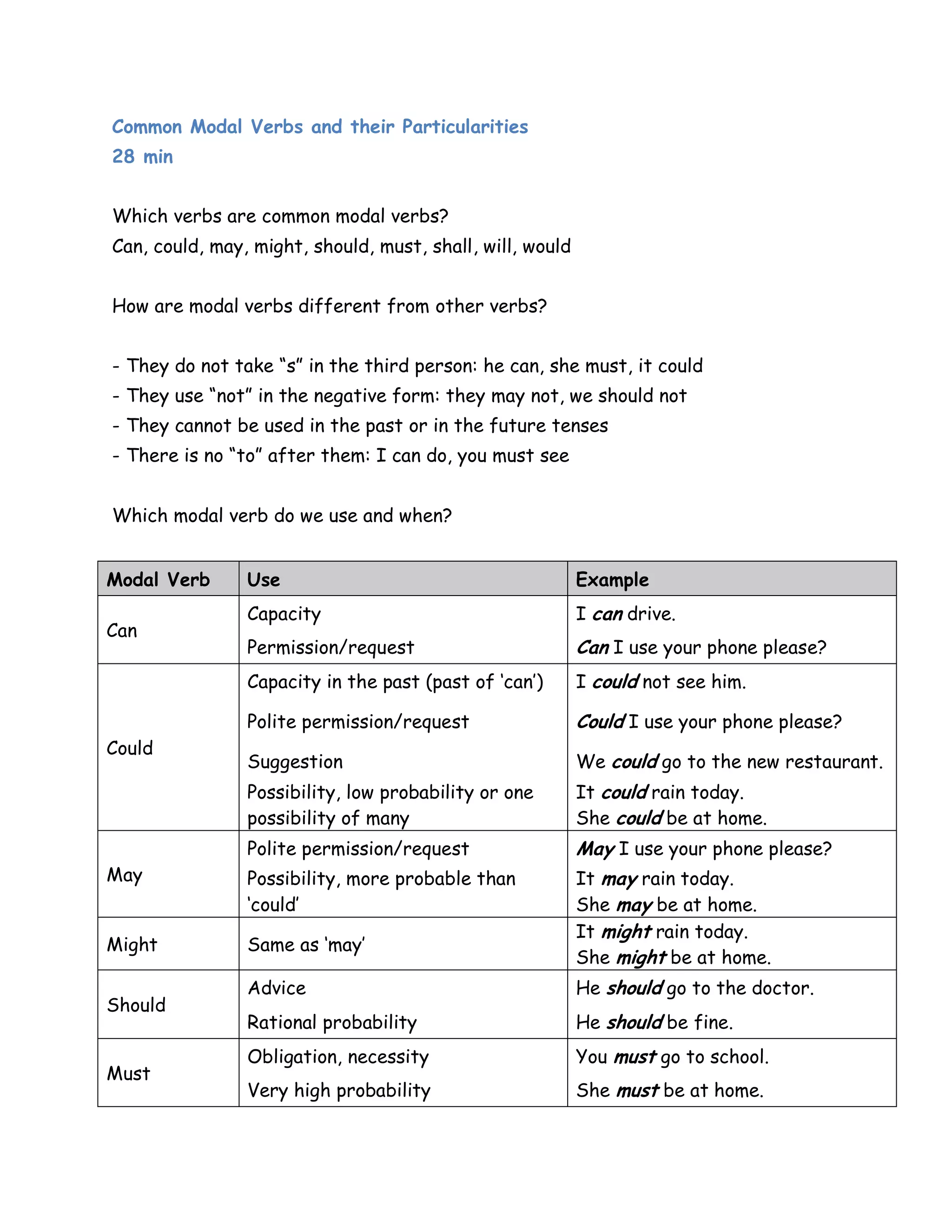
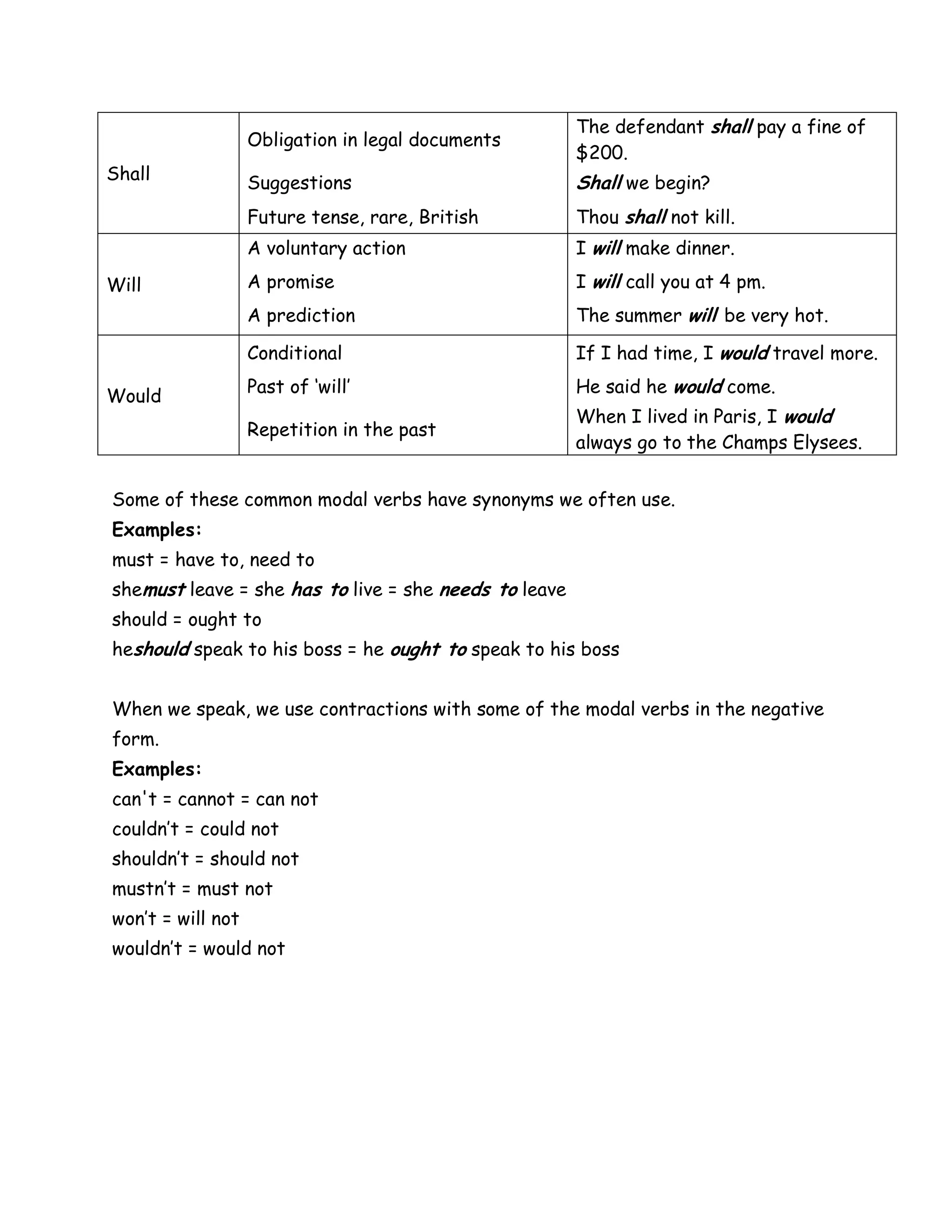
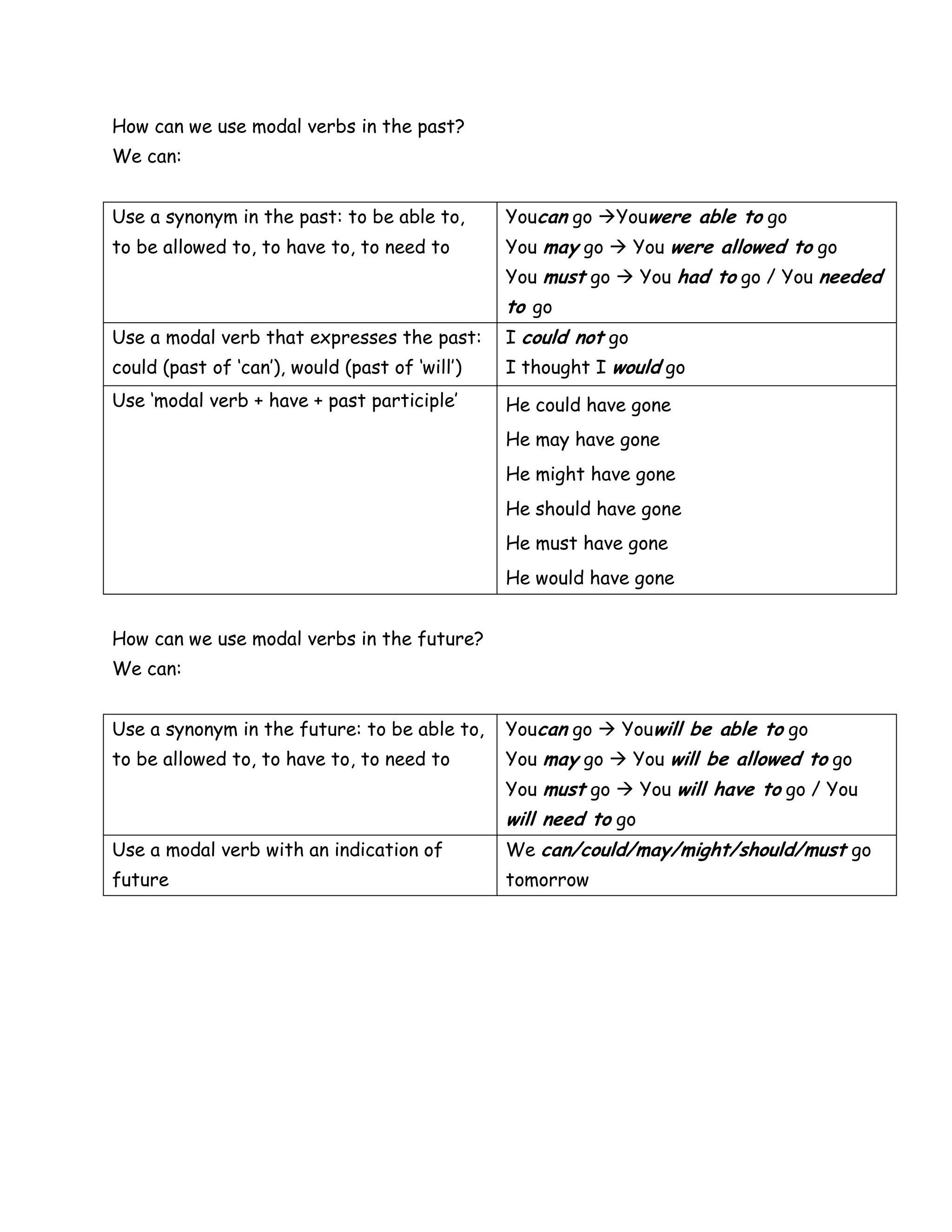
The document discusses modal verbs, which are a small group of verbs that are used differently than normal verbs. It lists common modal verbs such as can, may, should, must, and would. It explains how modal verbs are used, including how they do not take "s" in the third person or use "to" after them. It provides examples of how each modal verb is used to indicate capacity, permission, advice, obligation, prediction, and more. It also discusses how to use modal verbs in the past and future tenses.