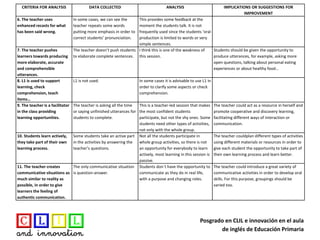
The document analyzes a classroom session on healthy food taught in English. It evaluates the session based on 11 criteria for effective CLIL teaching. The analysis found that while the teacher provided comprehensible input through images and repetition, students had limited opportunities to actively and creatively use English. It suggests giving students more opportunities to interact, produce language in pairs and groups, and participate in authentic communication activities to develop their oral skills.