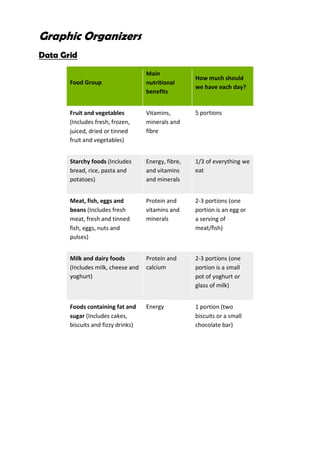
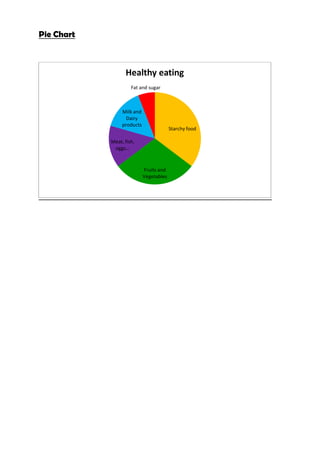
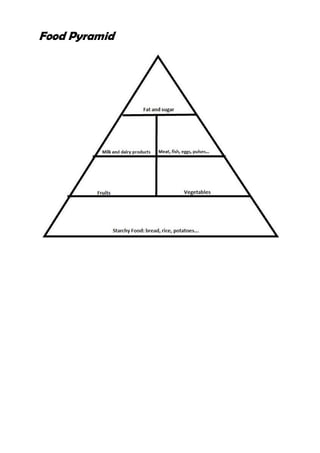
The document provides information about healthy eating and the five main food groups: fruits and vegetables; starchy foods; meat, fish, eggs and beans; milk and dairy products; and foods containing fat and sugar. It aims to teach learners about the nutrients each group provides, their health benefits, and recommended portions for a balanced diet. Key learning outcomes include being able to name the five food groups, identify foods that belong to each, and understand the nutrients and benefits of eating a variety of foods.