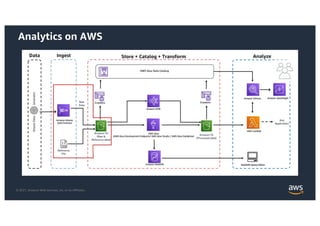
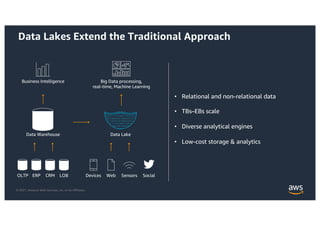
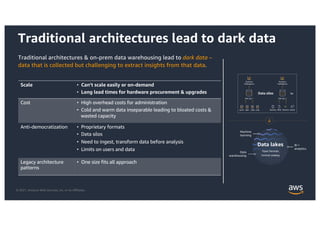
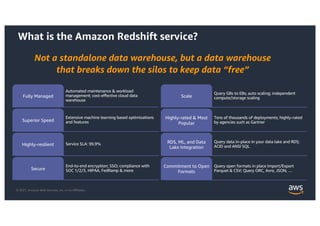
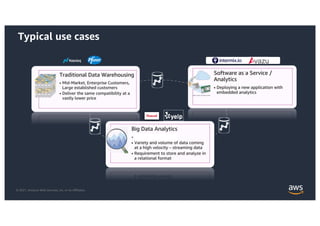
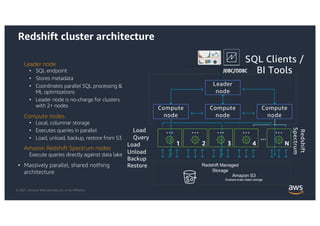
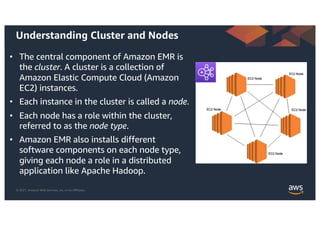
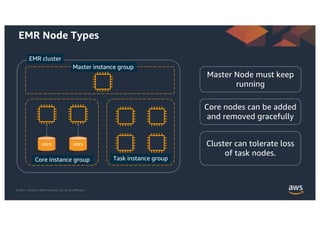
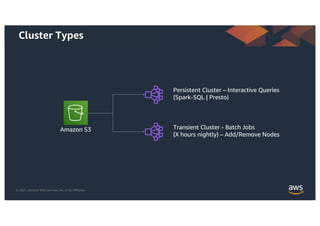
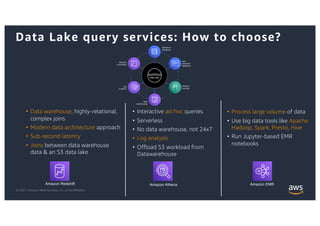
This document provides an agenda and overview for a workshop on building a data lake on AWS. The agenda includes reviewing data lakes, modernizing data warehouses with Amazon Redshift, data processing with Amazon EMR, and event-driven processing with AWS Lambda. It discusses how data lakes extend traditional data warehousing approaches and how services like Redshift, EMR, and Lambda can be used for analytics in a data lake on AWS.












![© 2021, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its Affiliates.
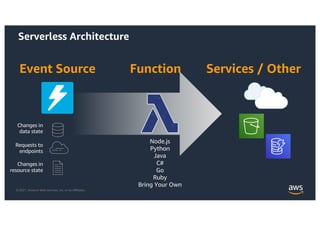
Anatomy of a Lambda Function
Handler function
• Function executed on invocation
• Processes incoming event
Event
• Invocation data sent to function
• Shape differs by event source
Context
• Additional information from Lambda service
• Examples: request ID, time remaining
def handler(event, context):
msg = ‘Hello {}’.format(
event[‘name’]
)
return { ‘message’: msg }
app.py](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module2-datalake-211022050944/85/Module-2-Datalake-28-320.jpg)