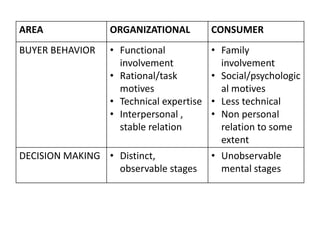
1) Consumer and organizational buying behavior differ in who is involved in the decision making, the motives behind purchases, and how rational/technical the process is. Organizational buying involves functional teams while consumer buying is usually an individual.
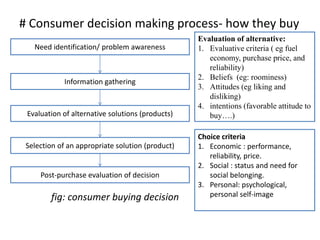
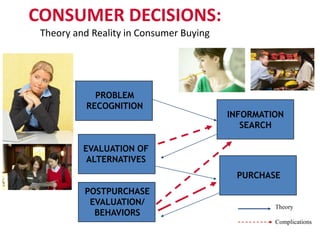
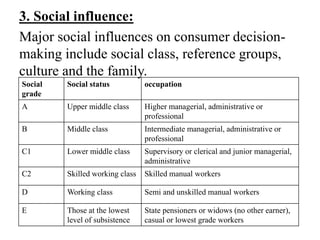
2) Consumer buying decisions involve need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase, and post-purchase evaluation. Personal factors like demographics, attitudes, and social influences impact consumer decisions.
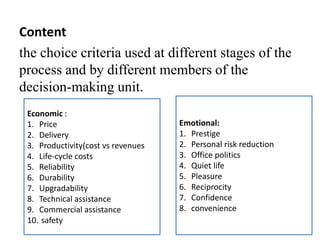
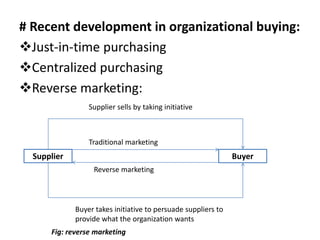
3) Organizational buying involves determining needs, searching for suppliers, analyzing proposals, selecting suppliers, and providing feedback. Economic and emotional criteria are used at different stages by various decision makers in the organization.