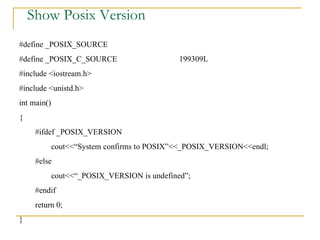
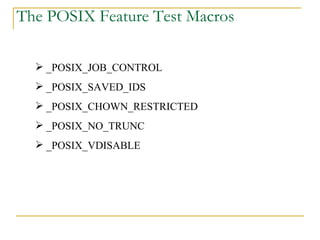
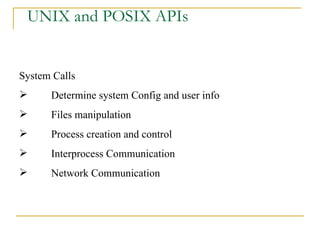
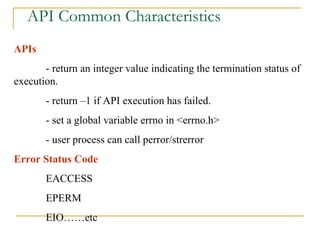
The document discusses the POSIX standards for operating system interfaces and APIs. It covers the history and development of POSIX, differences between ANSI C and C++, POSIX standards like POSIX.1 for file manipulation, POSIX feature test macros, limits checking APIs, and common characteristics of UNIX and POSIX APIs.