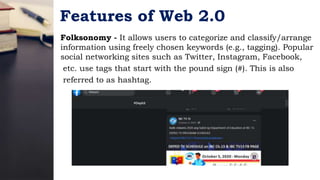
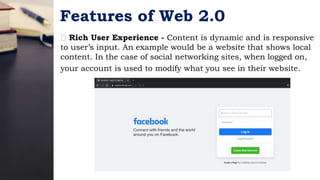
The document discusses trends in information and communication technology (ICT). It covers the evolution of the World Wide Web from Web 1.0 to Web 2.0 to Web 3.0, distinguishing between static read-only content in Web 1.0 versus interactive and user-generated content in Web 2.0. Web 3.0 utilizes artificial intelligence to better understand user preferences. Other trends discussed include convergence of technologies, the rise of social media, assistive media, and increasing use of mobile technologies and operating systems.