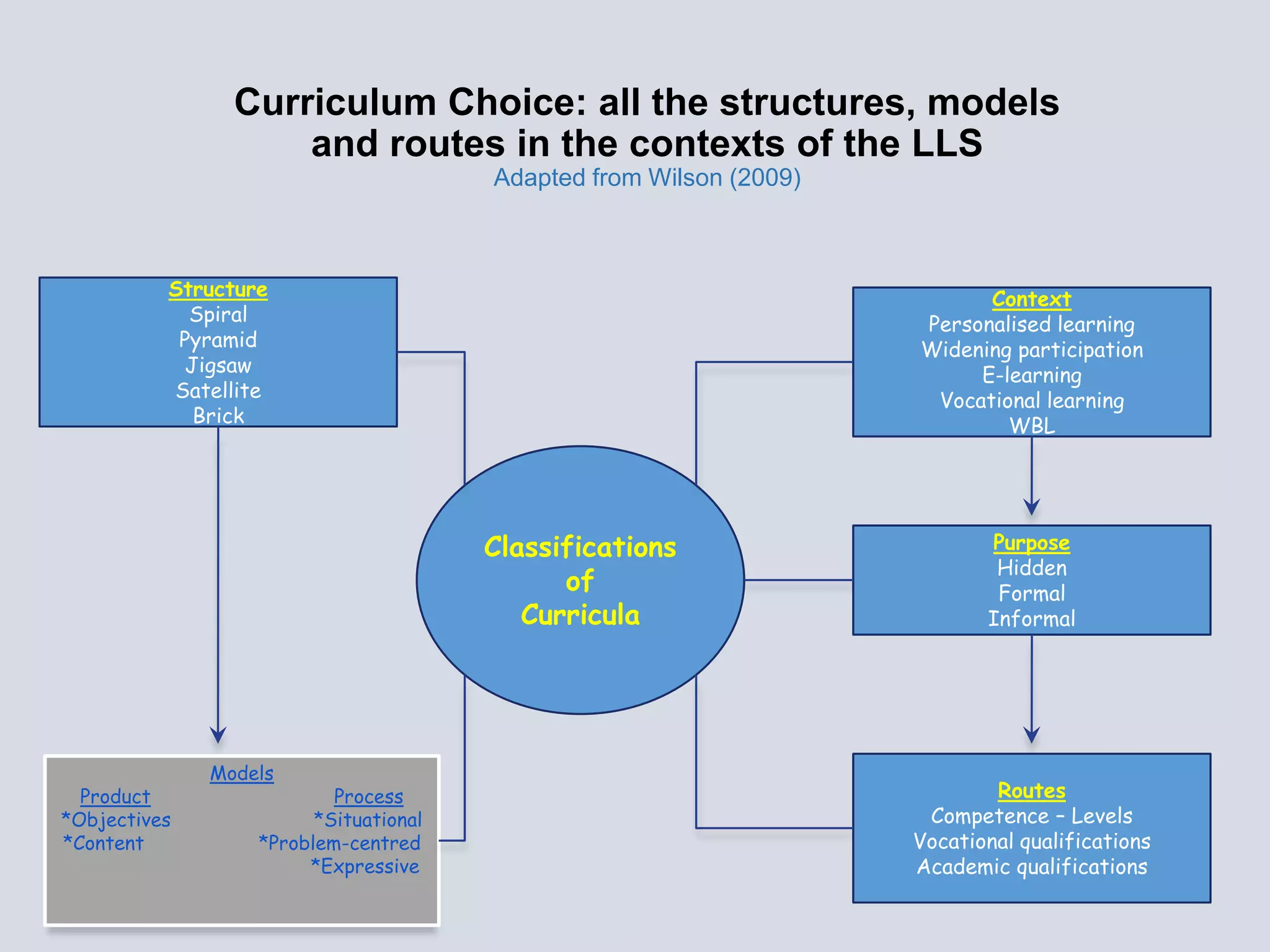
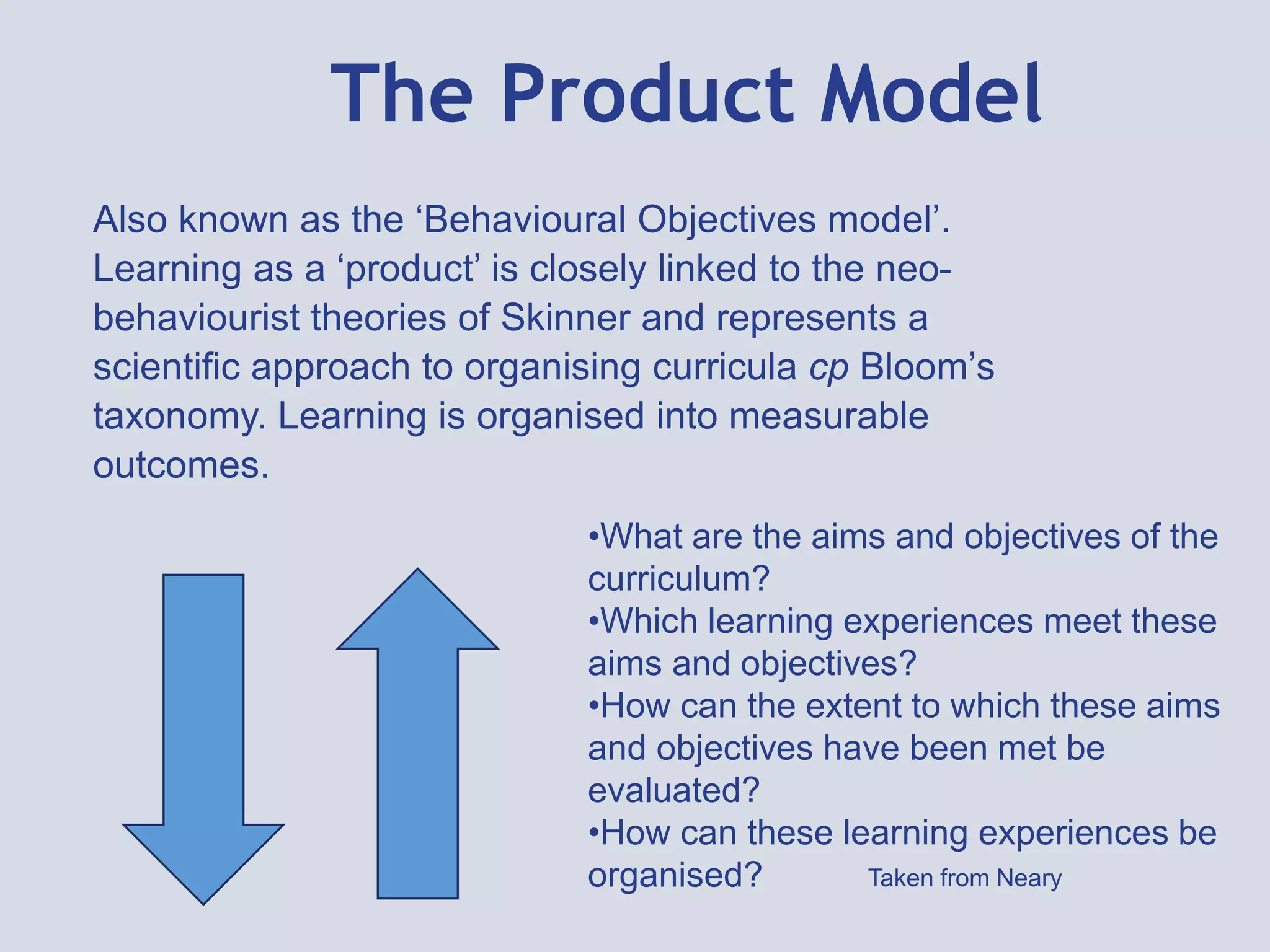
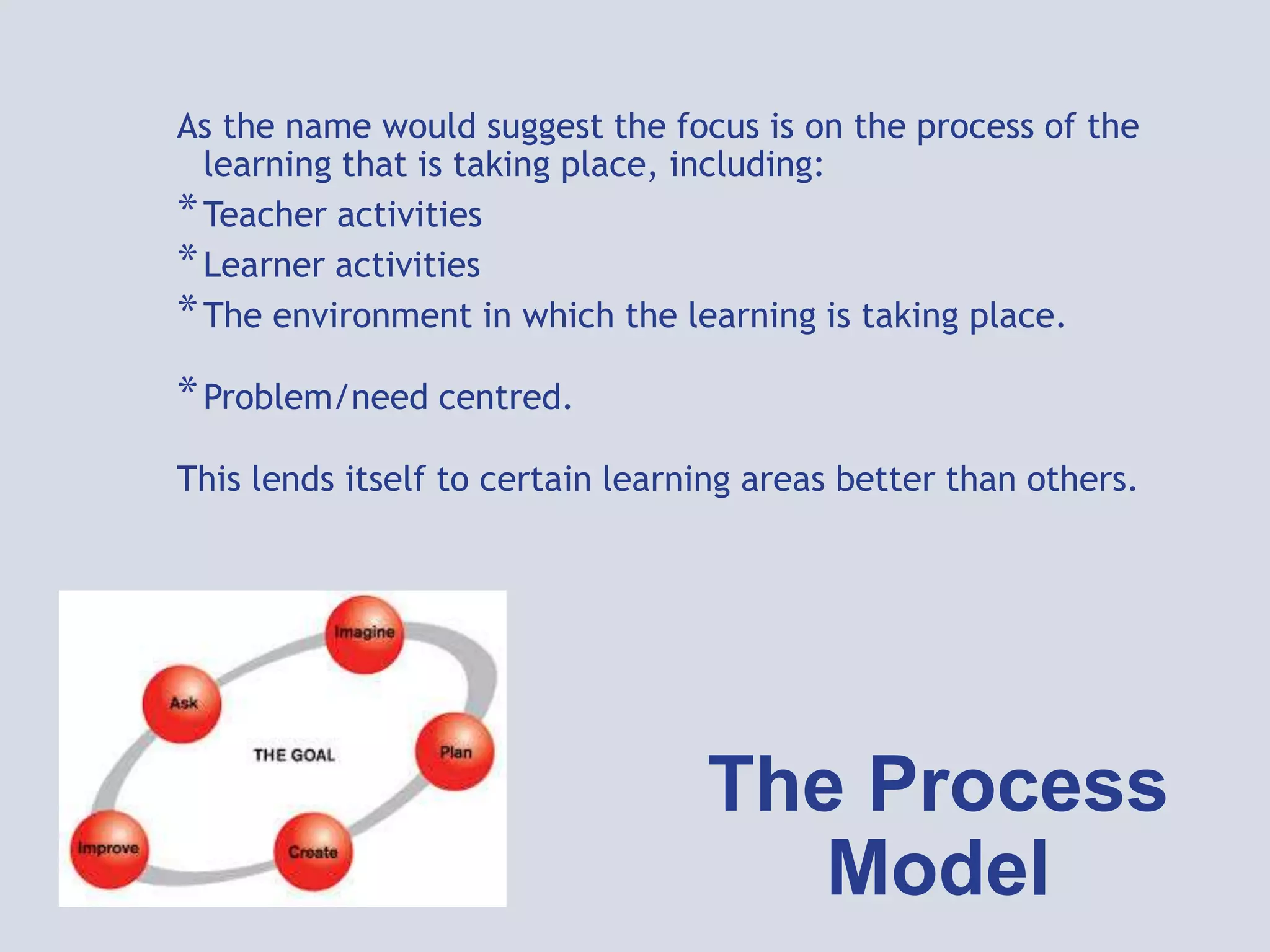
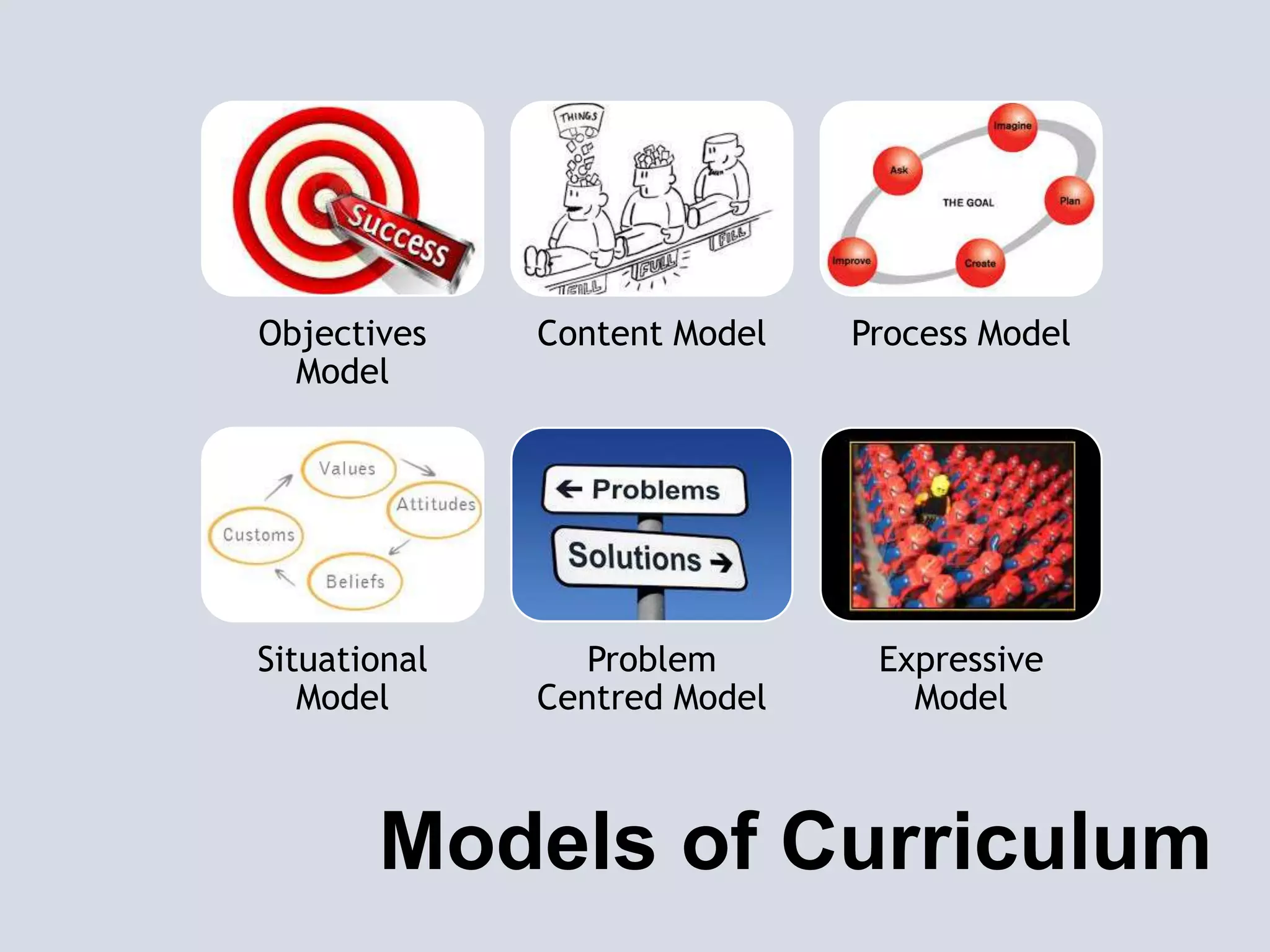
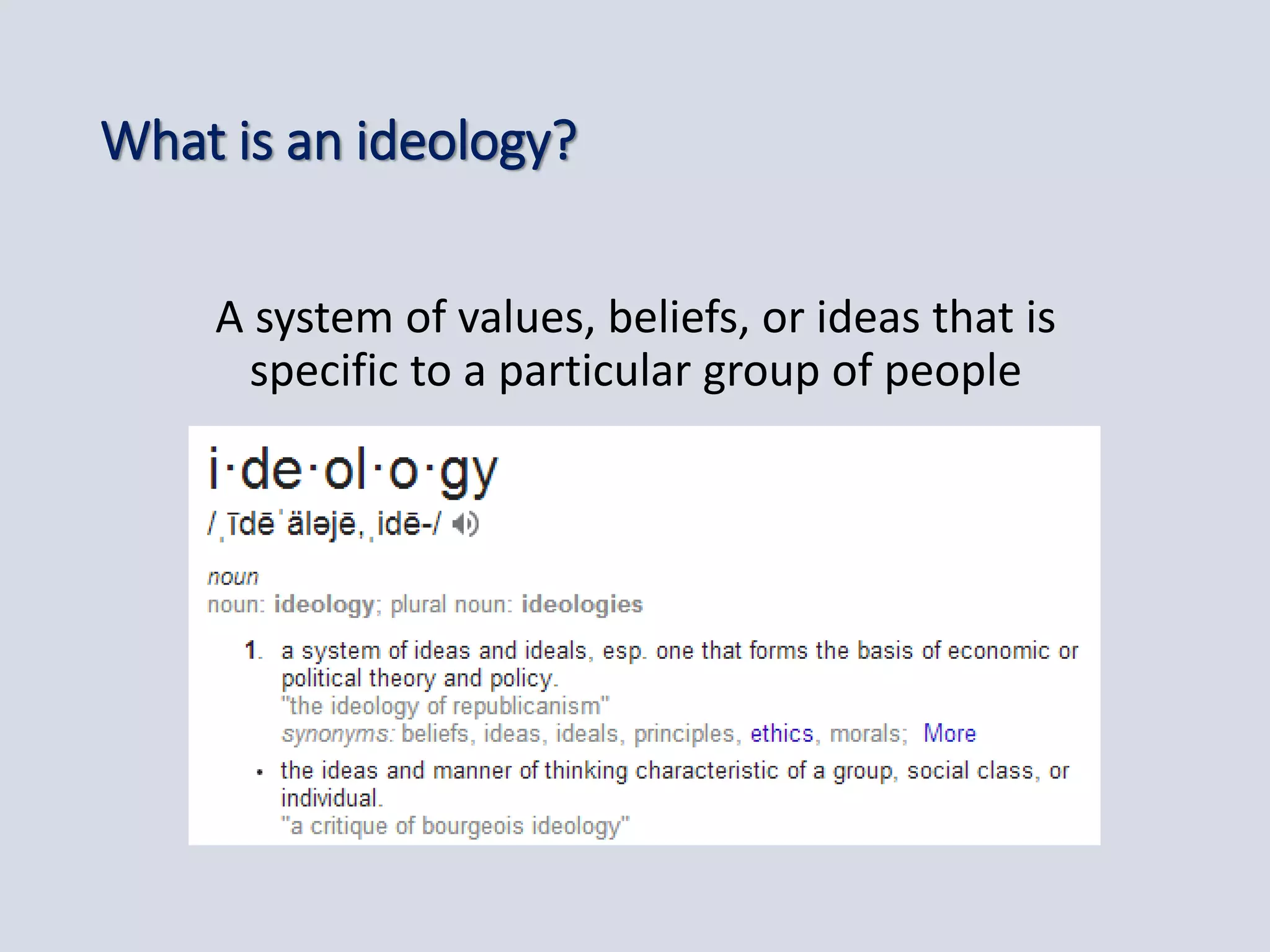
This document provides an overview of curriculum models and ideologies. It explores the product, process, situational, problem-centered, and expressive models of curriculum. The product model focuses on measurable objectives and outcomes, while the process model emphasizes teacher and learner activities and the learning environment. Different curriculum ideologies like liberal humanism, academicism, instrumentalism, progressivism, and reconstructivism are also discussed. Learners research assigned models and evaluate which ideology underpins their own curriculum.