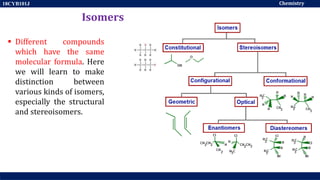
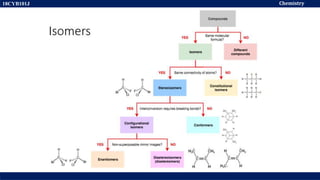
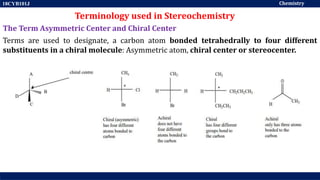
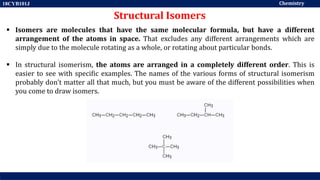
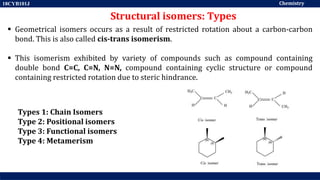
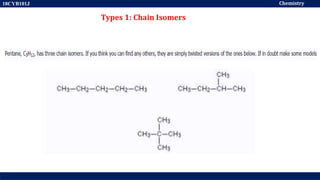
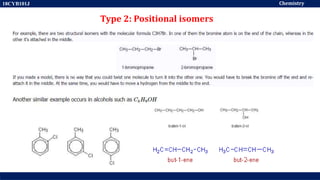
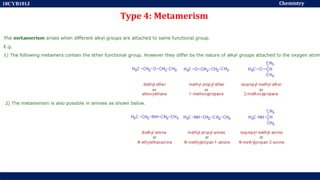
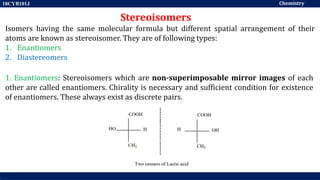
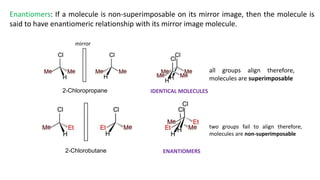
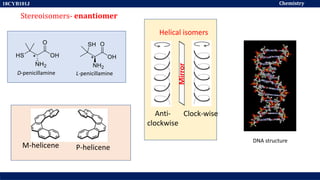
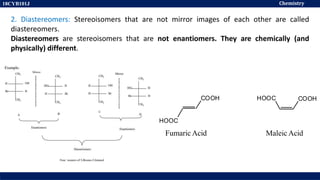
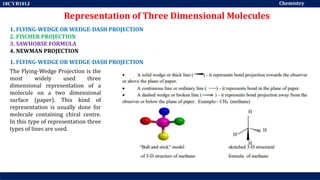
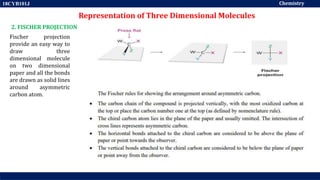
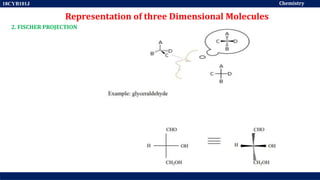
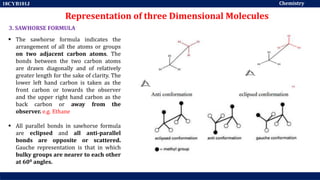
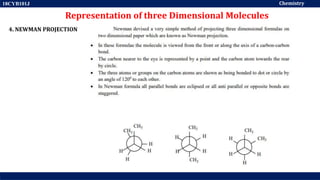
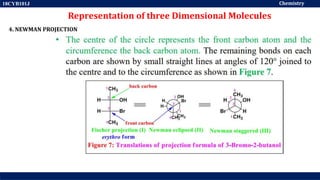
This document discusses structural isomers and stereoisomers. It defines stereochemistry as dealing with the three-dimensional representation of molecules in space. It notes that stereoisomers, which have the same molecular formula but different spatial arrangements of atoms, can have different biological effects. As an example, it describes how the drug thalidomide was prescribed as a mixture of stereoisomers, with one causing serious birth defects. The document also defines different types of isomers like structural isomers, enantiomers and diastereomers. It outlines several methods for representing 3D molecular structures like wedge-dash, Fischer, sawhorse and Newman projections.