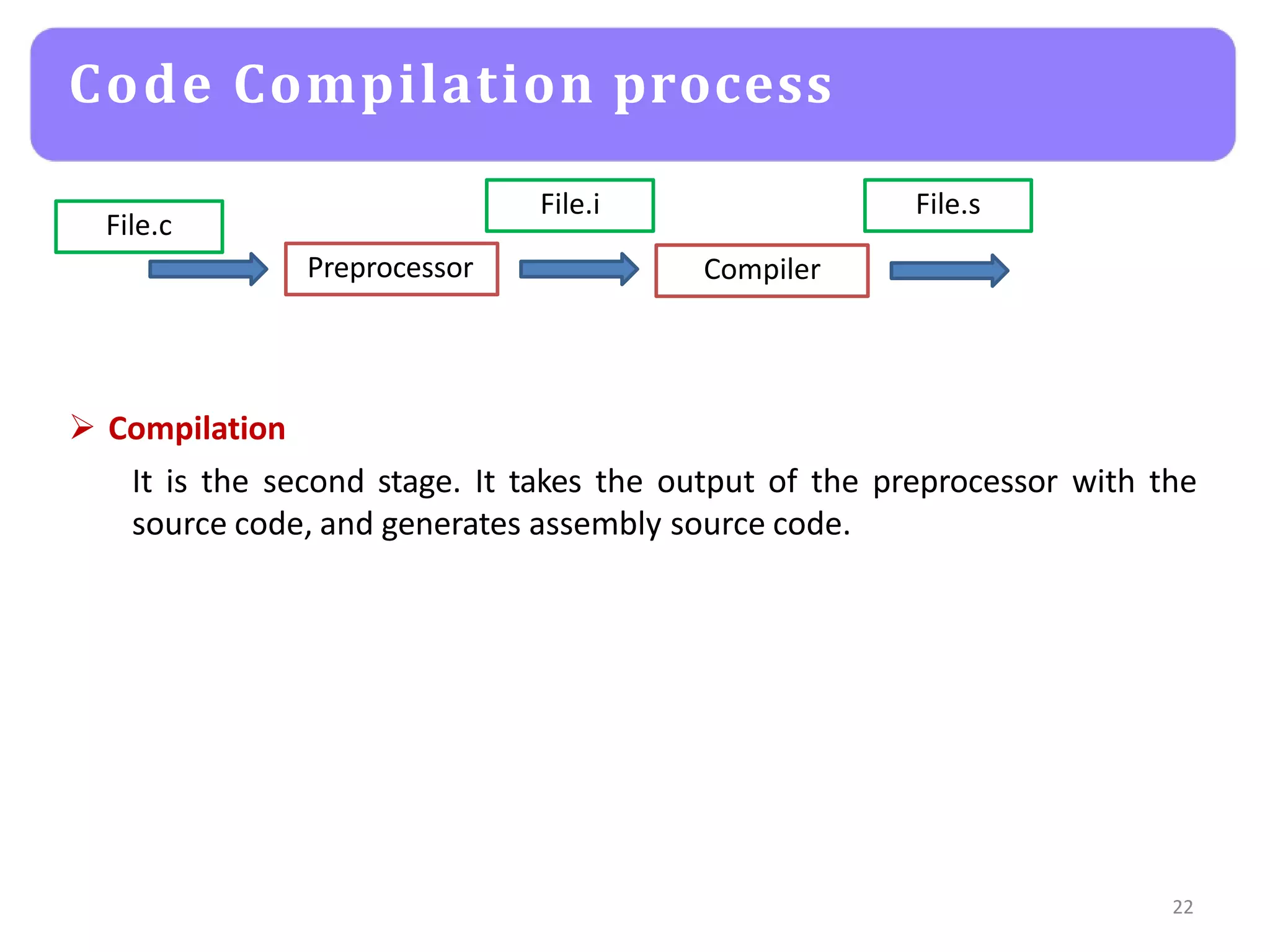
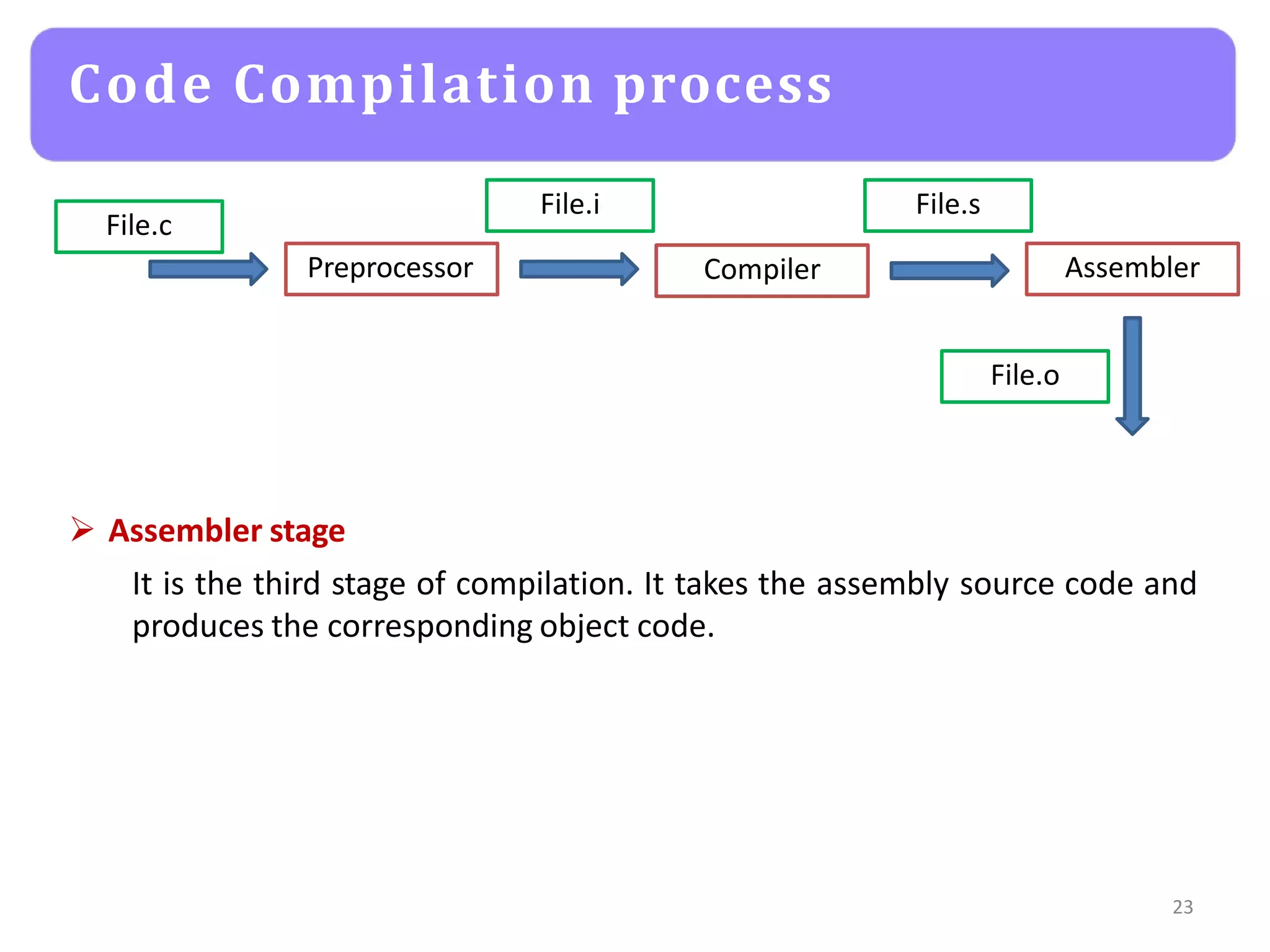
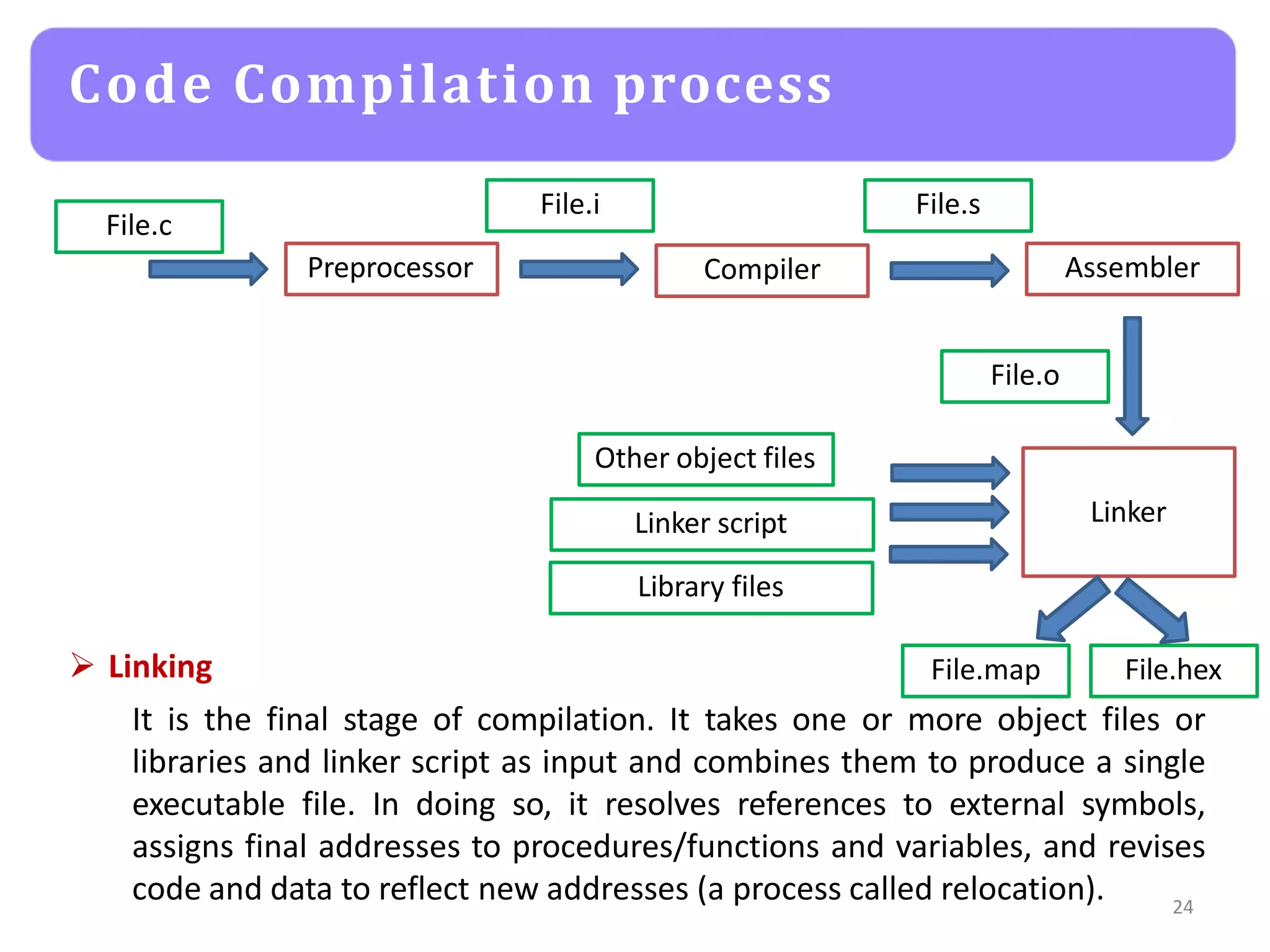
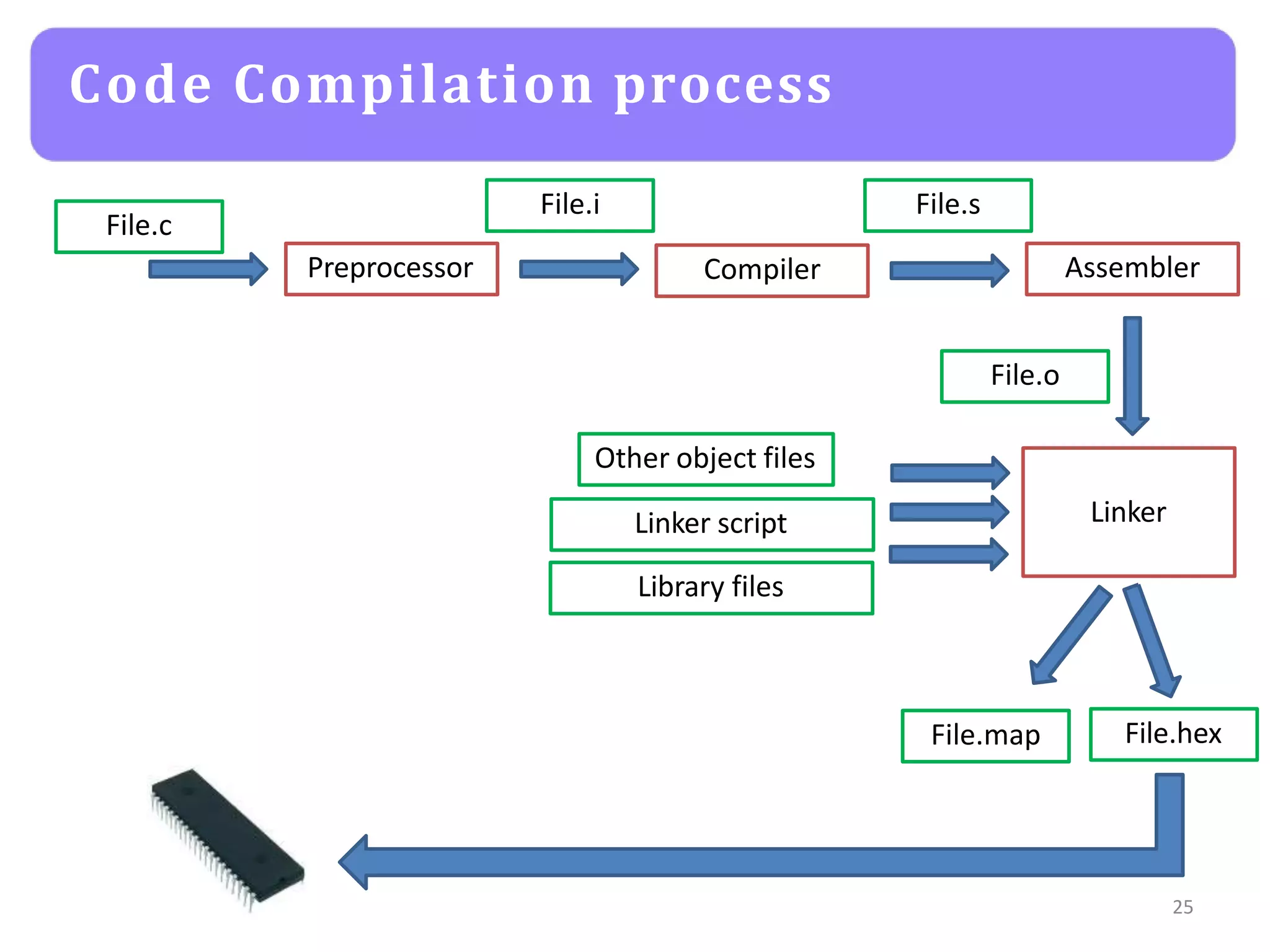
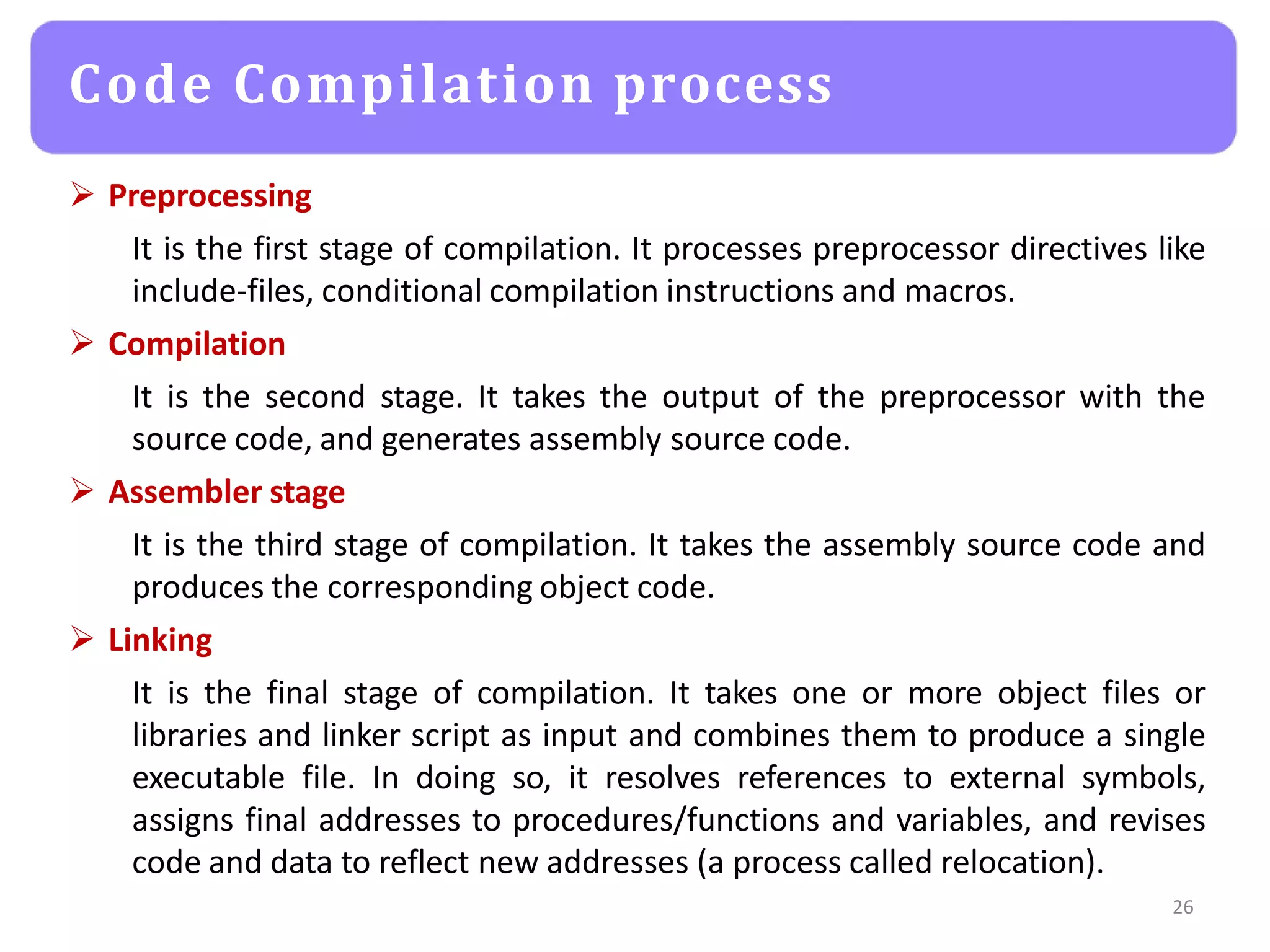
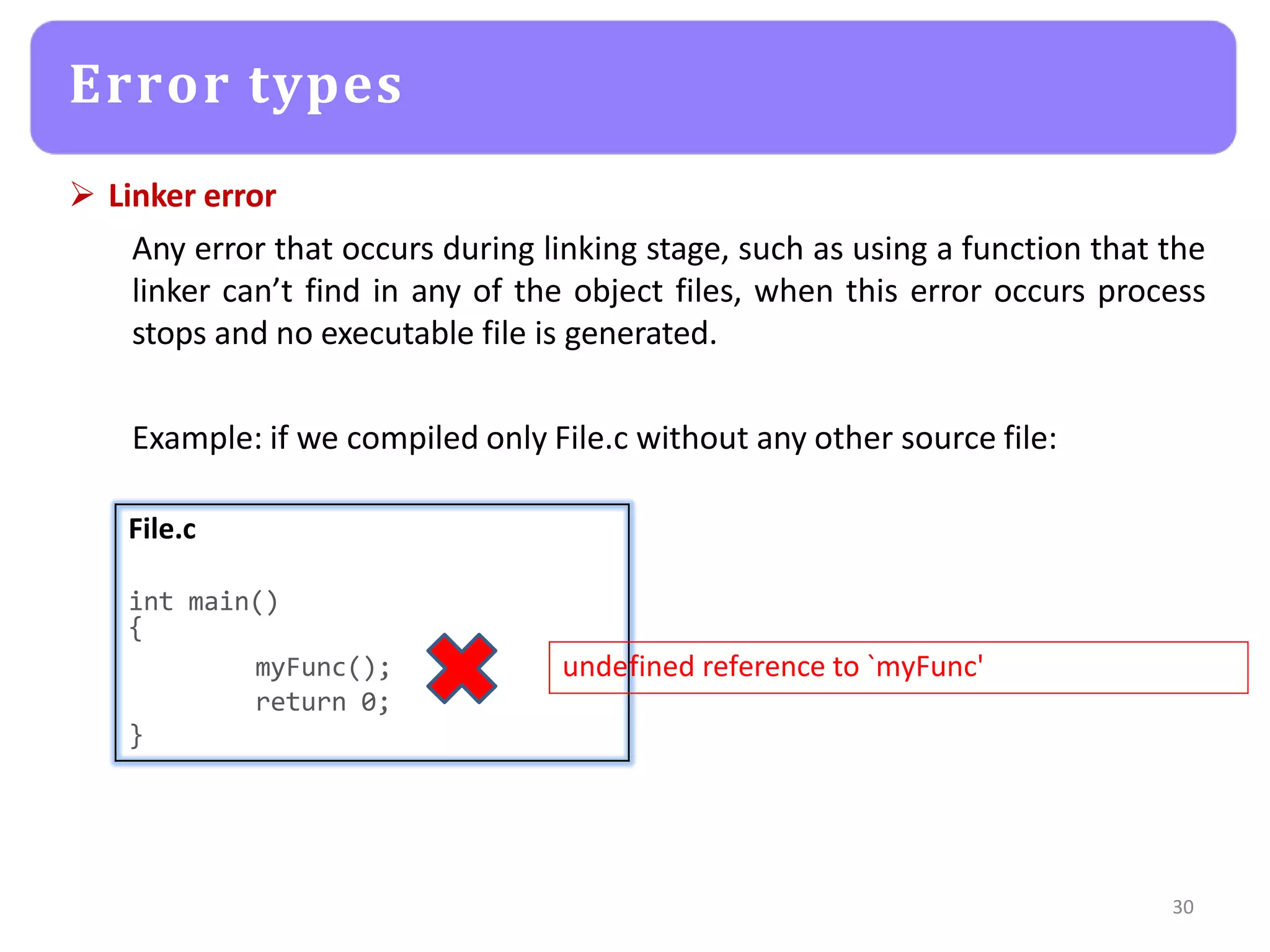
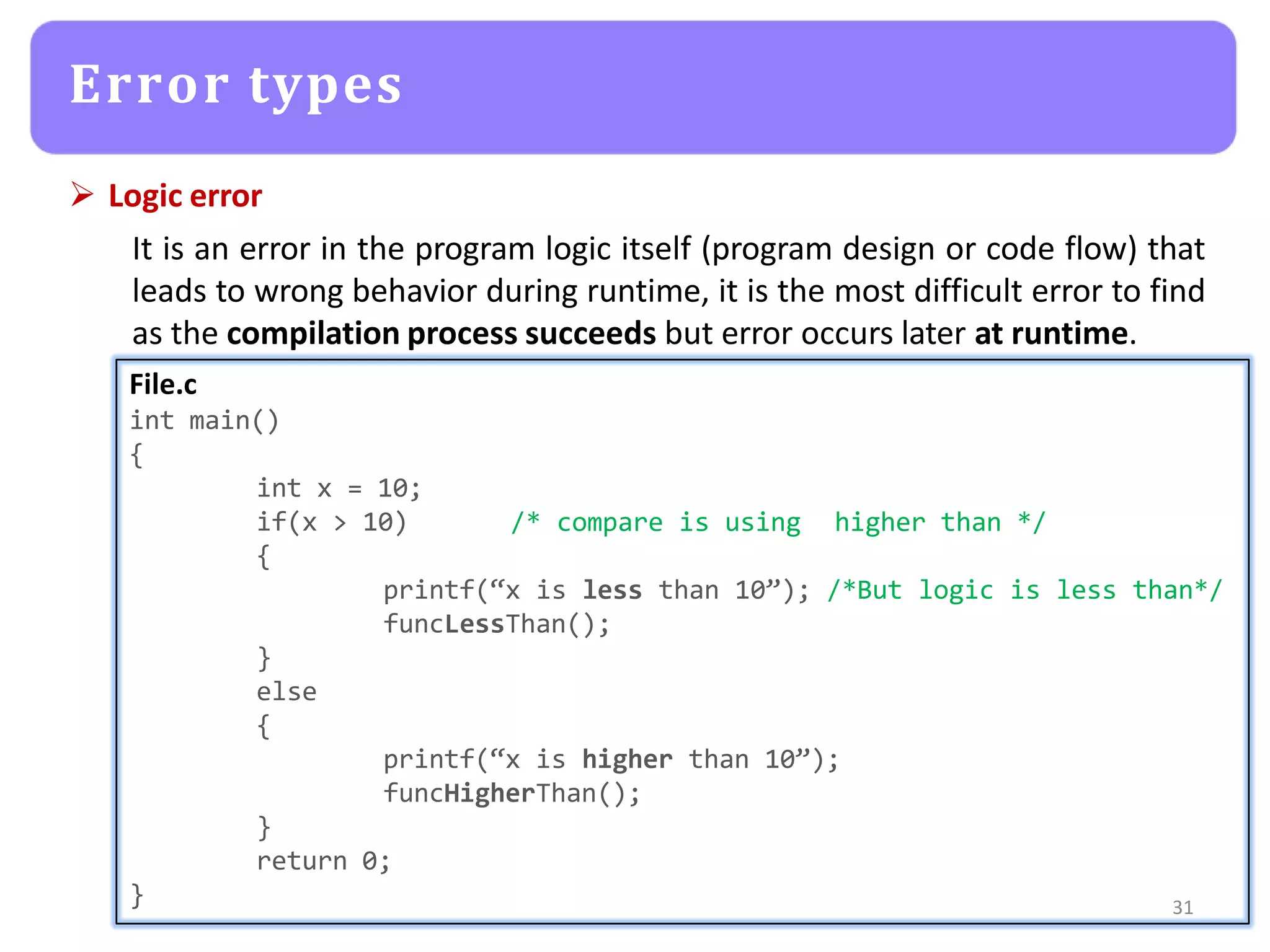
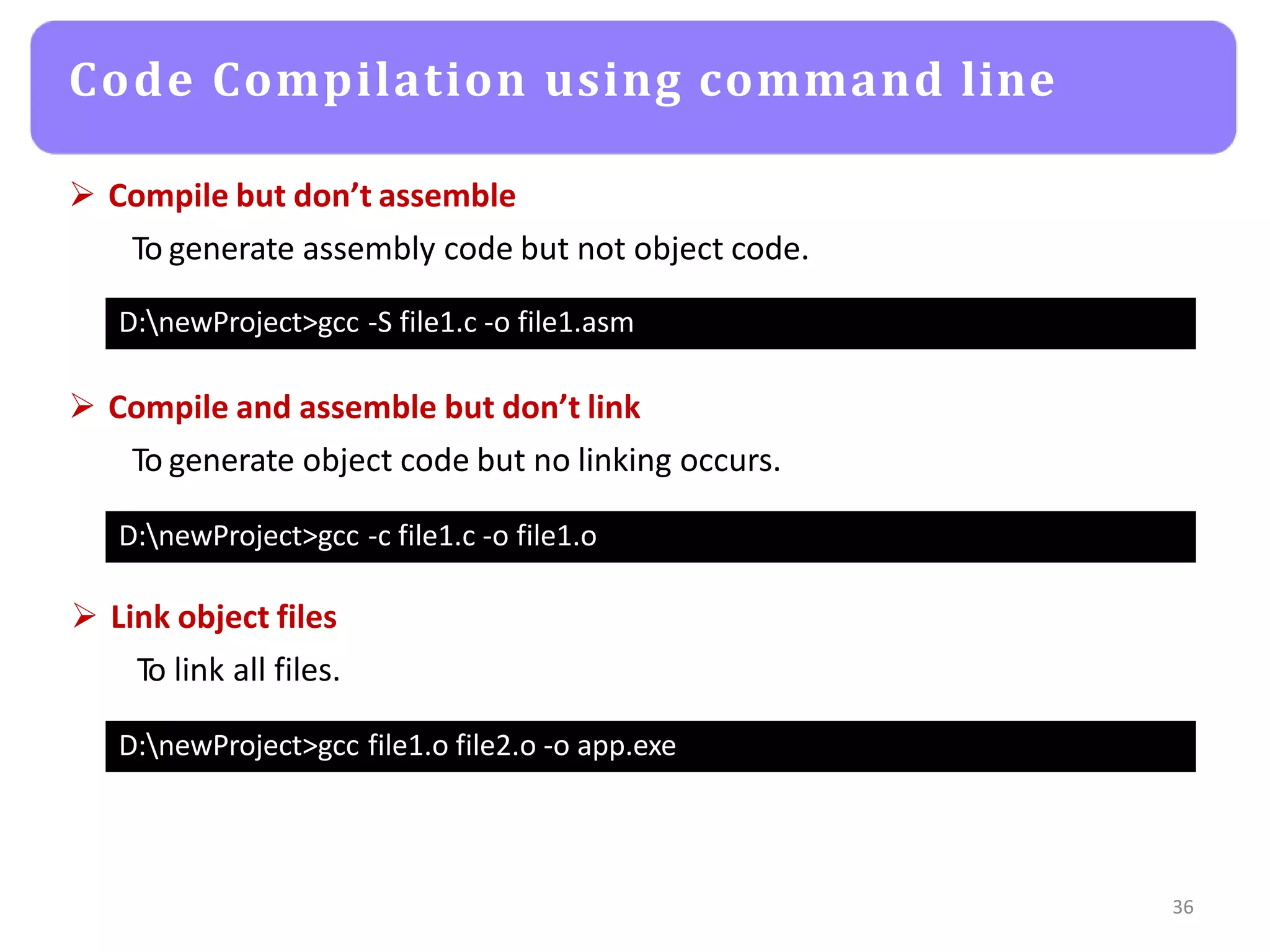
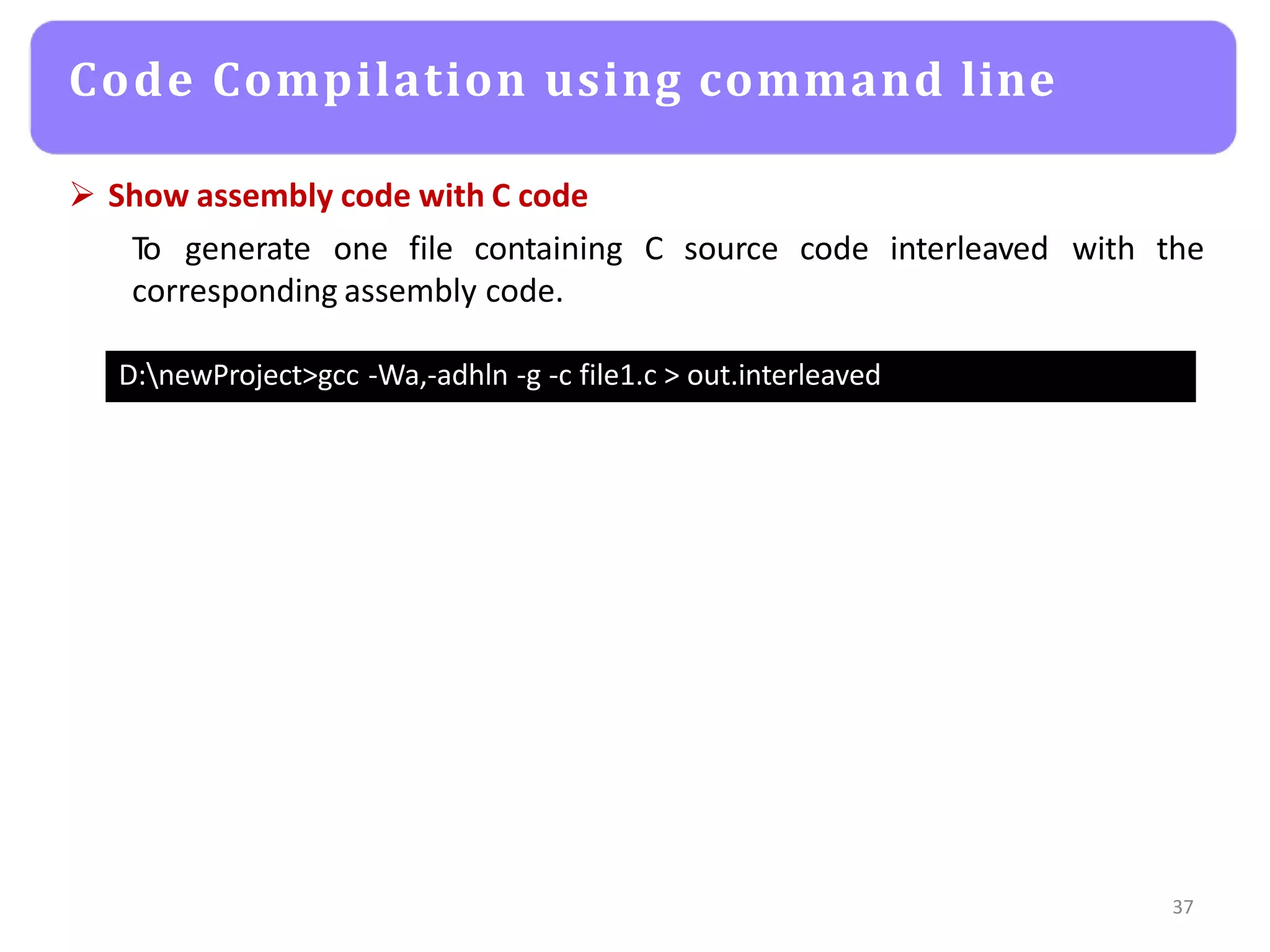
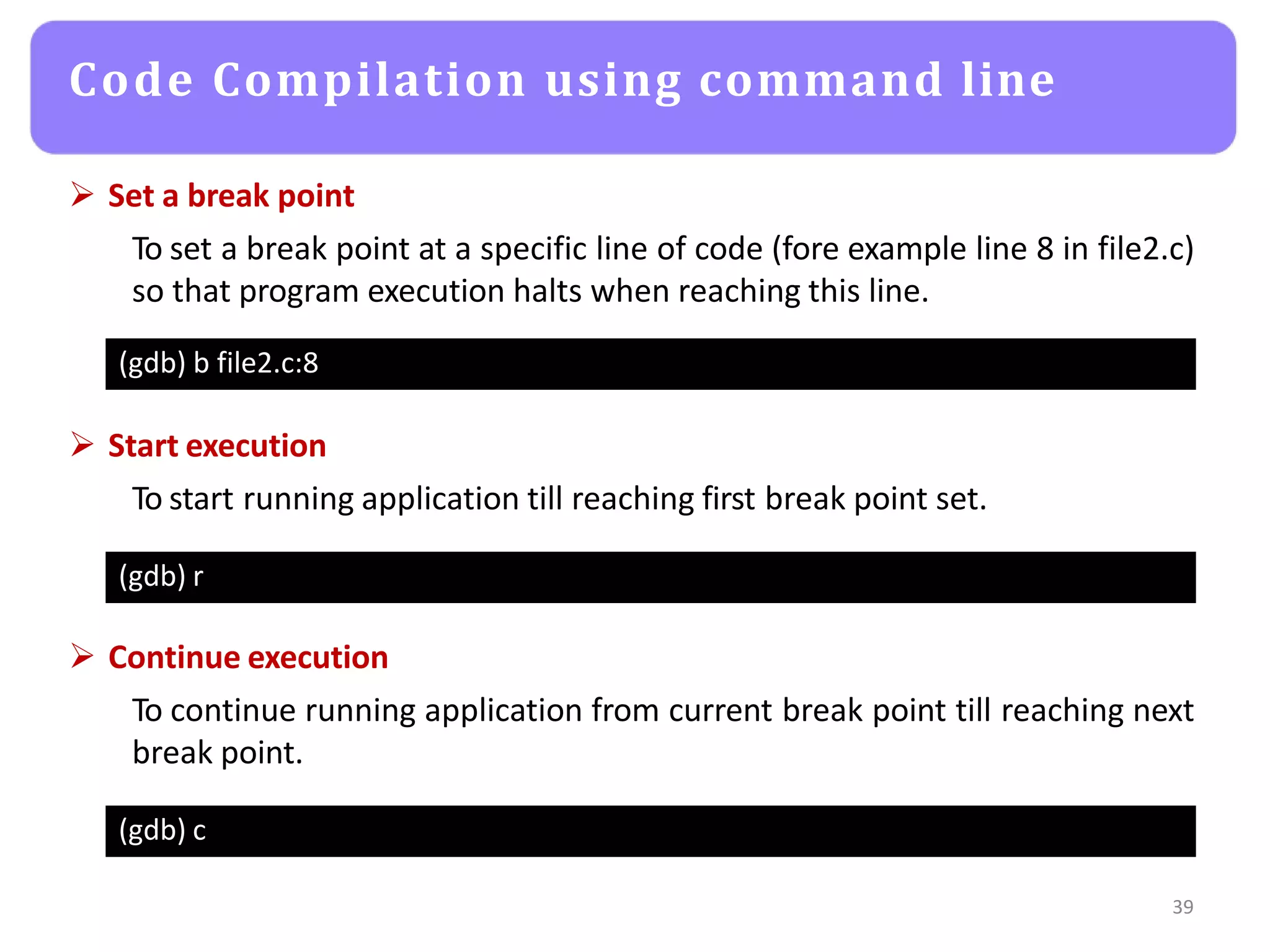
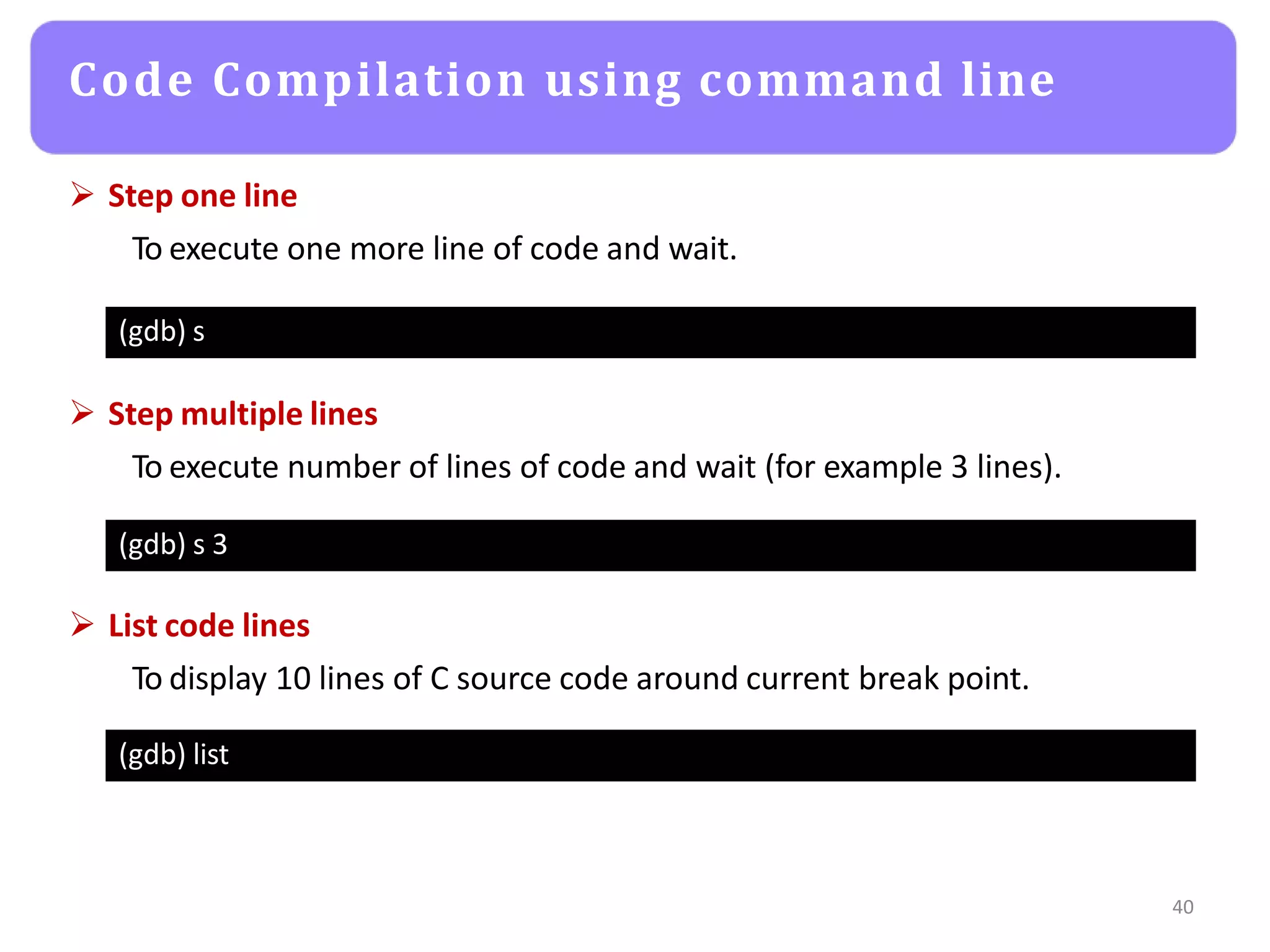
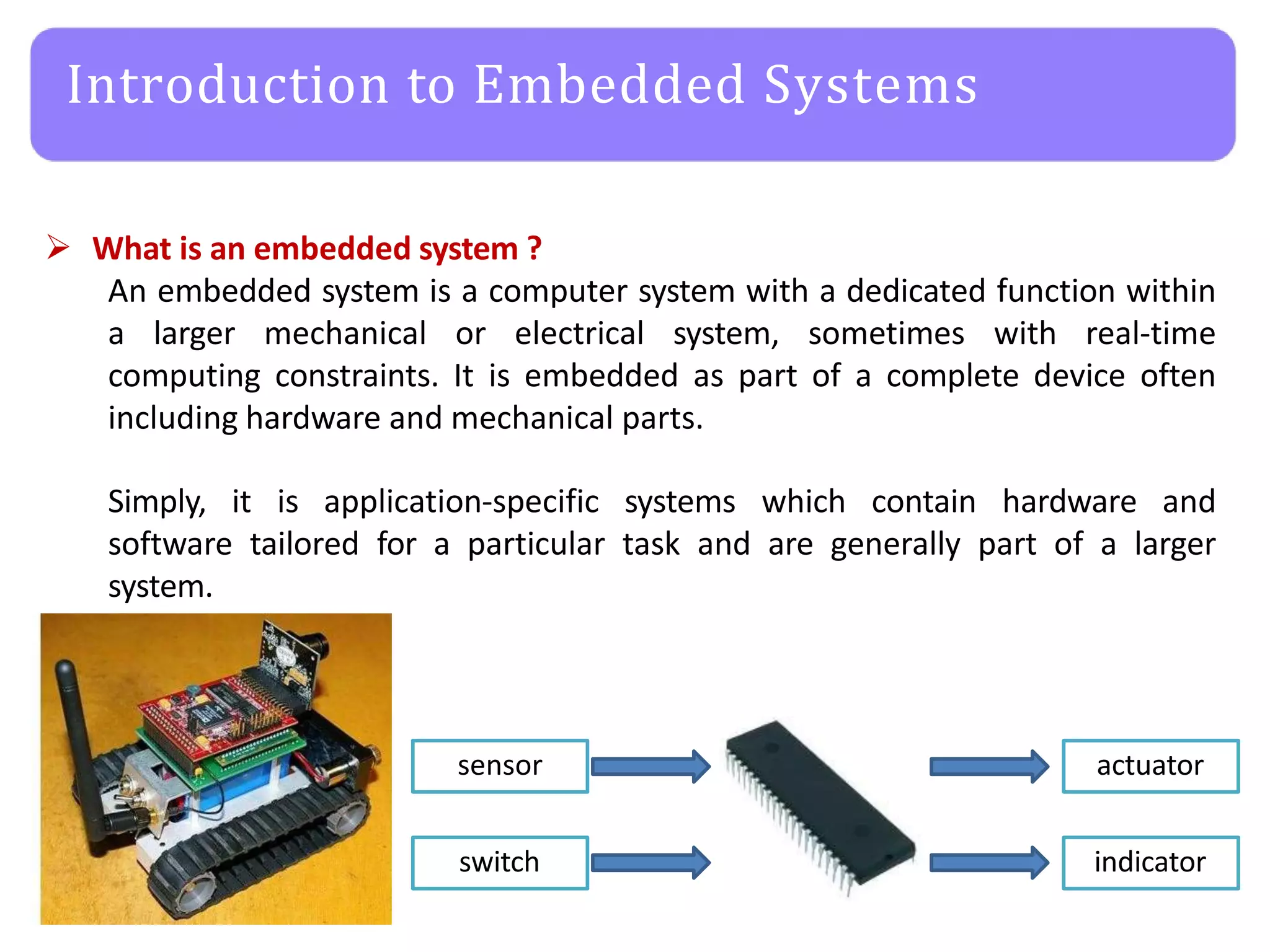
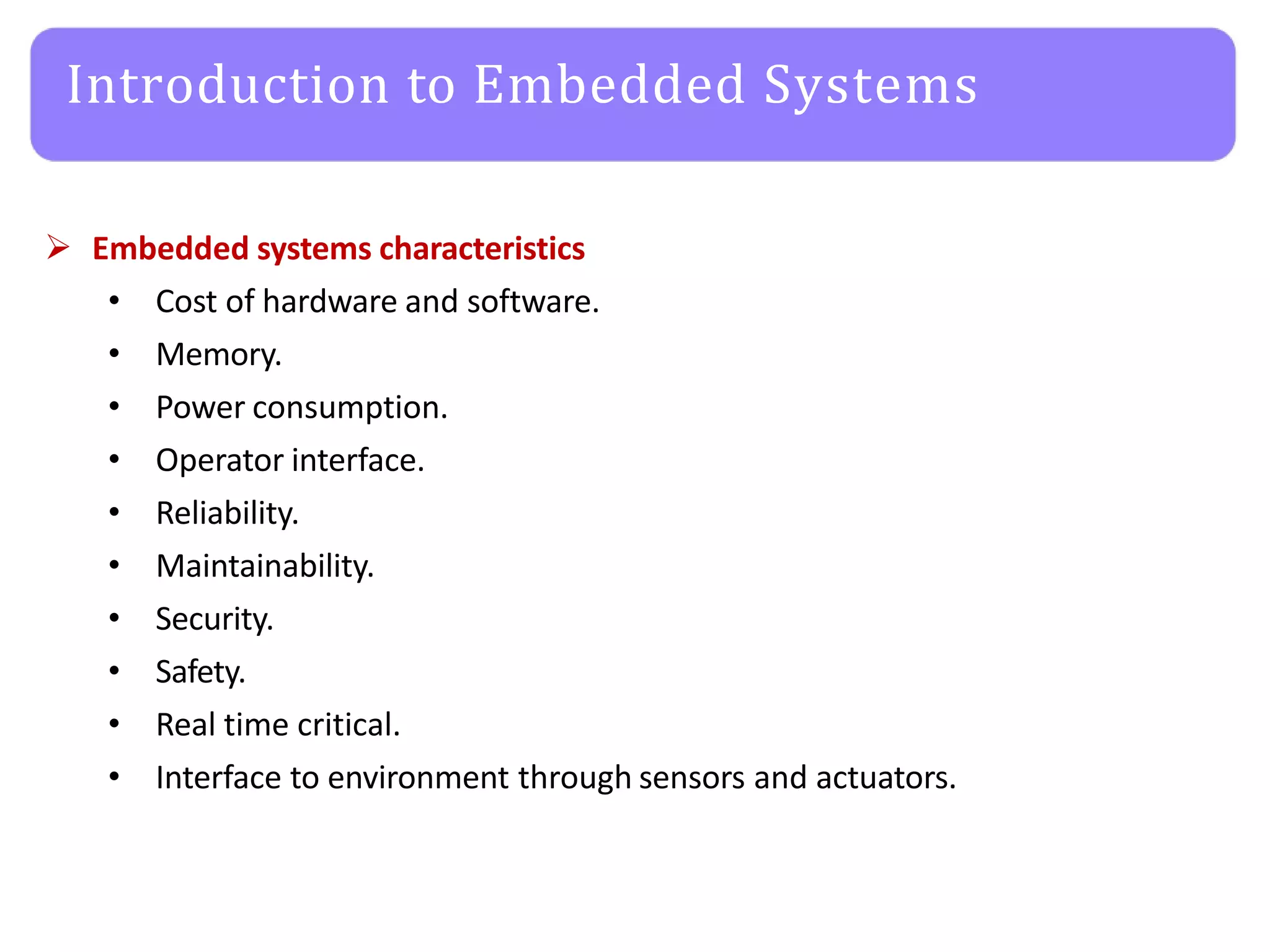
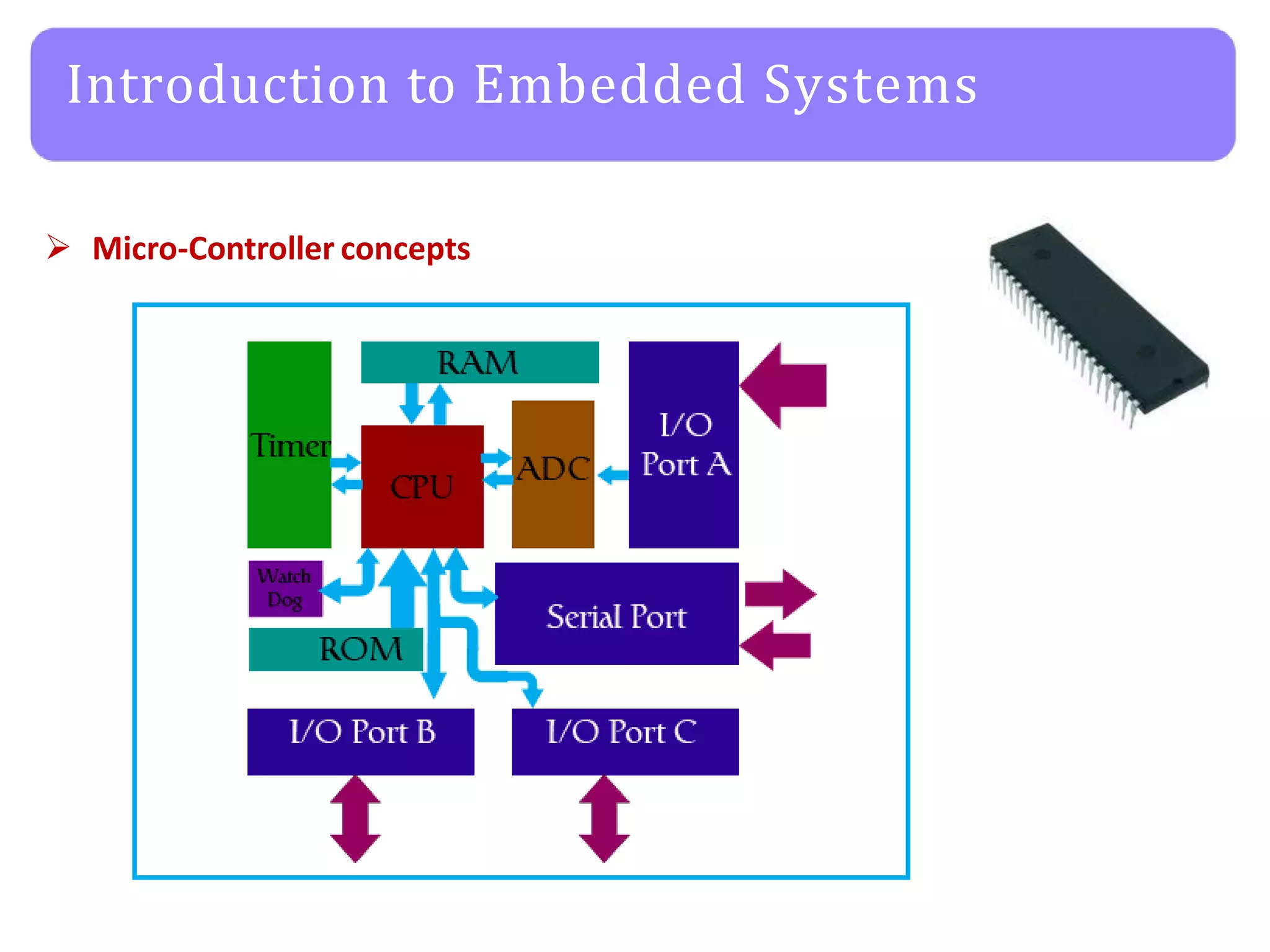
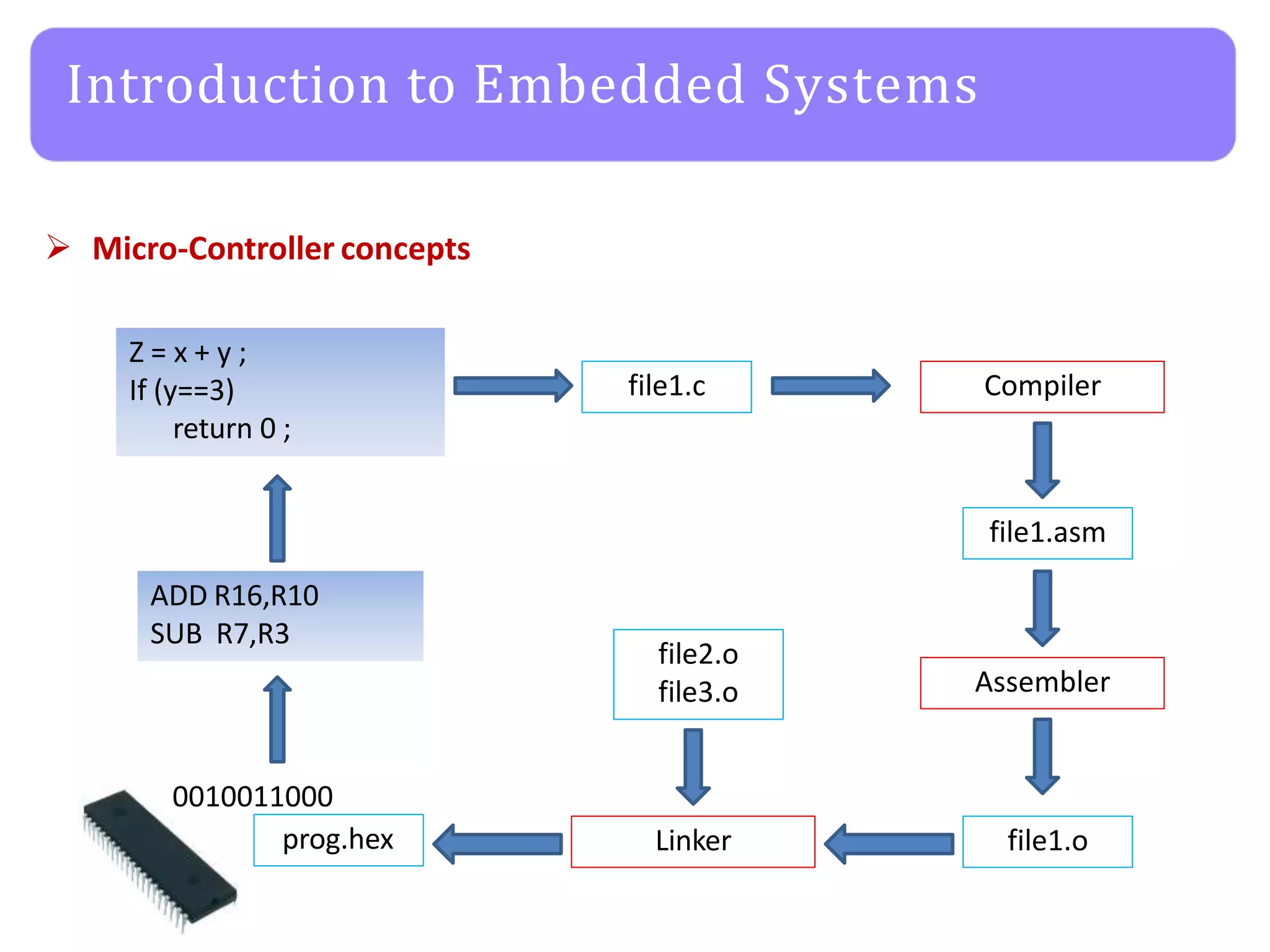
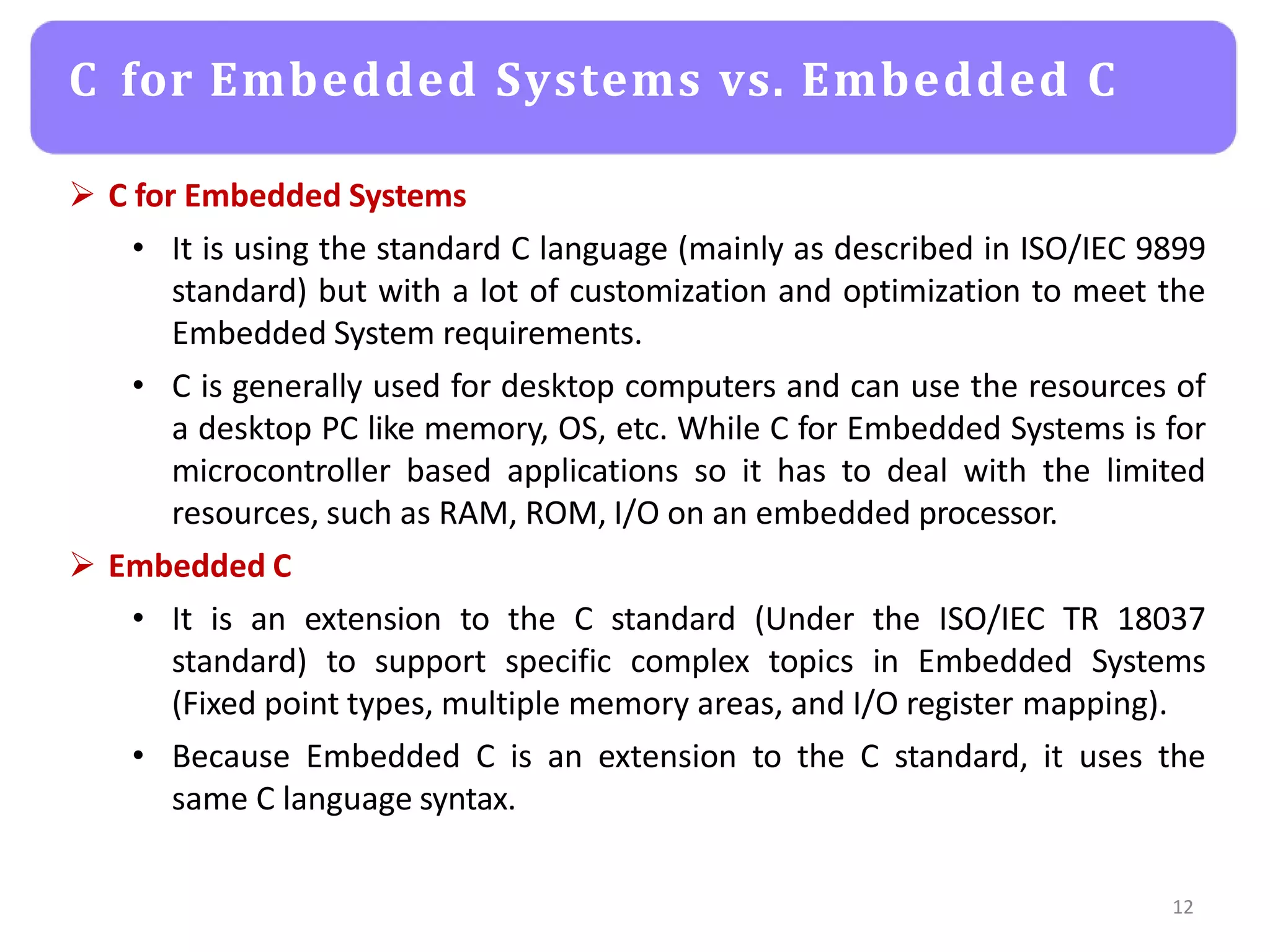
The document provides an agenda for an embedded C programming lecture that includes the following topics: definitions of embedded systems and the differences between C for embedded systems and embedded C, the code compilation process and types of errors, code compilation using the command line, and a quick revision of C language syntax. It concludes with assigning a task for students.






![ Examples on preprocessor directives:
• #pragma:
The #pragma directive is the method specified by the C standard for
providing additional information to the compiler, beyond what is
conveyed in the language itself.
Example for gcc compiler:
#pragma optimize(“”, off)
Example for ghs compiler:
/* Disable any optimization */
#pragma ghs section “.bss” = “.mySection”
/* It will put this array in section called “.mySection”
in memory*/
int myArray[1000];
#pragma ghs section
Note that #pragma is compiler dependent so caution shall be taken
when using it as it affects code portability. 21
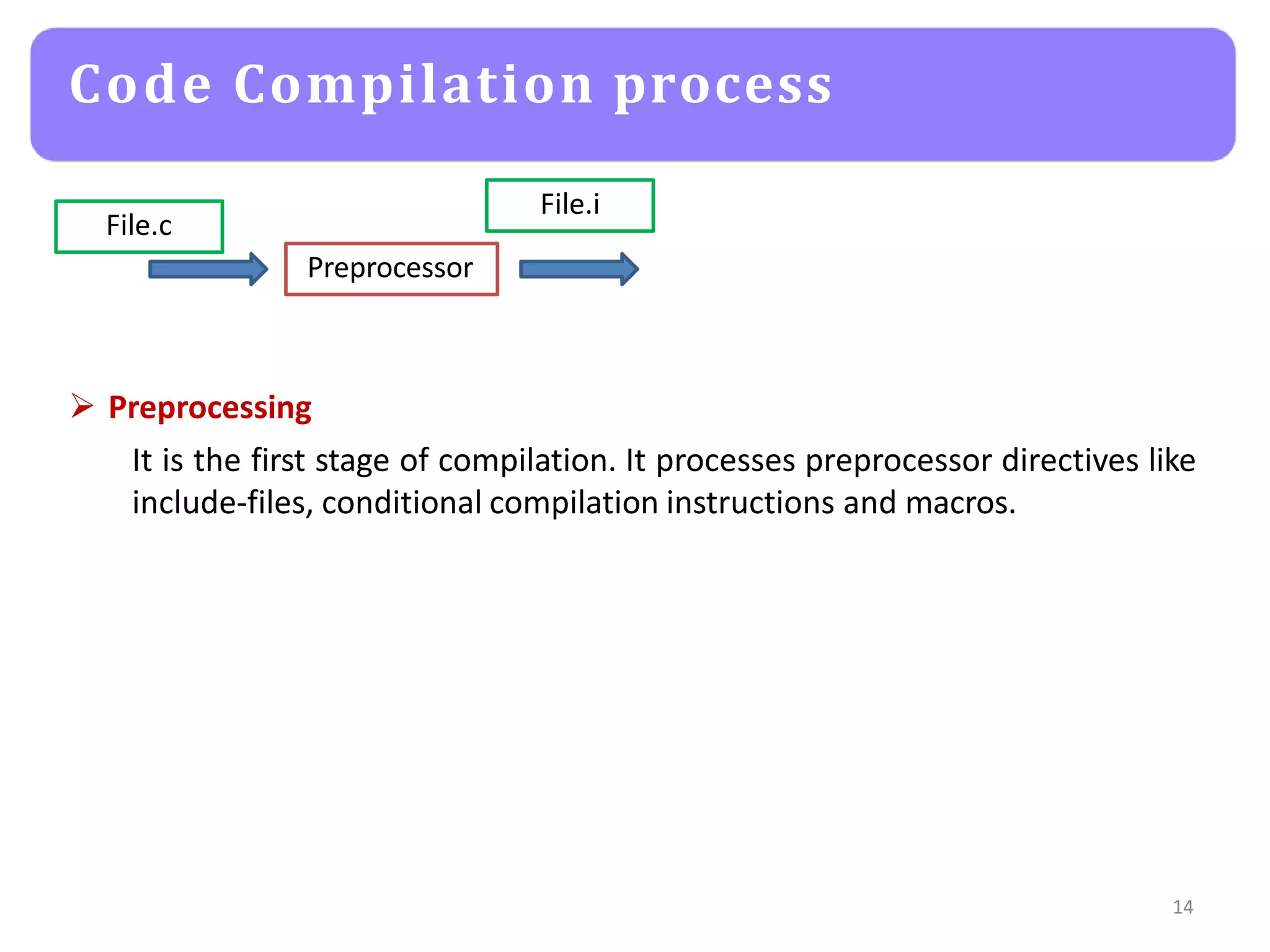
Code Compilation process](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embeddedc-lecture1-160404055102-230429165658-9a4b0a7b/75/embeddedc-lecture1-160404055102-pptx-21-2048.jpg)