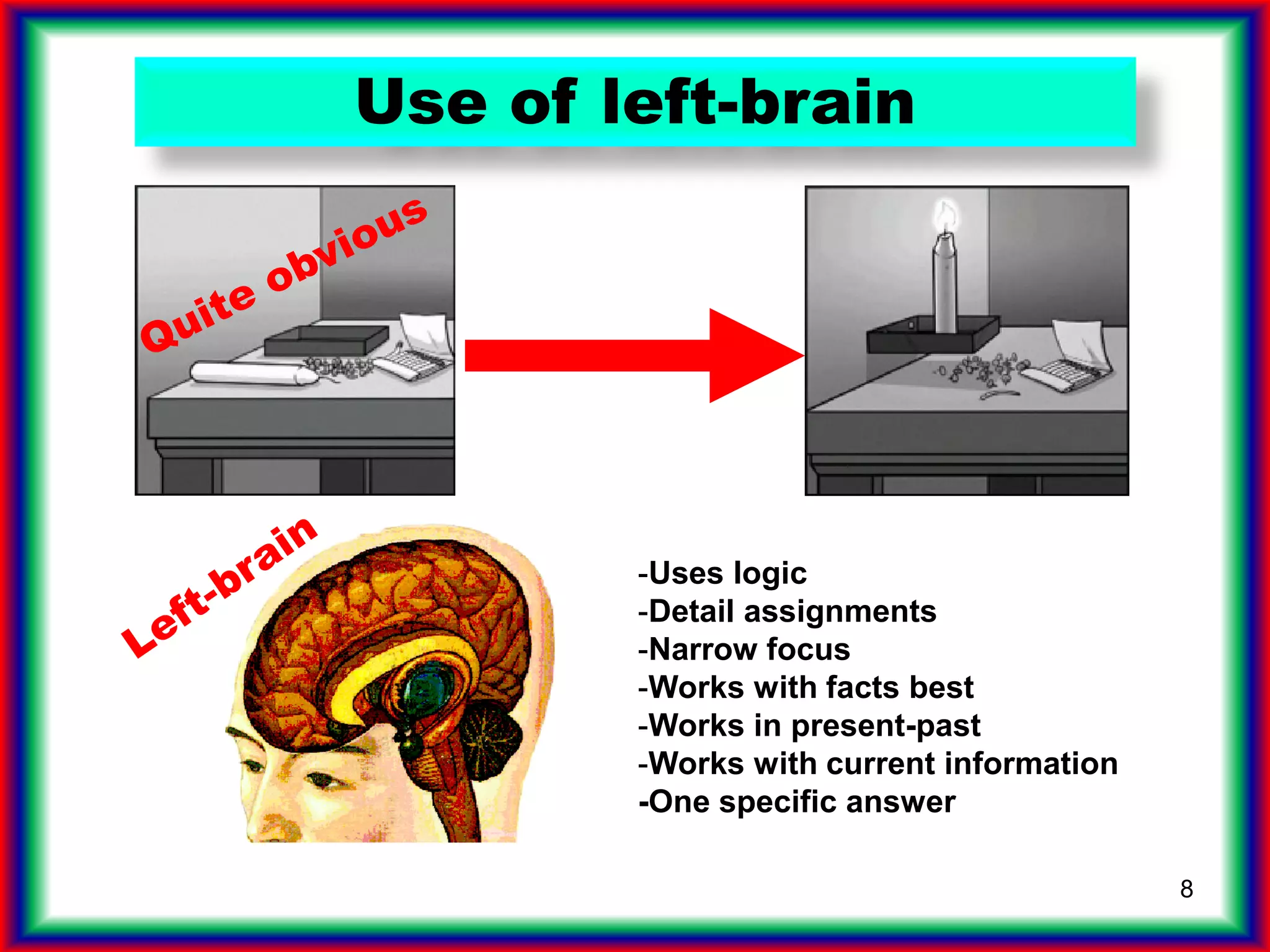
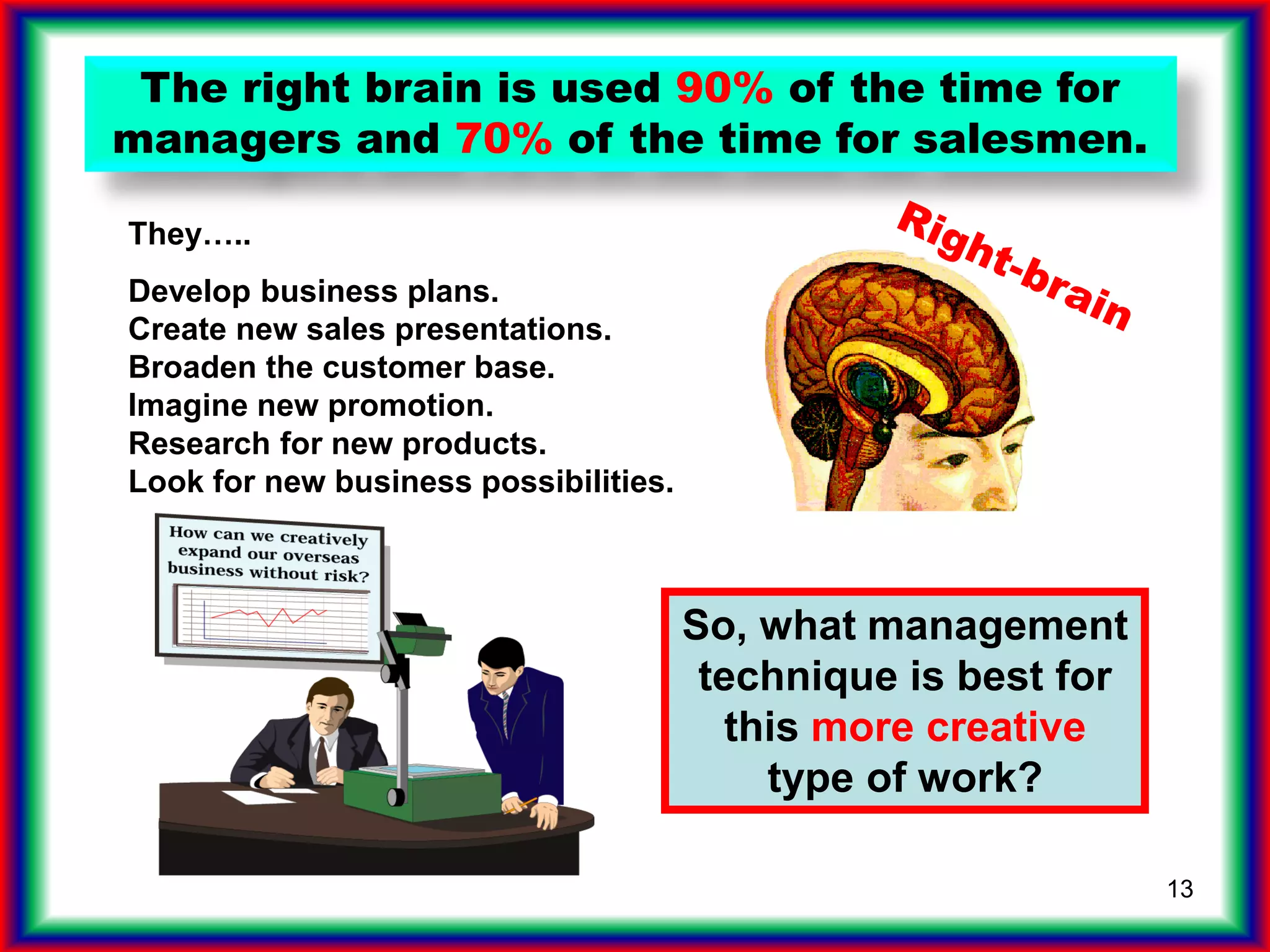
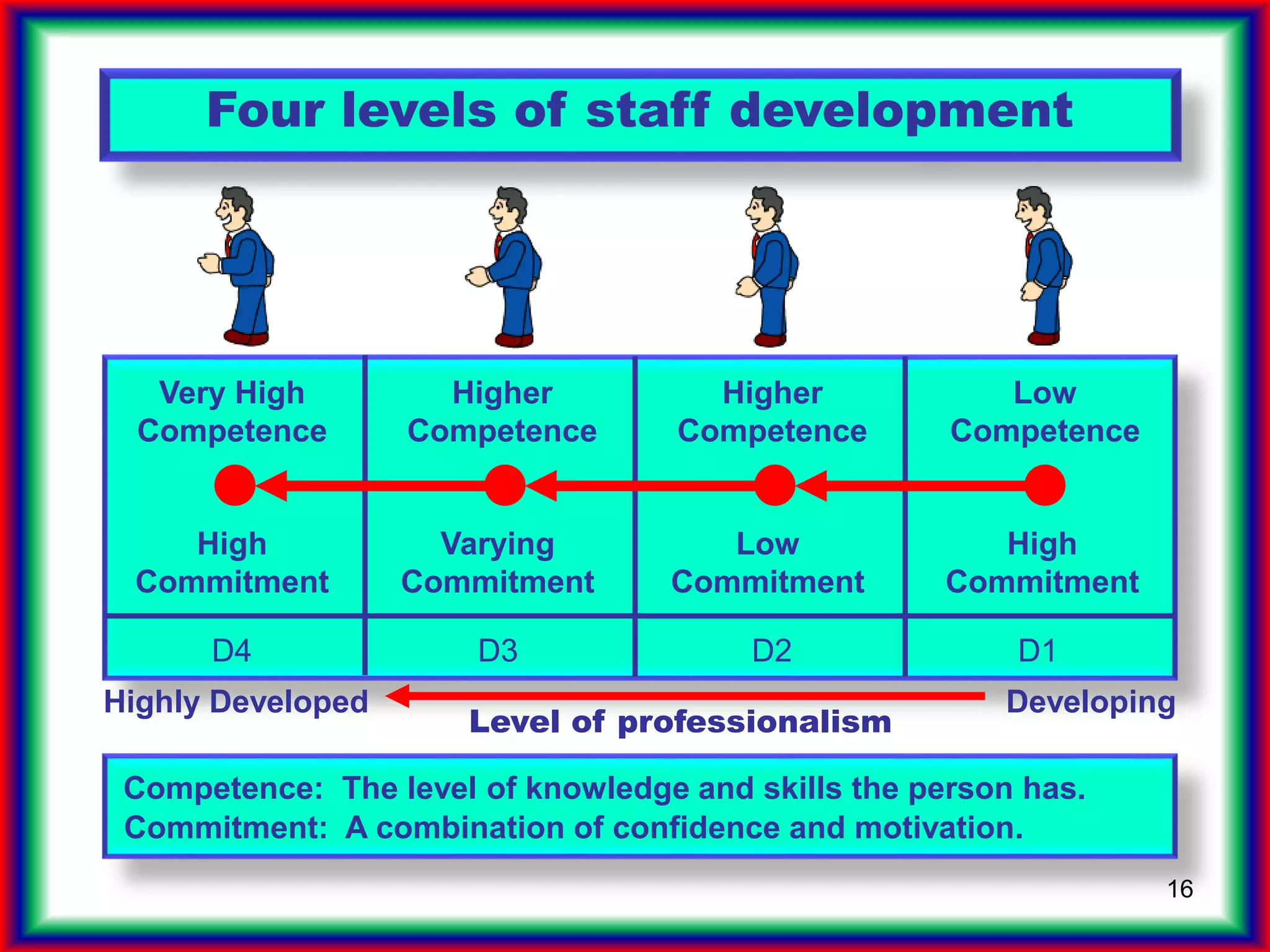
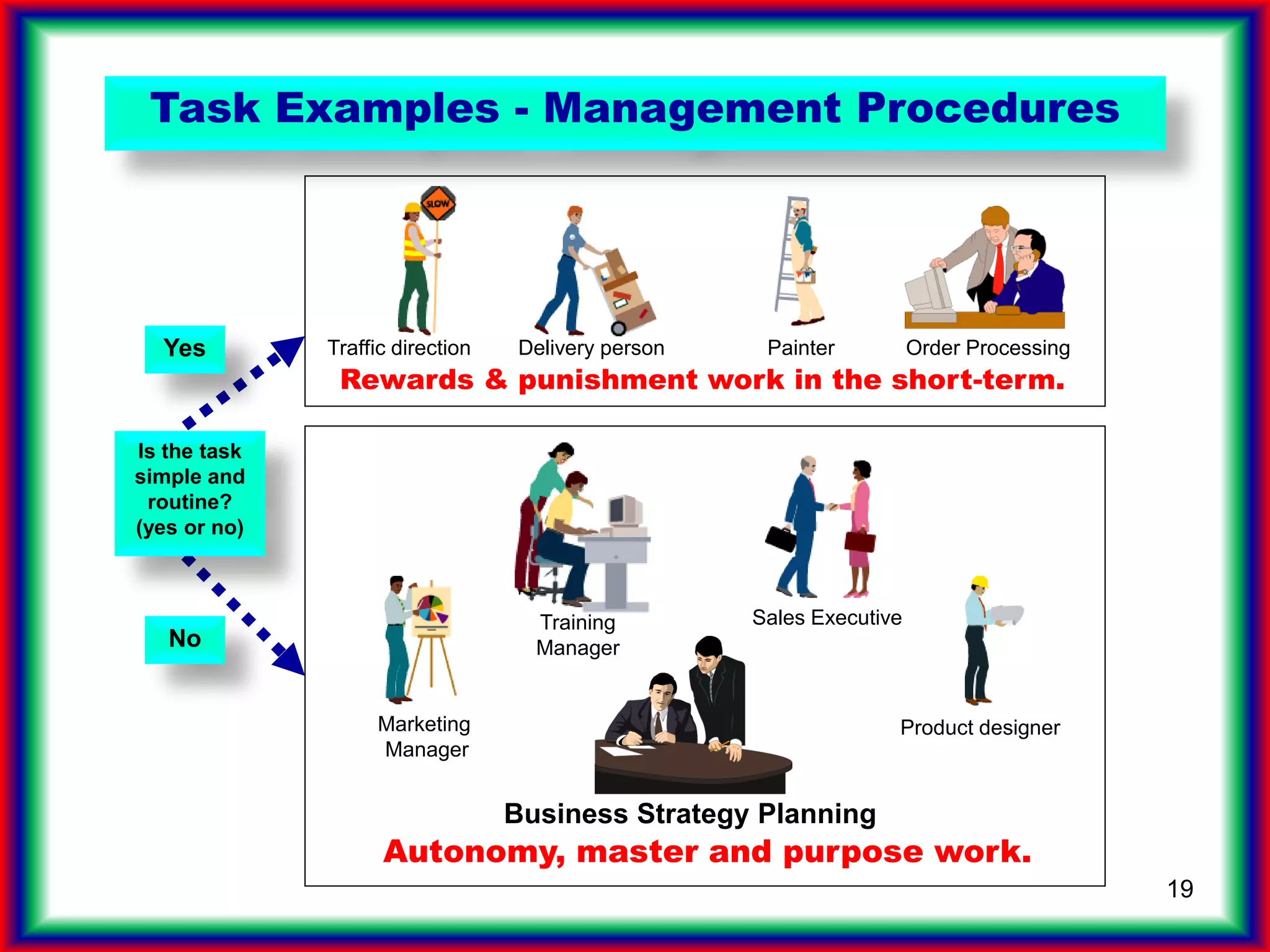
The document summarizes key points from the book "Drive" about engagement-driven management styles being more effective than traditional reward/punishment styles, especially for complex creative tasks. It describes an experiment where groups trying to attach a candle to a wall without a box performed better without incentives. Engagement styles focus on autonomy, mastery, and purpose over directives and rewards/punishments. These foster creativity needed for future jobs over simplistic left-brain tasks prone to automation. Companies should assess if jobs allow autonomy, mastery and purpose to attract high-drive employees.