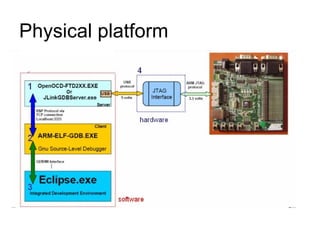
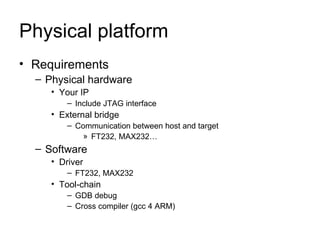
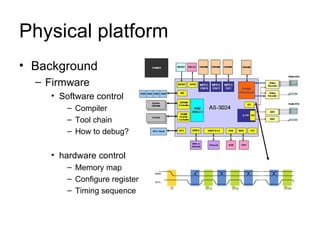
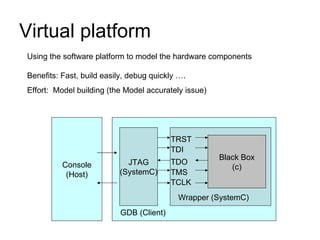
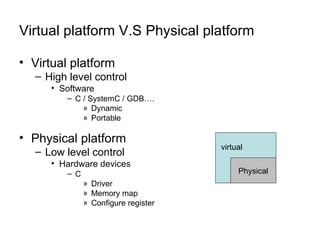
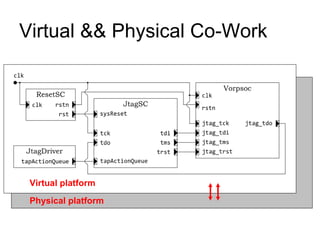
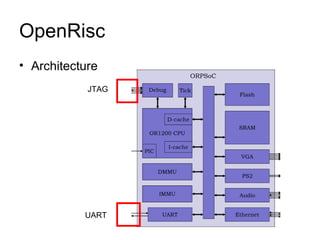
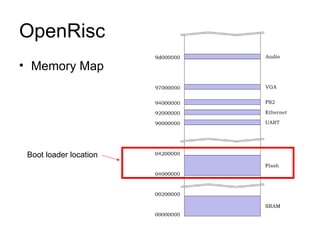
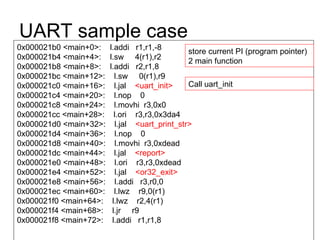
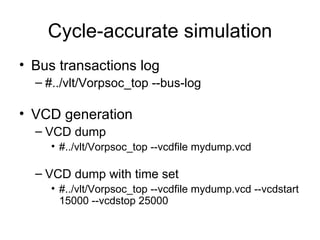
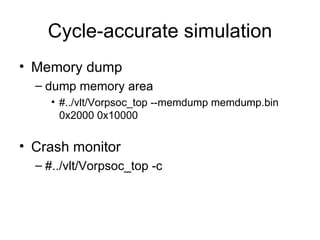
This document discusses building a virtual platform for the OpenRISC architecture using SystemC and transaction-level modeling. It covers setting up the toolchain, writing test programs, and simulating the platform using event-driven or cycle-accurate simulation with Icarus Verilog or the Vorpsoc simulator. The virtual platform allows fast development and debugging of OpenRISC code without requiring physical hardware.