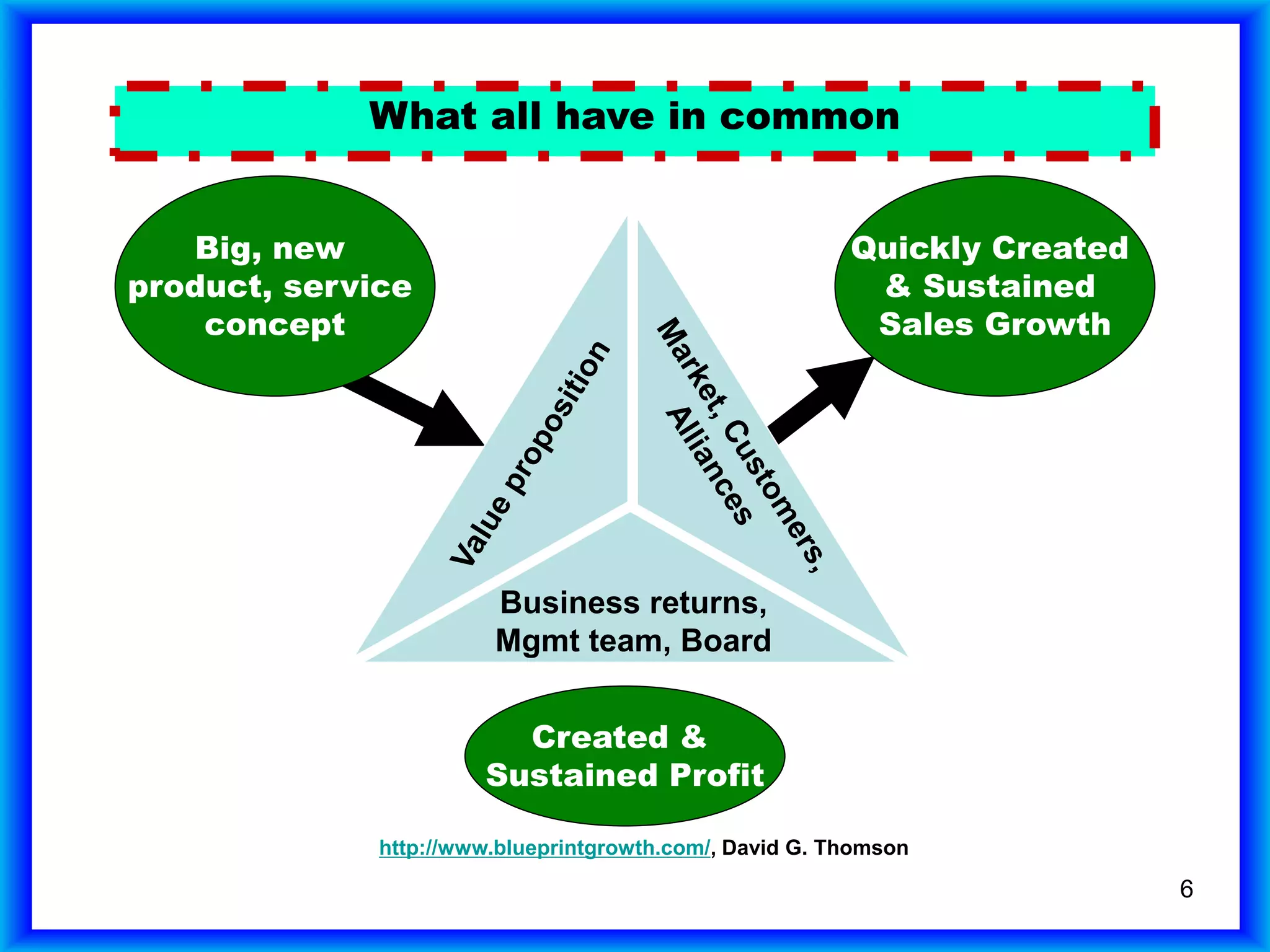
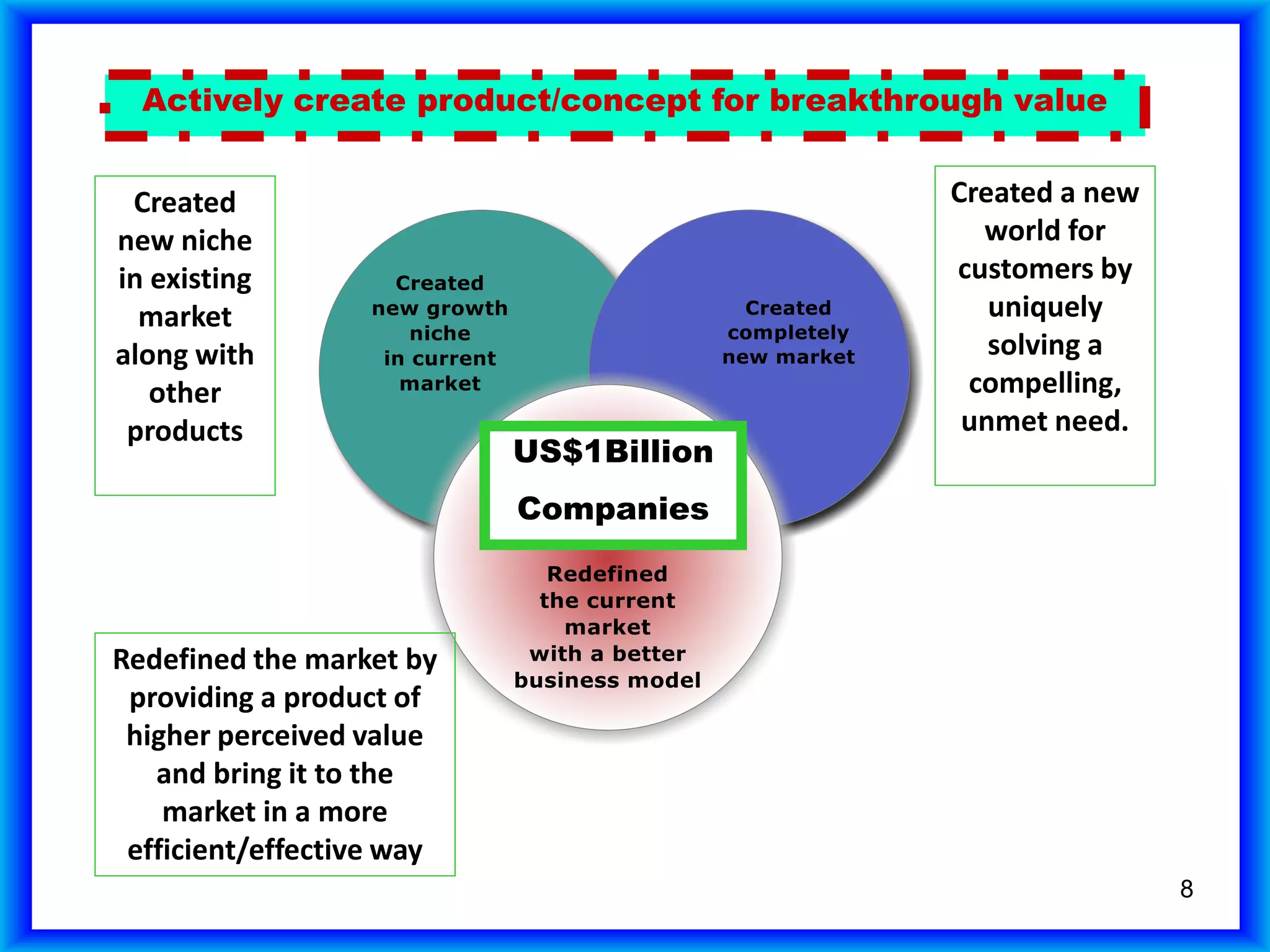
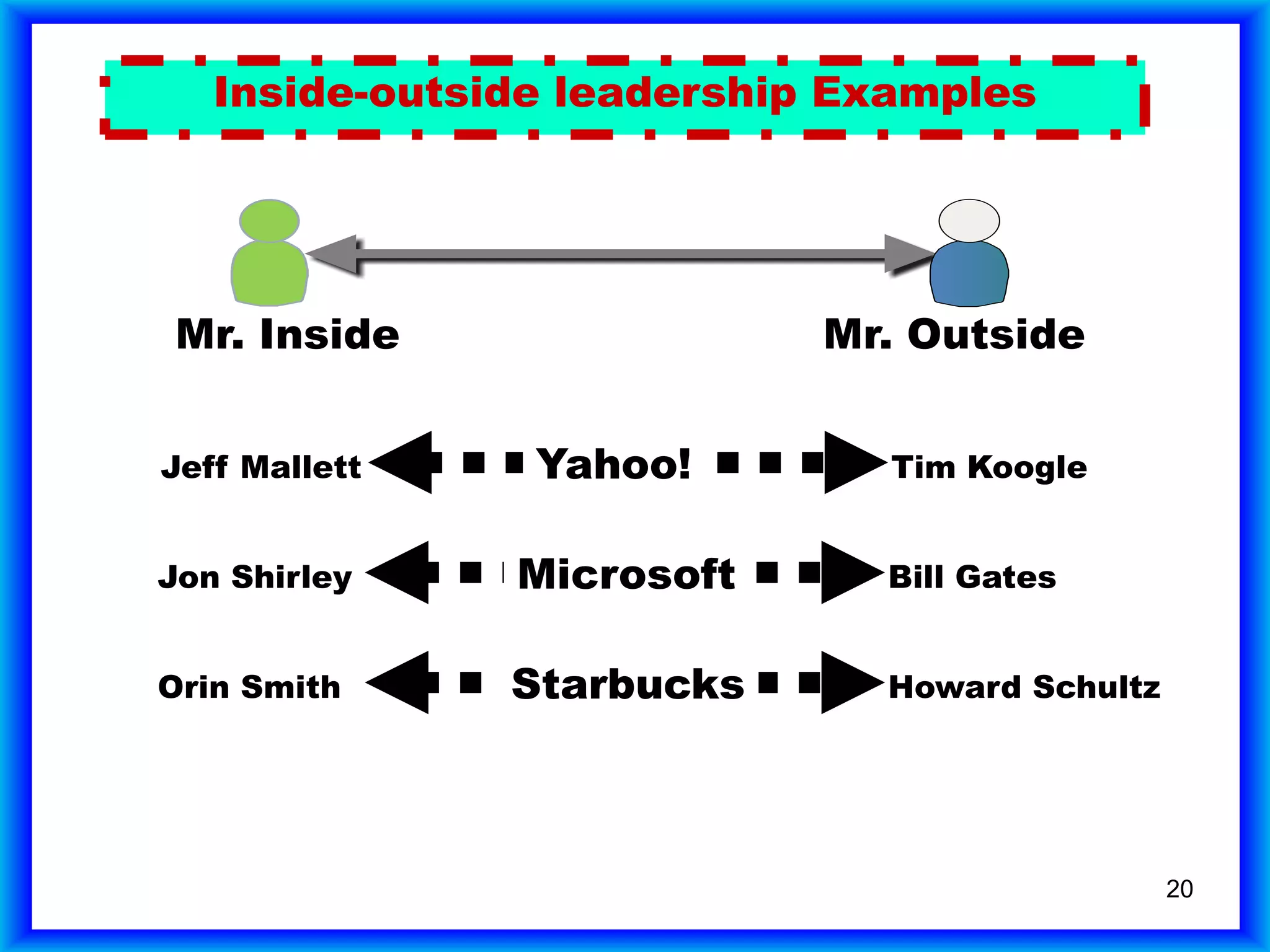
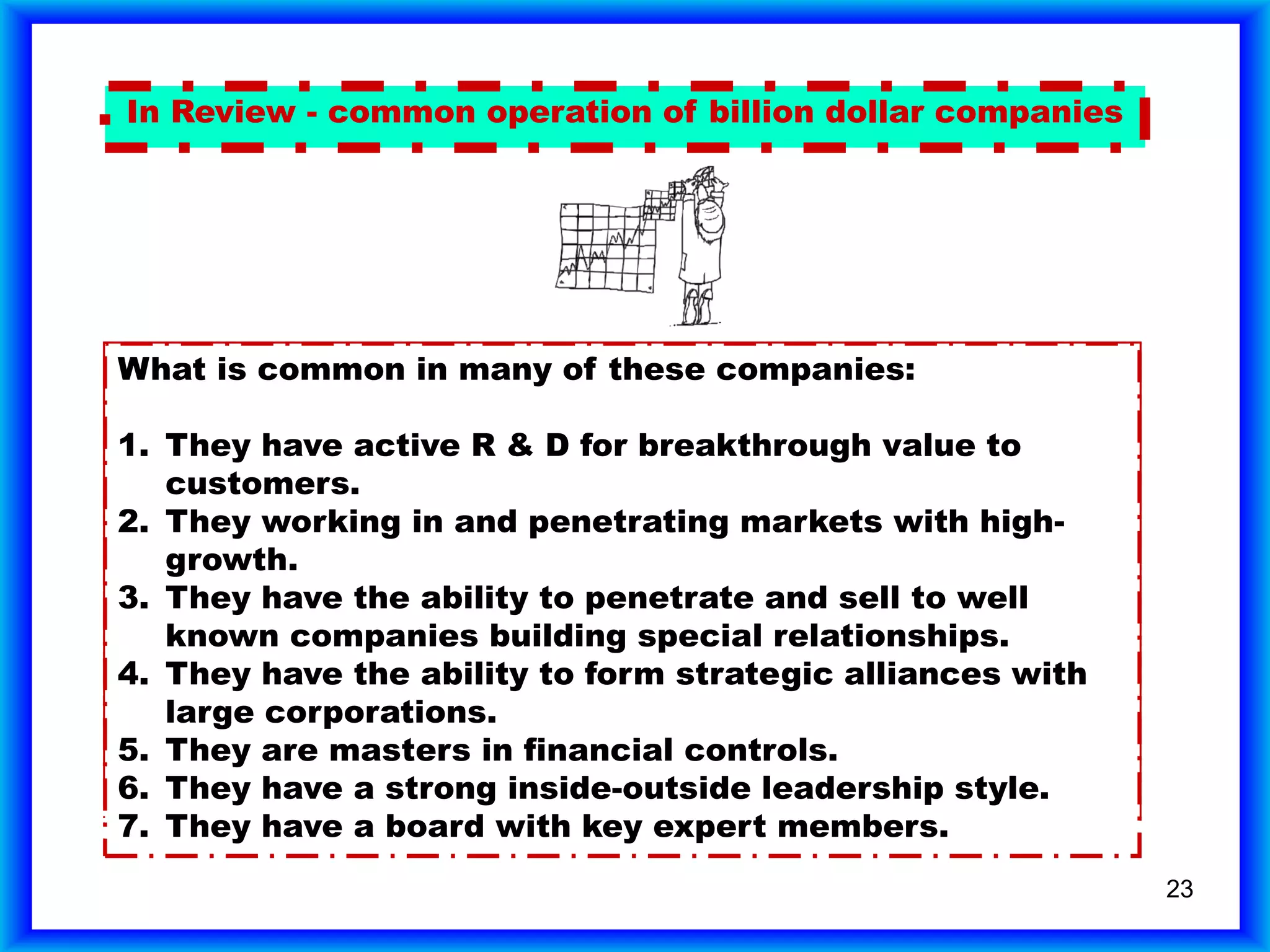
The document summarizes a study of companies that had an IPO in 1980 and achieved $1 billion in sales. It found that: 1) One in 20 private companies submitted an IPO, with average initial sales of $170 million; 2) Of those that submitted an IPO, one in 20 reached $1 billion in sales, which is one in 400 companies overall; 3) Only 387 of the 7,454 companies studied (5%) achieved $1 billion in sales.