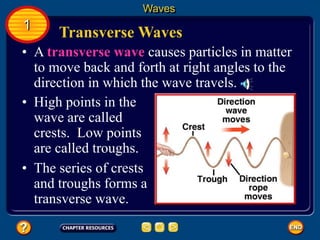
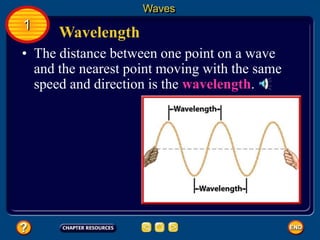
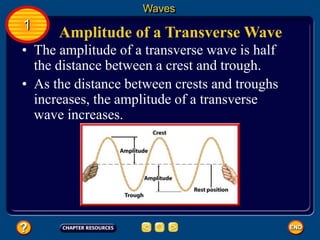
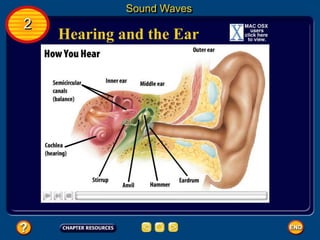
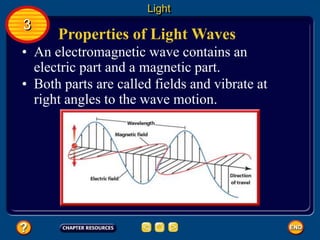
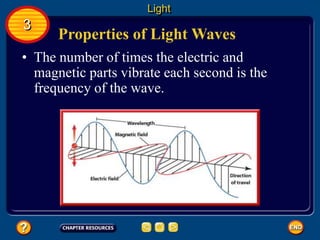
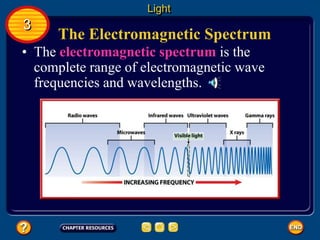
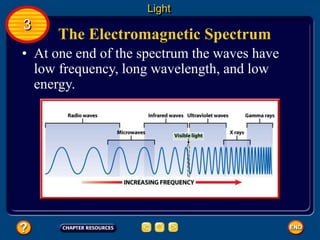
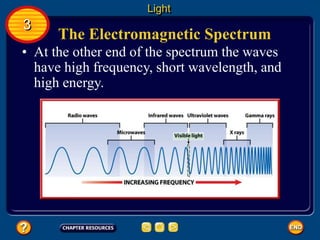
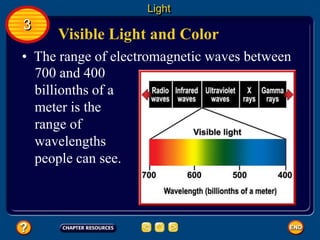
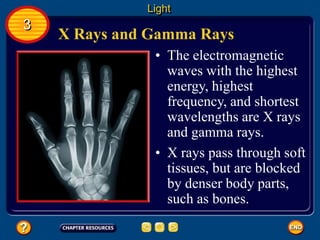
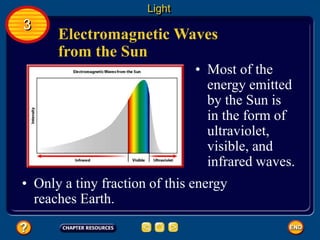
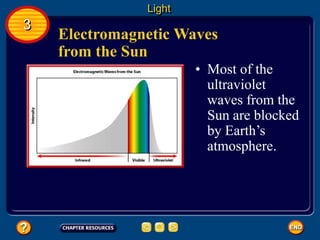
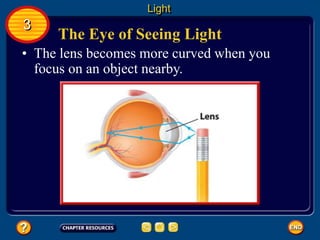
Waves transfer energy and can be transverse or electromagnetic. Transverse waves cause particles to move at right angles to the wave's direction of travel, with crests and troughs forming the wave pattern. Electromagnetic waves contain electric and magnetic fields that vibrate perpendicular to the direction of travel. Properties like wavelength, frequency, and amplitude describe a wave's characteristics. Waves transfer energy and can reflect, refract, or diffract as they encounter different materials.