The document discusses the hydrosphere and the hydrologic cycle. It can be summarized as:
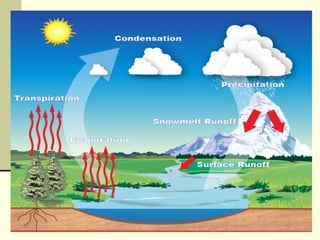
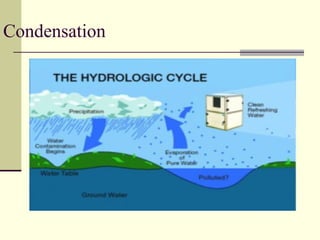
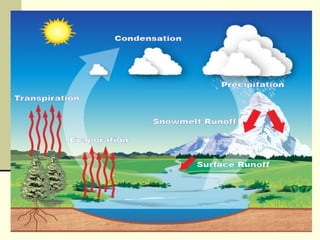
The hydrosphere refers to all water on Earth, including oceans, freshwater, ice, and water vapor in the atmosphere. Water is essential for life and exists in liquid form between 0-100 degrees Celsius. The hydrologic cycle is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth, including evaporation, transpiration by plants, condensation into clouds, precipitation, and runoff into lakes, rivers, and groundwater. This cycle is driven by energy from the sun and Earth's gravity.