This document provides information about compilers and related tools for the TNS/E platform, including:
- The TNS/E compilers for COBOL, C/C++, pTAL, and their differences from TNS/R compilers like obsolete directives and pragmas.
- New features supported by the TNS/E compilers like C99 support for C/C++ and additional Guardian procedure calls for pTAL.
- Changes to compiler behavior and evaluations that could affect code ported from TNS/R.


![TNS/E COBOL CompilerTNS/E COBOL Compiler
◦ Guardian environment:
ECOBOL/IN <src-file> [,OUT <list-file>] [options]/
[<obj-file>][;directives,…]
◦ OSS environment:
ecobol myProg.cbl –o myProg.exe
◦ Creates code 800 linkfile
Executable if RUNNABLE directive used
2 - Compilers 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mod02compilers-130509072629-phpapp02/85/Mod02-compilers-3-320.jpg)





![TNS/E C/C++ CompilerTNS/E C/C++ Compiler
◦ The TNS/E C/C++ compiler complies with the
following standards:
C - ANSI X3J11/88-159 ISO/IEC 9899:1990 (E)
C++ - ISO/IEC 14882 1998-09-01
◦ Guardian C:
CCOMP/IN <src-file> [,OUT <list-file>] [options]/
[<objfile>][;directives,…]
◦ Guardian C++:
CPPCOMP/IN <src-file> [,OUT <list-file>] [options]/
[<objfile>][;directives,…]
◦ OSS C/C++:
c89 myProg.c –o myProg.exe –Wtarget={TNS/E|TNS/R}
OSS defaults to current platform
2 - Compilers 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mod02compilers-130509072629-phpapp02/85/Mod02-compilers-10-320.jpg)










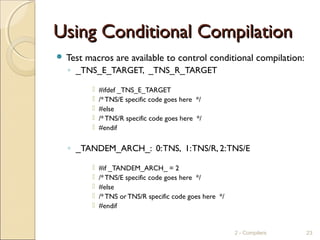
![TNS/E epTAL CompilerTNS/E epTAL Compiler
◦ Guardian environment:
EPTAL/IN <src-file> [,OUT <list-file>] [options]/ [<obj-
file>][;directives,…]
◦ Creates code 800 linkfile
2 - Compilers 24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mod02compilers-130509072629-phpapp02/85/Mod02-compilers-24-320.jpg)
![Obsolete DirectivesObsolete Directives
◦ ?SAVEGLOBALS — Gives error
◦ ?USEGLOBALS — Gives error
◦ ?BEGINCOMPILATION — Ignored
◦ ?[NO]CALL_SHARED — Ignored
◦ ?SRL — Ignored
◦ ?[NO]GP_OK — Ignored
◦ ?PUSHGP_OK — Ignored
◦ ?POPGP_OK — Ignored
2 - Compilers 25](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mod02compilers-130509072629-phpapp02/85/Mod02-compilers-25-320.jpg)


![Function ChangesFunction Changes
$AXADR Not supported Replace with standard interface
(see ref. manual)
$EXECUTIO Not supported Remove from the program
$FREEZE Allowed as DEFINE
name
Replace with the $TRIGGER (new
in TNS/E)
$HALT Allowed as DEFINE
name
Replace with the $TRIGGER (new
in TNS/E)
$INTERROGATE[H]IO Not supported Remove from the program
$LOCATESPTHDR Not supported Remove from the program
$LOCKPAGE Not supported Remove from the program
$READBASELIMIT Not supported Remove from the program
$READSPT Not supported Remove from the program
$STACK_ALLOCATE Behavior change Address and size rounded up to
16-bytes (was 8 bytes)
$UNLOCKPAGE Not supported Remove from the program
$WRITEPTE Not supported Remove from the program
2 - Compilers 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mod02compilers-130509072629-phpapp02/85/Mod02-compilers-28-320.jpg)