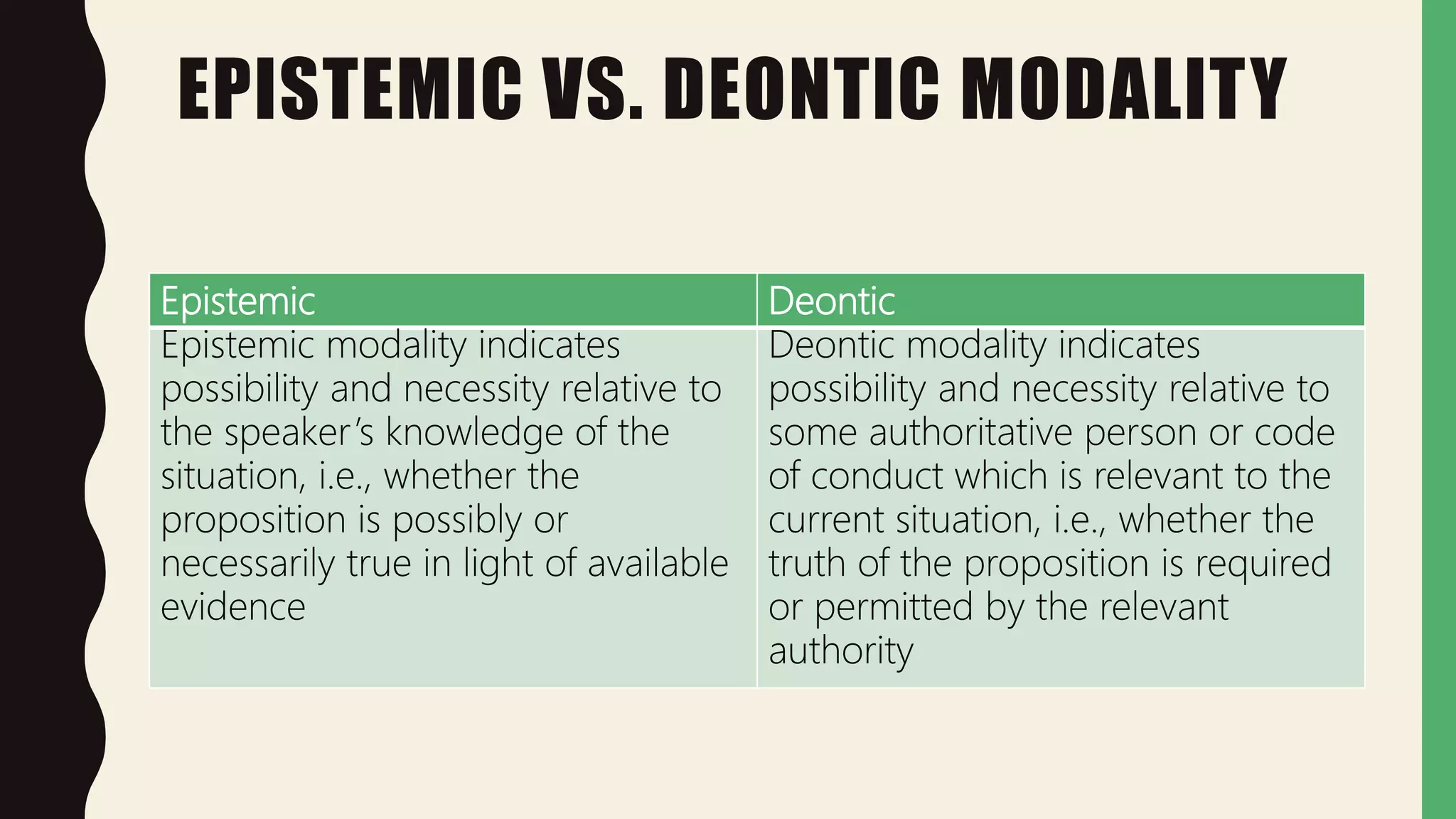
This document discusses modality in language. It defines modality as being expressed through modal auxiliaries like may, must, should. Modality can indicate possibility, necessity, or obligation based on knowledge or authority. There are two main types: epistemic modality reflects knowledge, while deontic modality reflects authority or rules. The strength and type of modality depend on context rather than the words themselves.



![EXAMPLES
• (2) a. John didn’t show up for work. He must be sick.
• [spoken by co-worker; Epistemic]
• b. John didn’t show up for work. He must be fired.
• [spoken by boss; Deontic]
• (3) a. The older students may leave school early (unless the teachers watch
• them carefully).
• b. The older students may leave school early (if they inform the
• headmaster first).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modality-201207085440/75/Modality-5-2048.jpg)