1) The document discusses using modeling and simulation in business process management to provide value during business transformations.
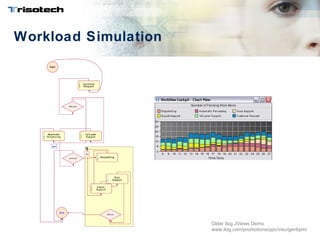
2) It explores how simulation could be used for communication, training, analysis, and validation and gives examples of visual, scenario, and numeric simulations.
3) The document outlines some best practices for business process modeling simulations including aligning the simulation and business goals and using the right expertise.
![Modeling and Simulation in Business Process Management Denis Gagné CEO, Trisotech, Canada. [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modeling-and-simulation-in-business-process-management4644/75/Modeling-and-Simulation-in-Business-Process-Management-1-2048.jpg)