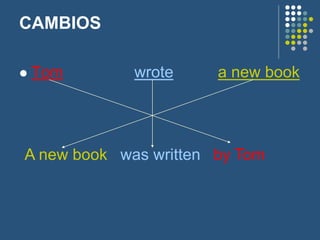
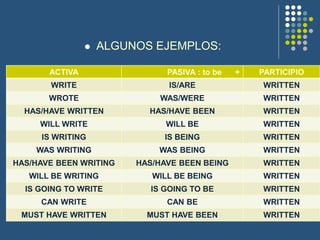
The document discusses the passive voice in Spanish. It provides examples of changing sentences from active to passive voice. The passive is formed using the verb "to be" and the past participle. The agent is sometimes included after "by". Exceptions include verbs with two objects, reporting verbs, prepositional verbs, and causative verbs like "have" and "get". The passive voice is used when the agent is unknown, unimportant, or to focus on the object rather than subject of the sentence. Exercises are provided to practice changing sentences between active and passive voice and translating sentences between Spanish and English.