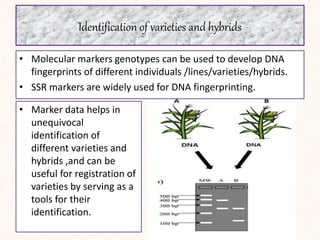
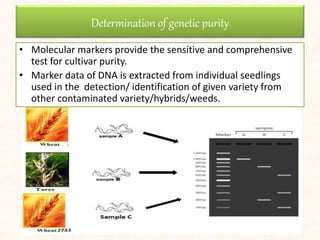
3. Molecular markers have important applications in plant breeding like marker-assisted selection, genetic diversity analysis, germplasm characterization, variety identification, and gene pyramiding.
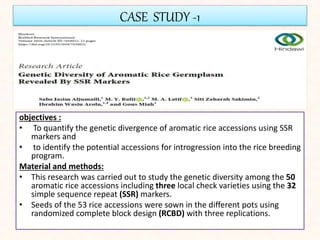
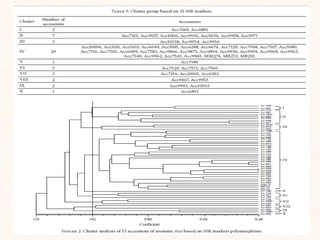
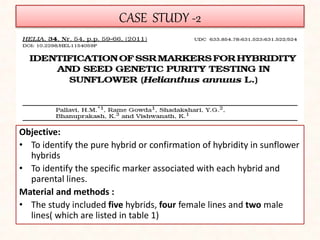
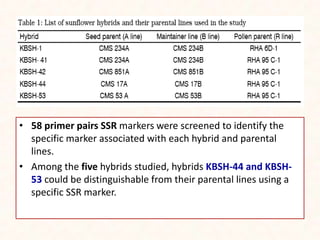
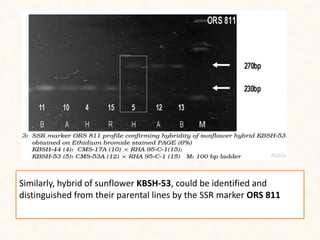
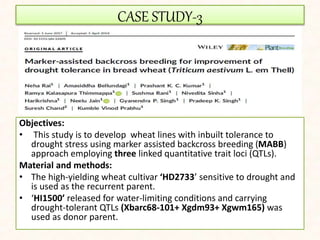
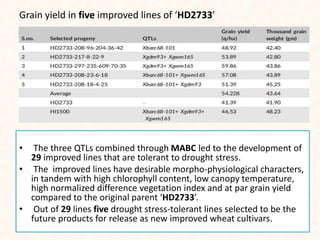
4. Two case studies demonstrate the use of SSR markers to study genetic diversity in aromatic rice accessions and identify hybrids in sunflower. Specific markers were