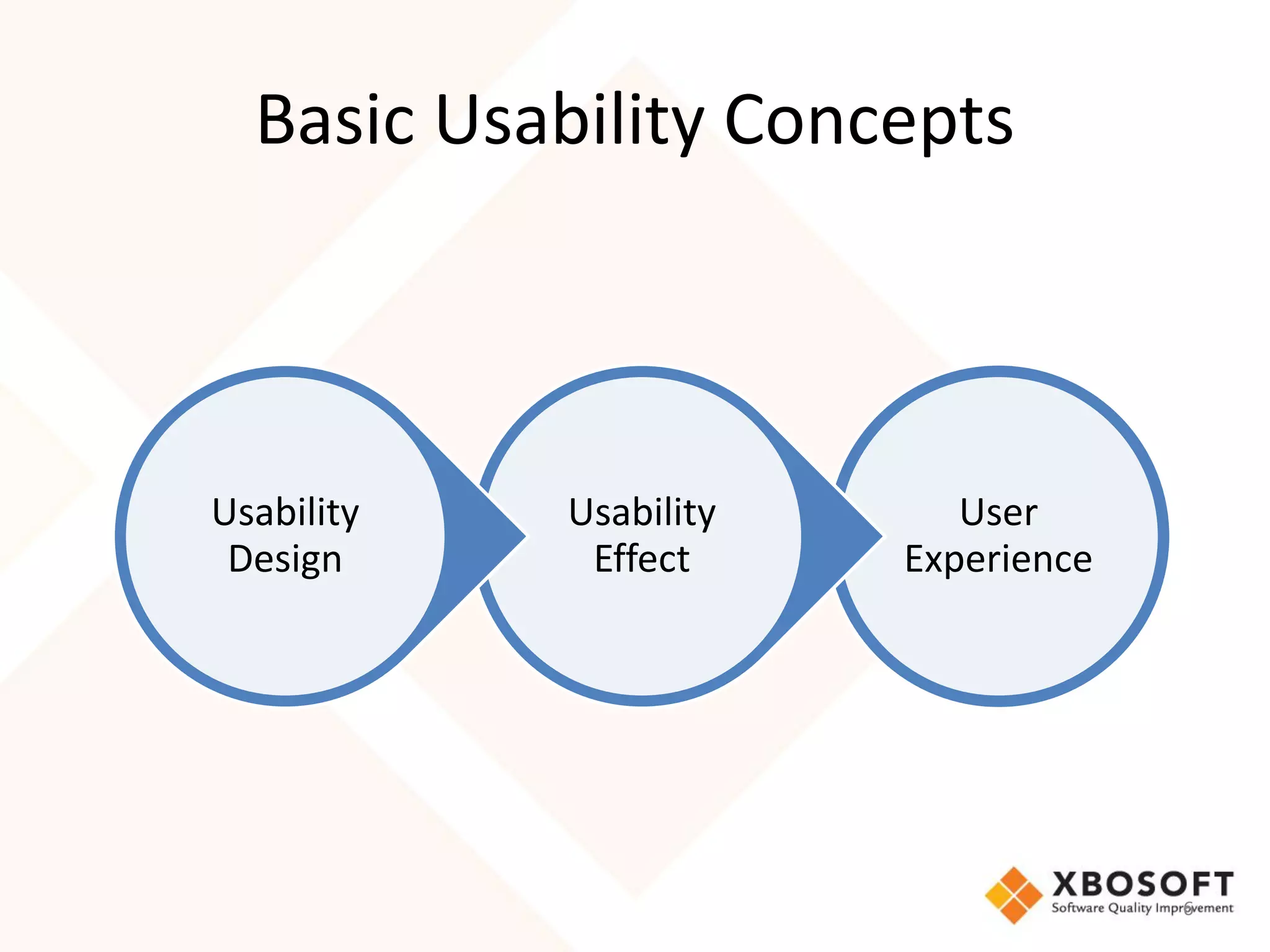
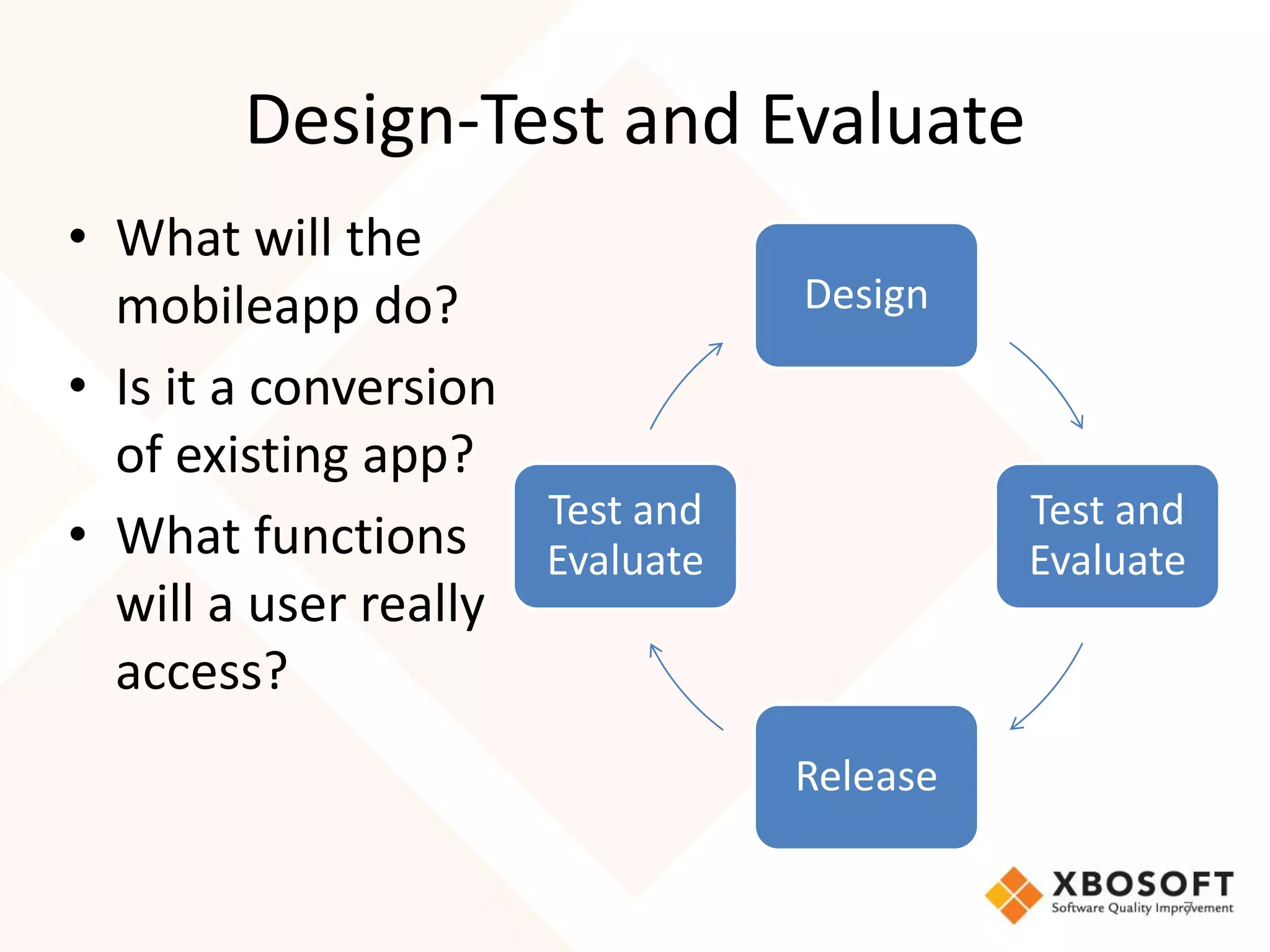
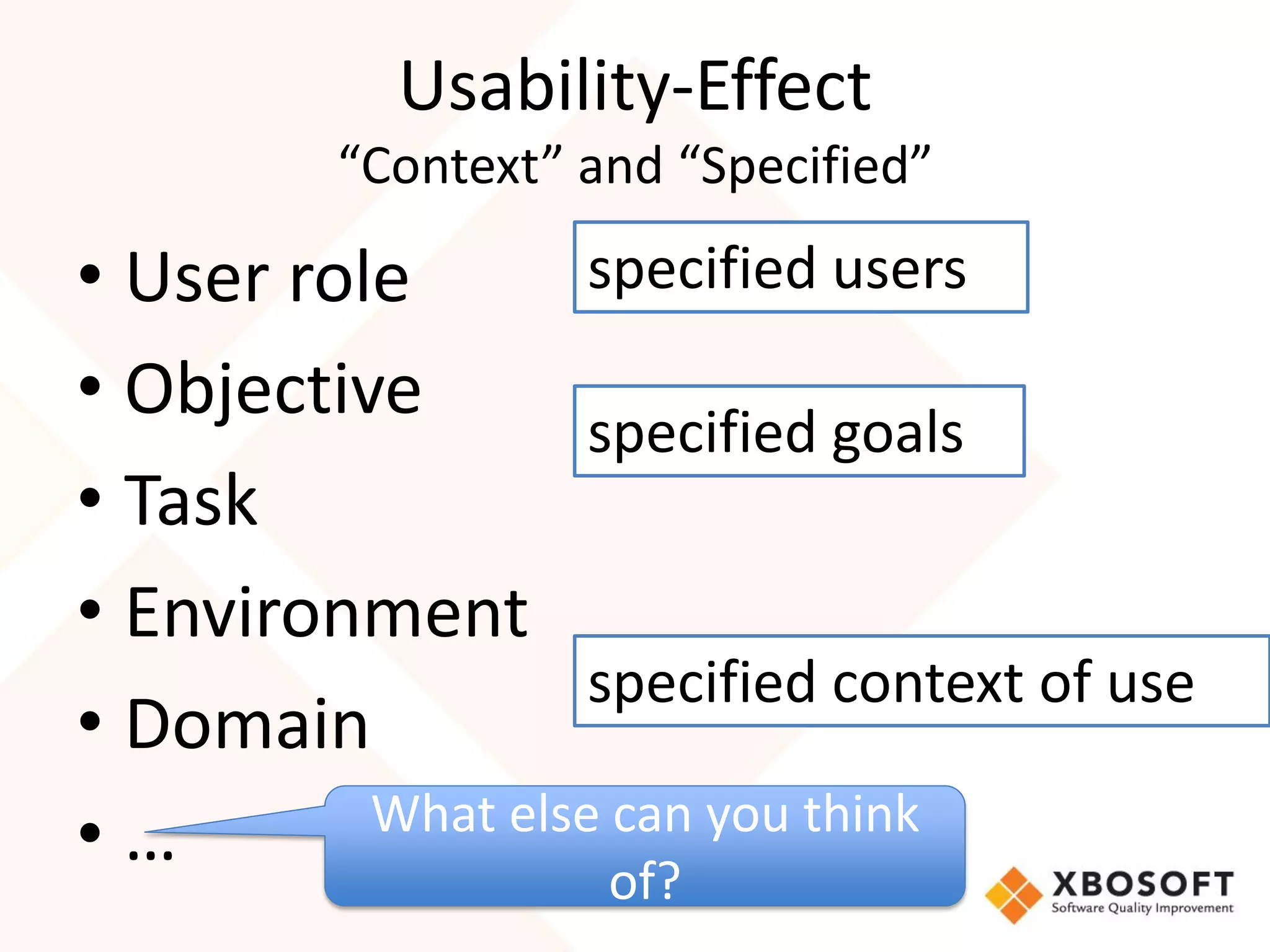
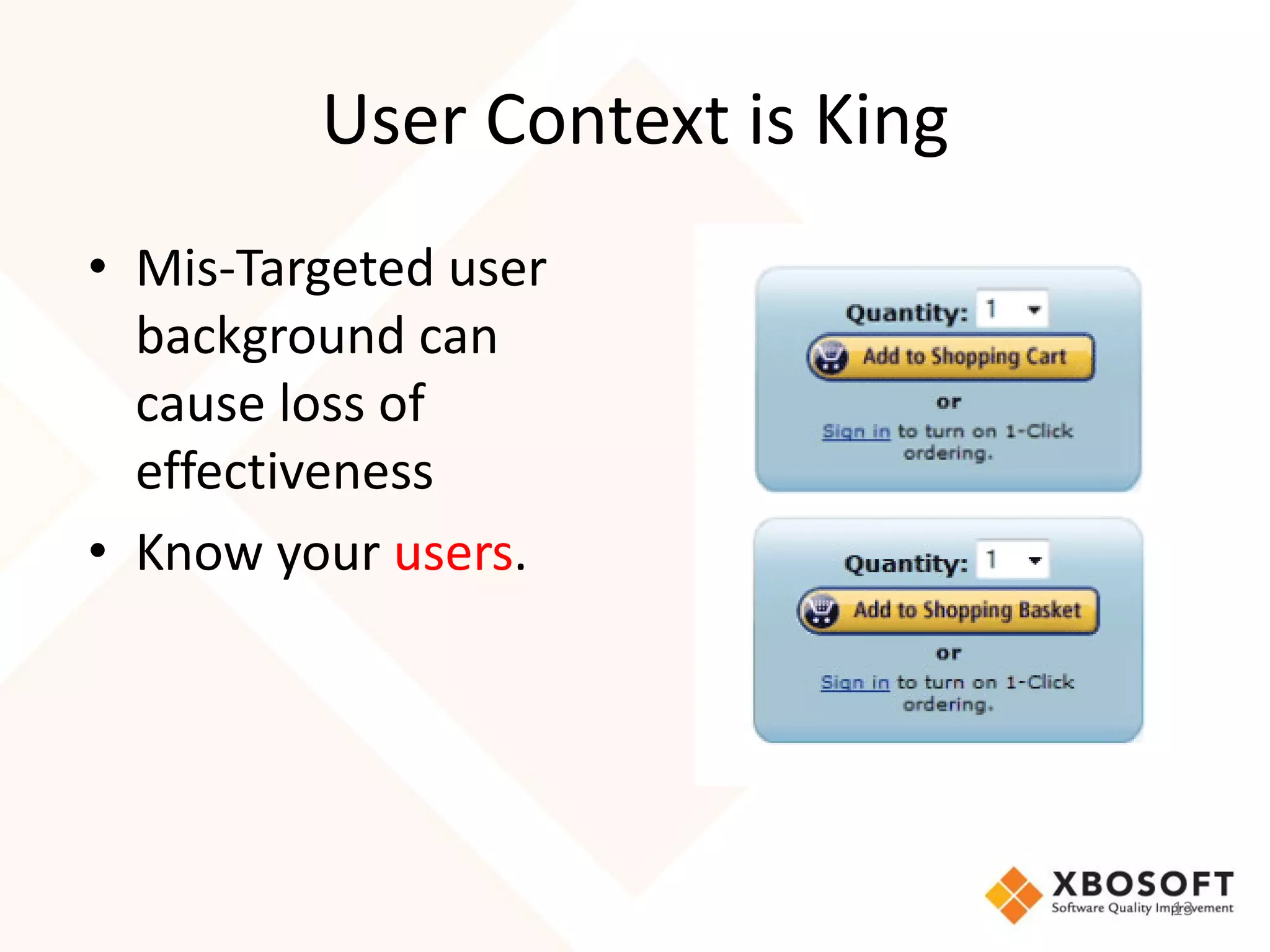
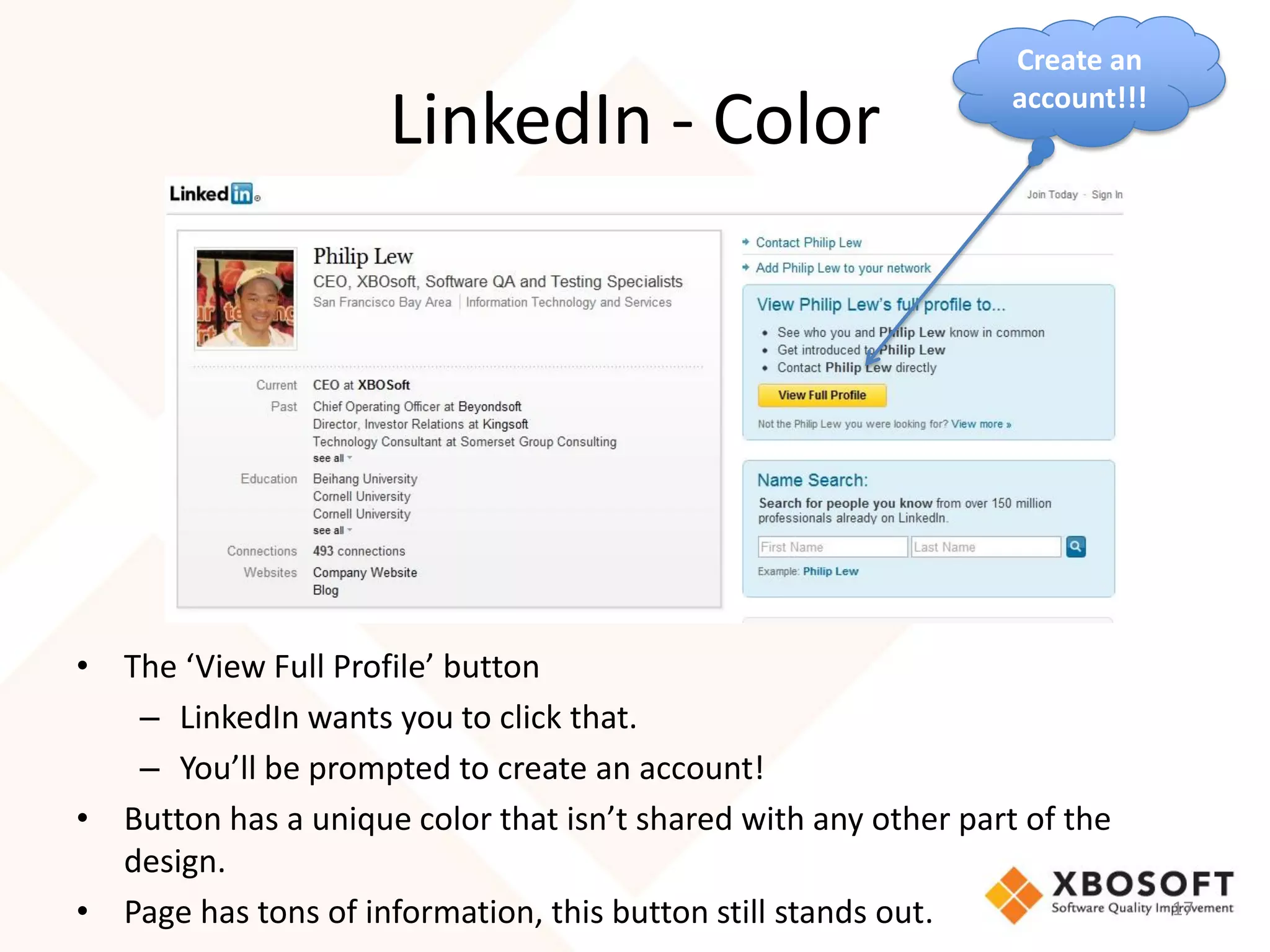
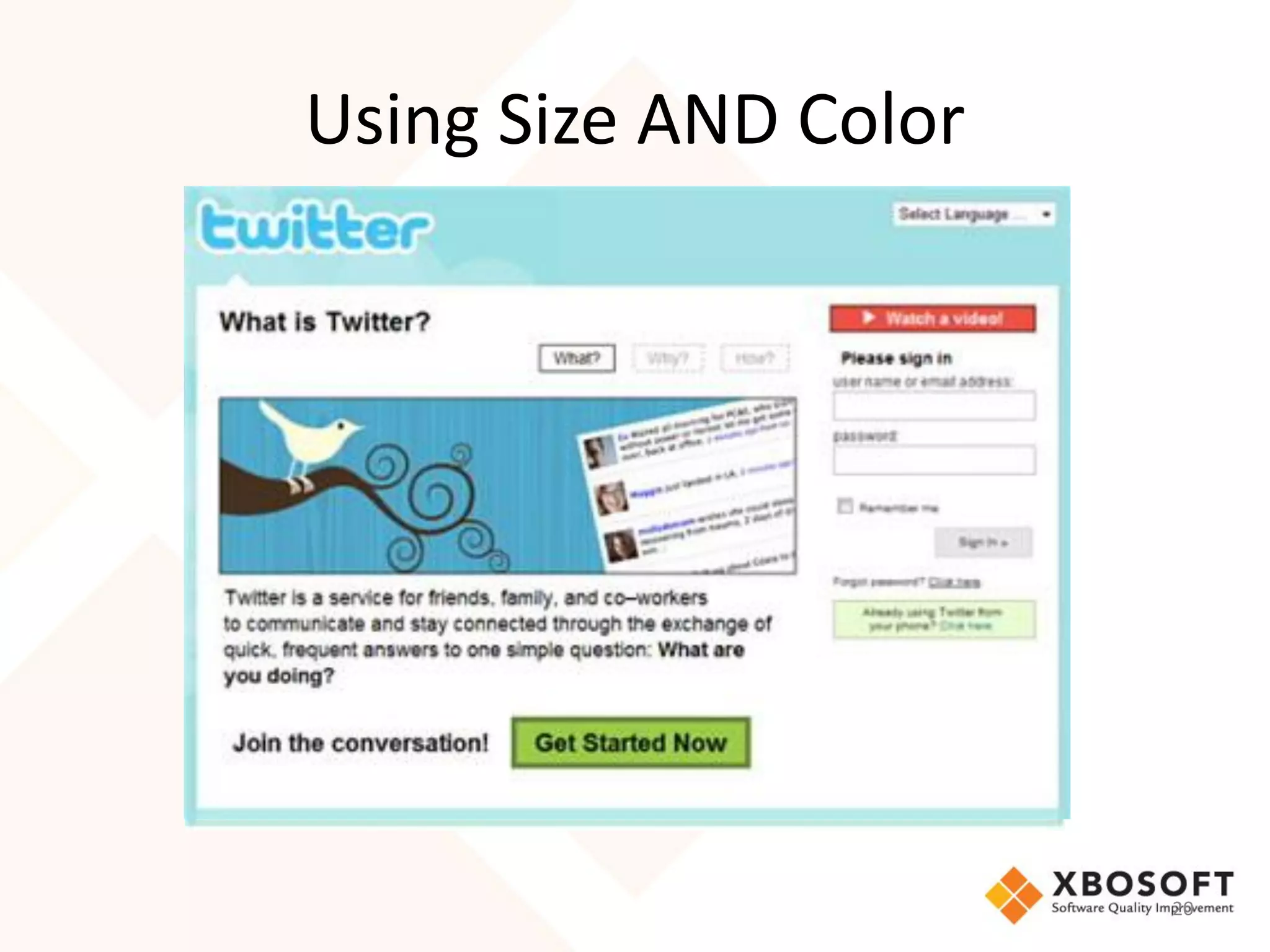
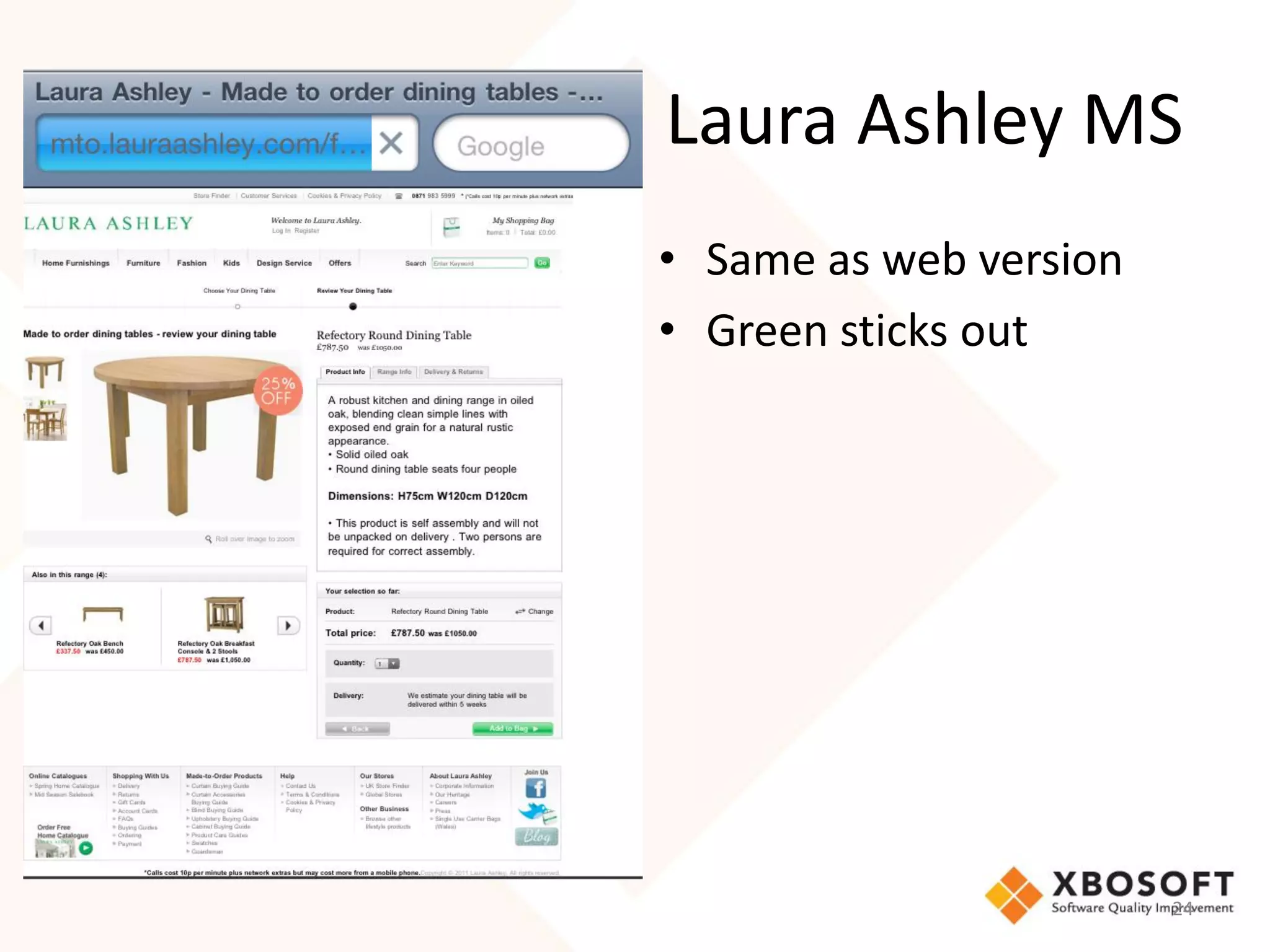
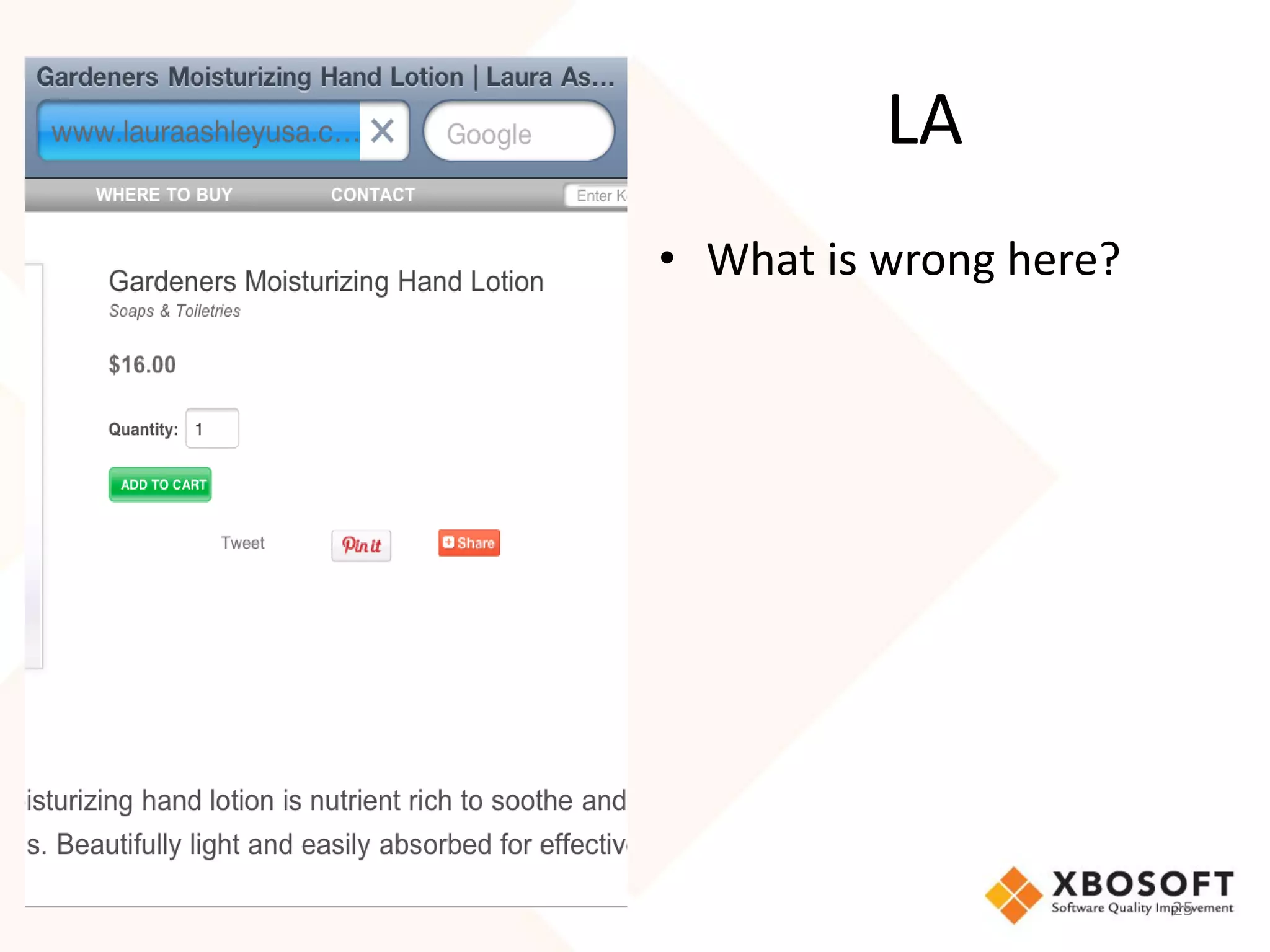
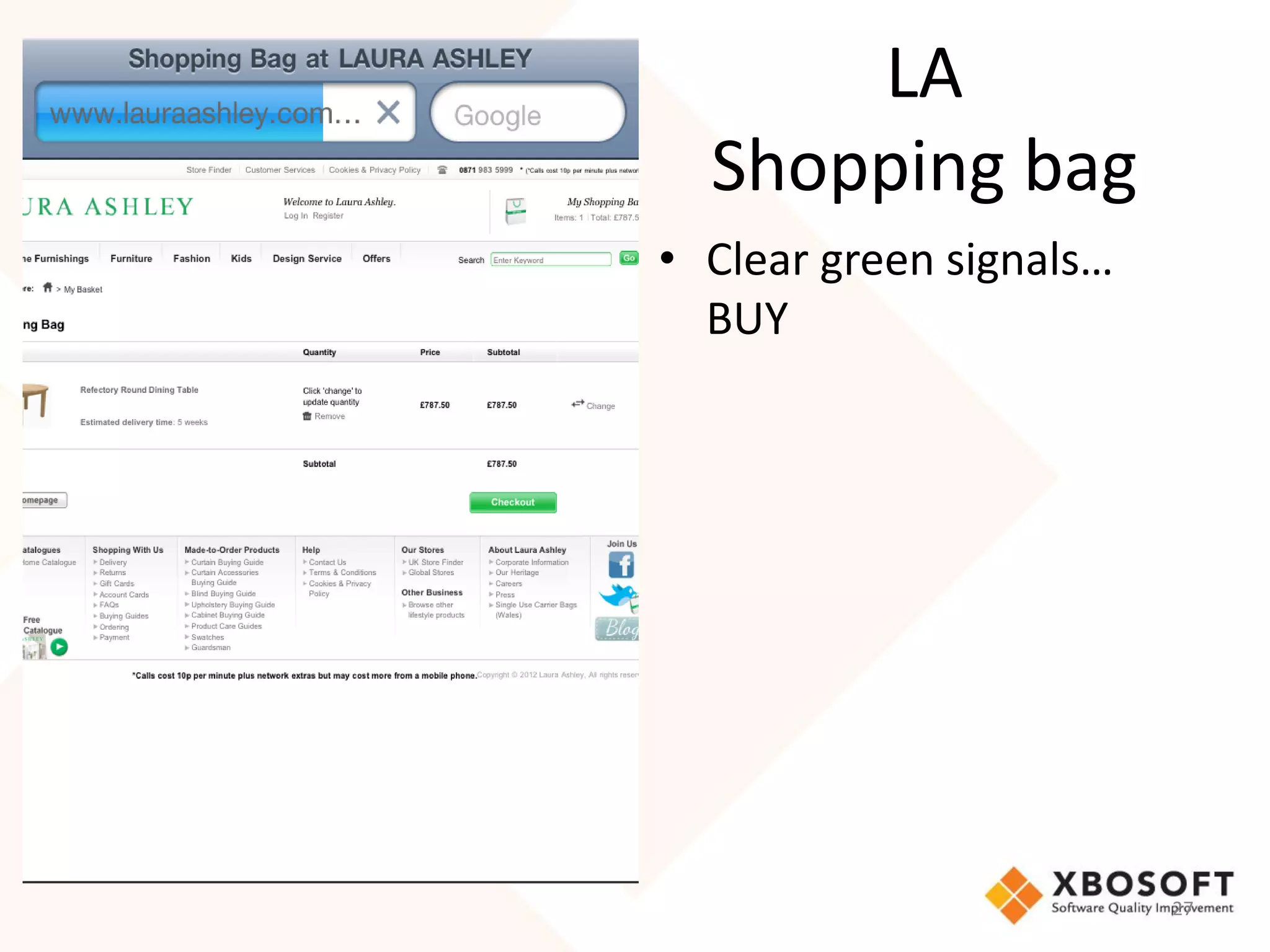
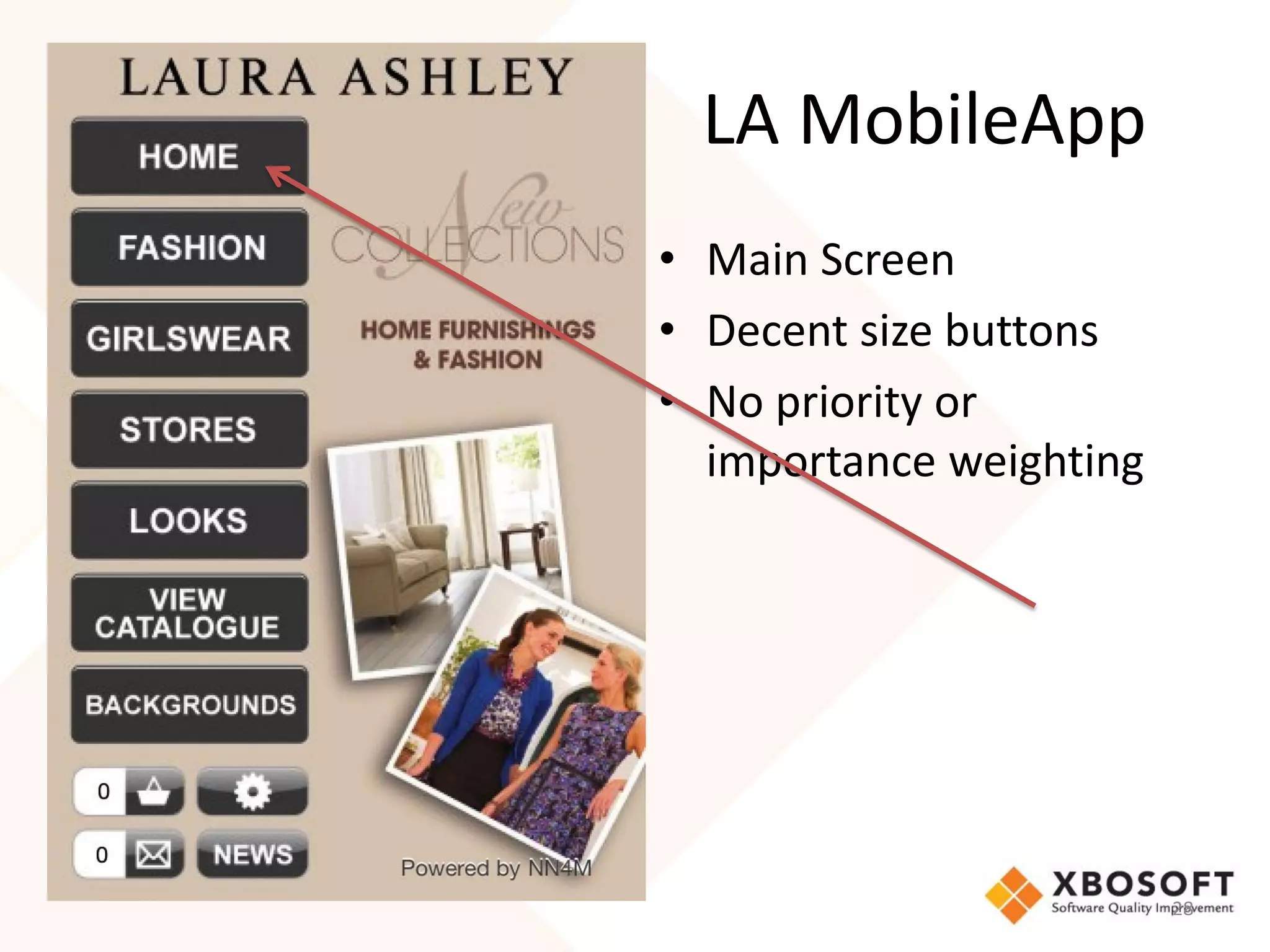
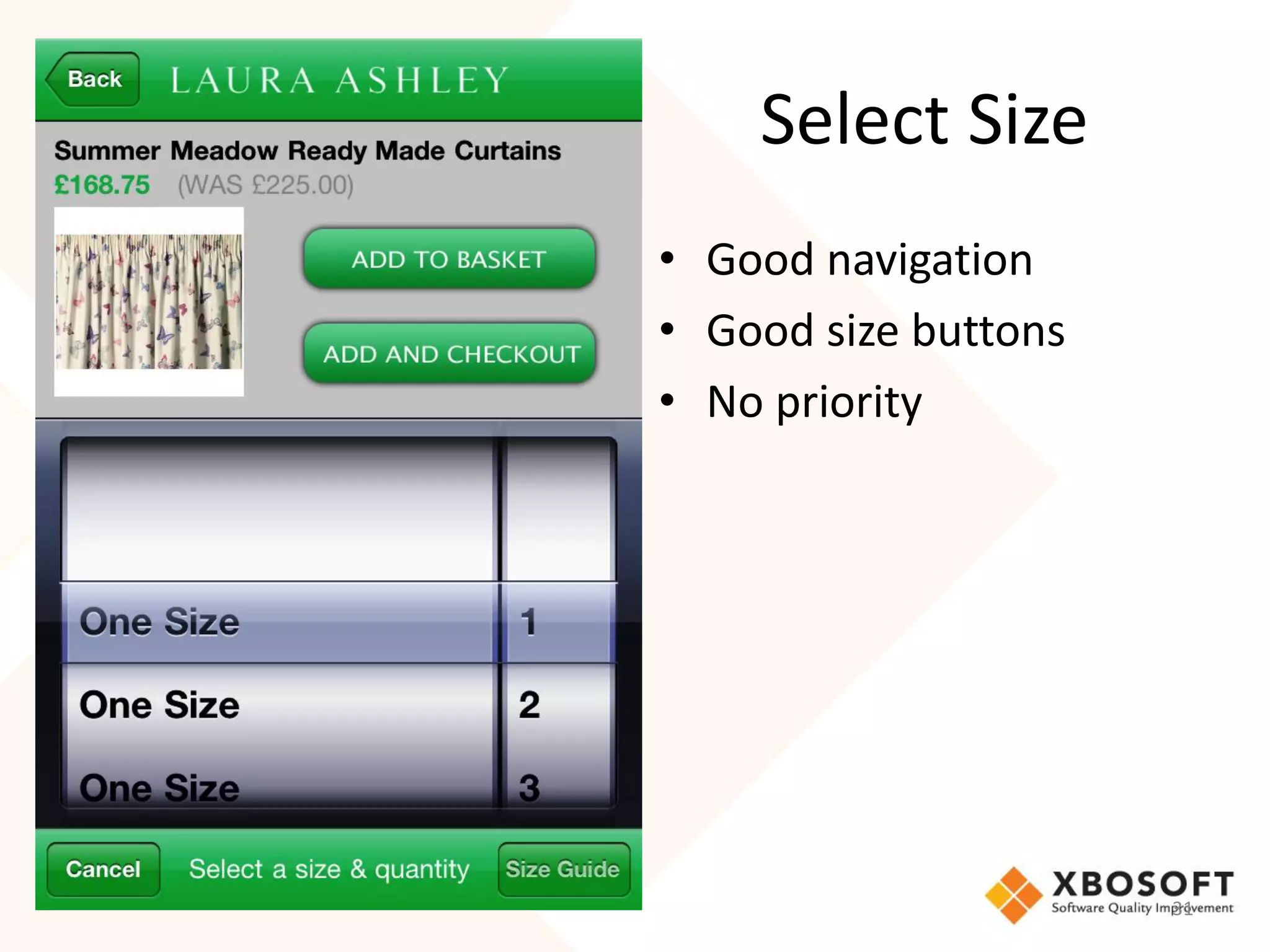
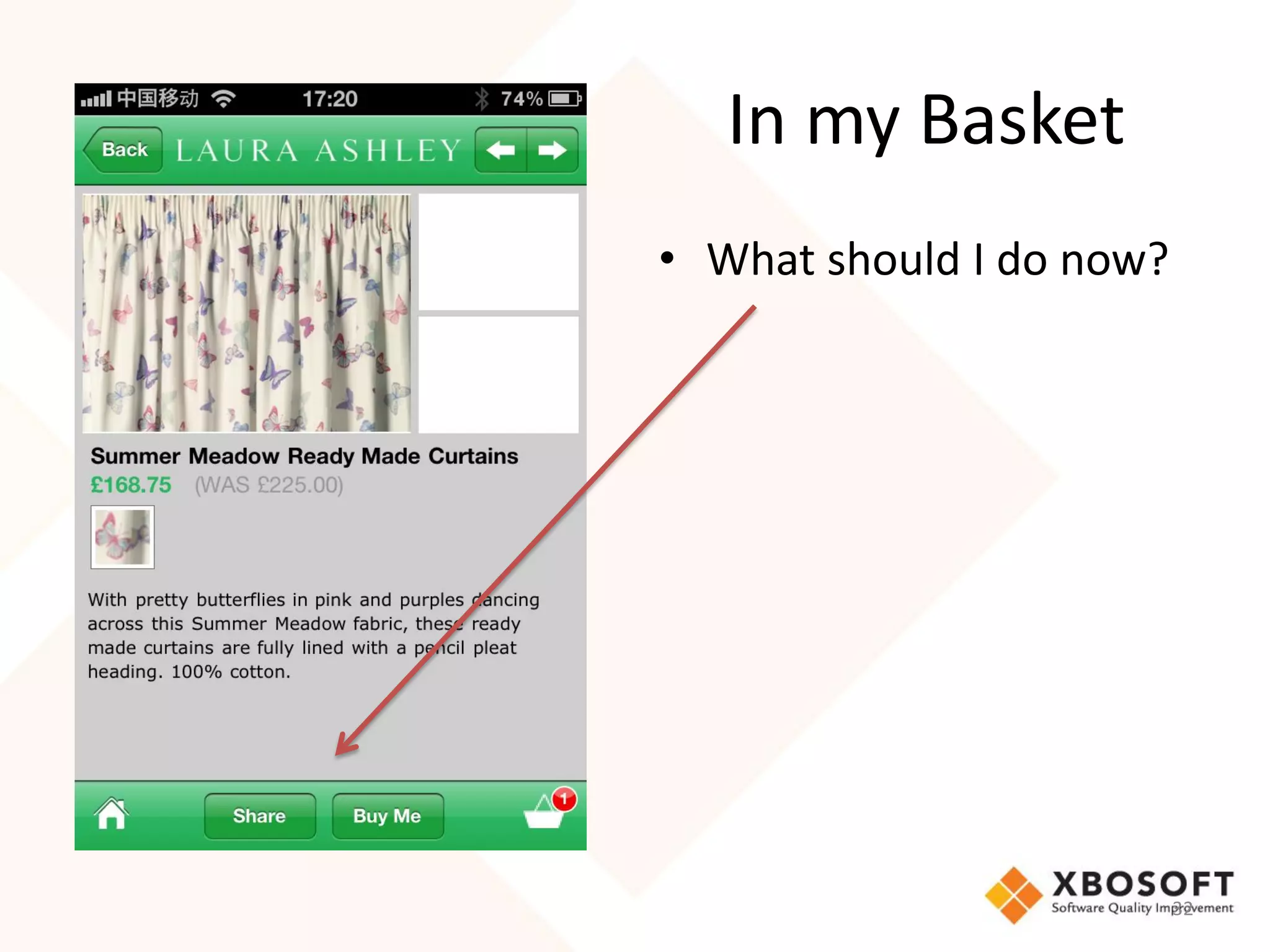
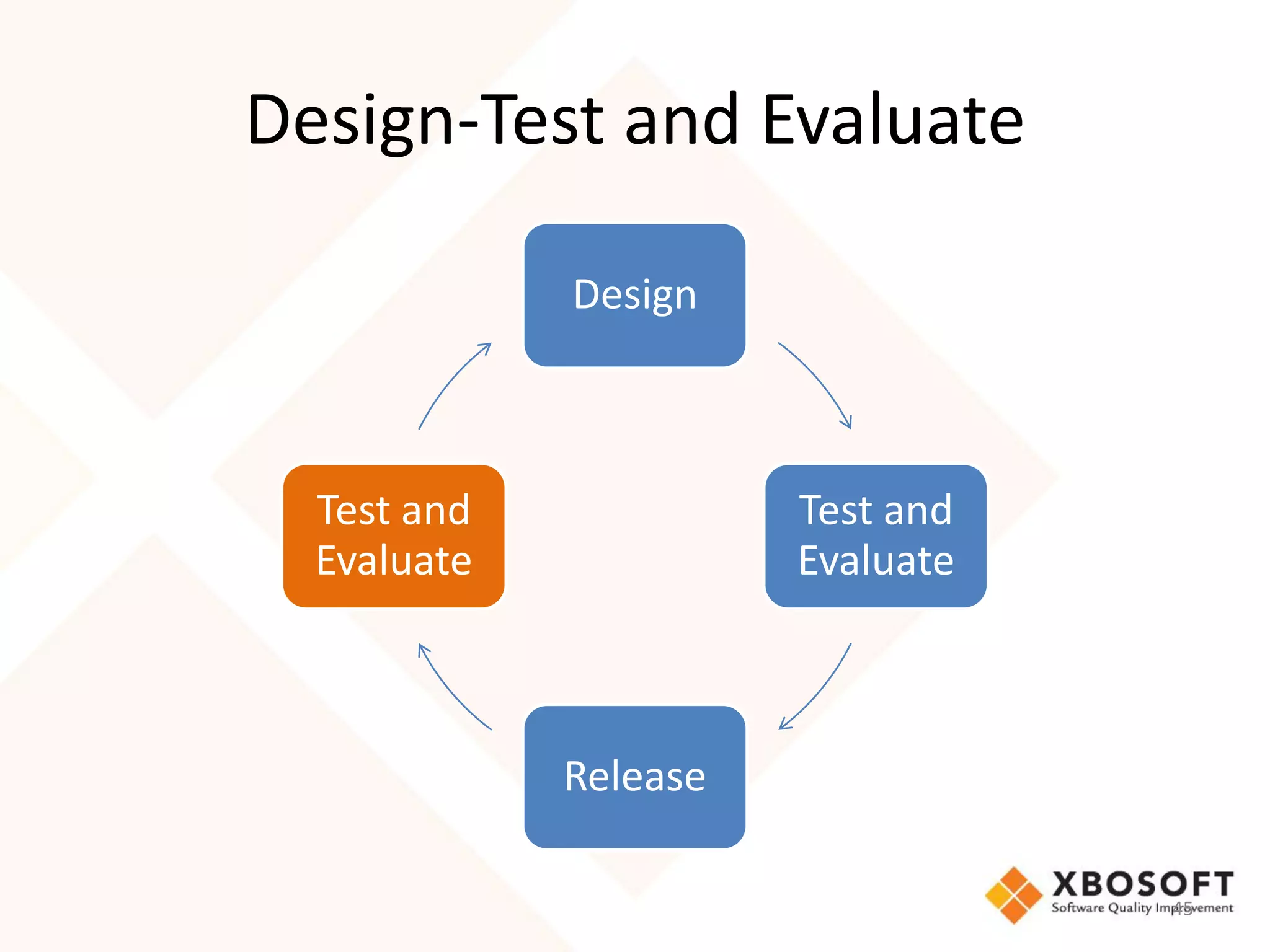
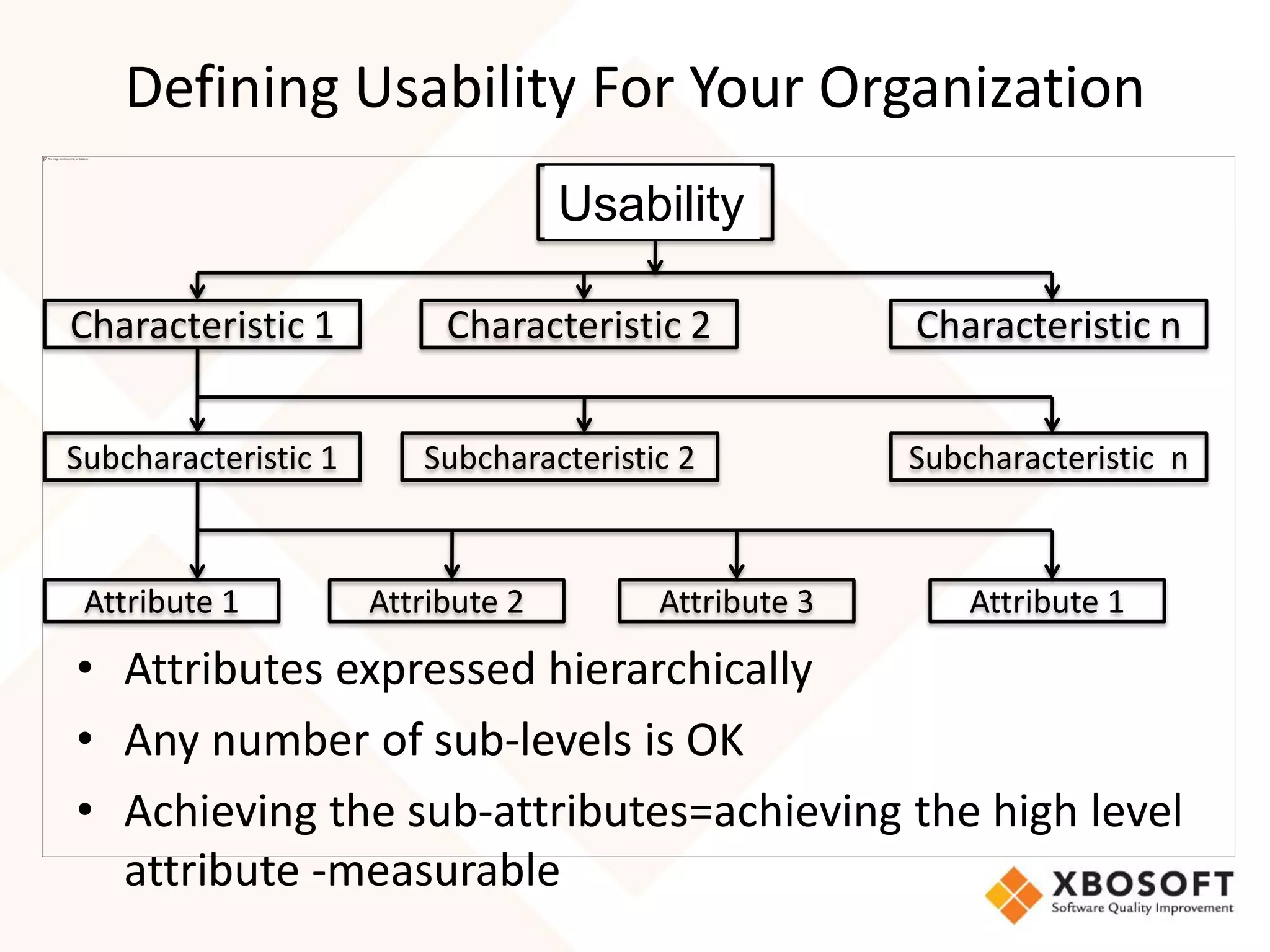
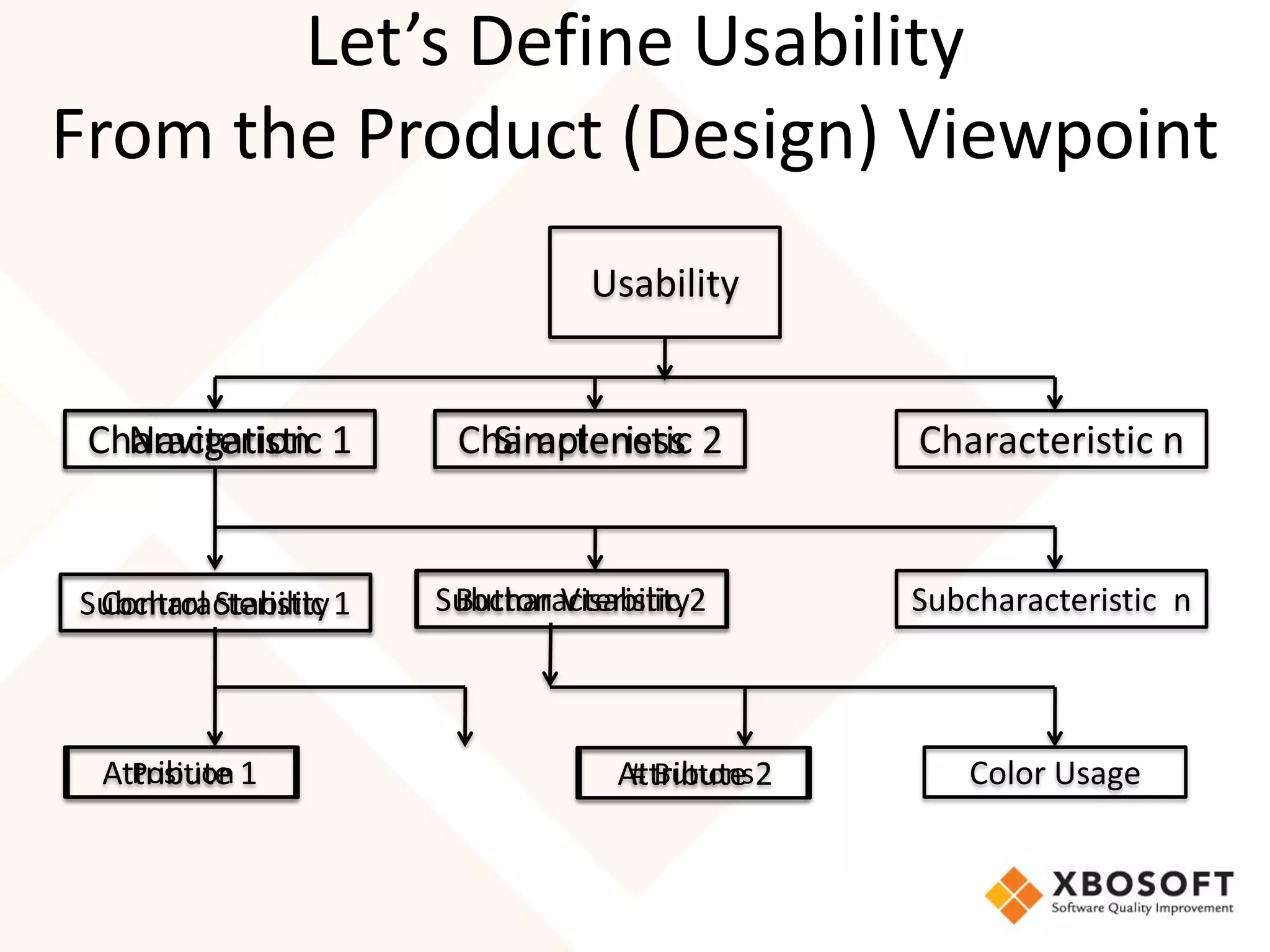
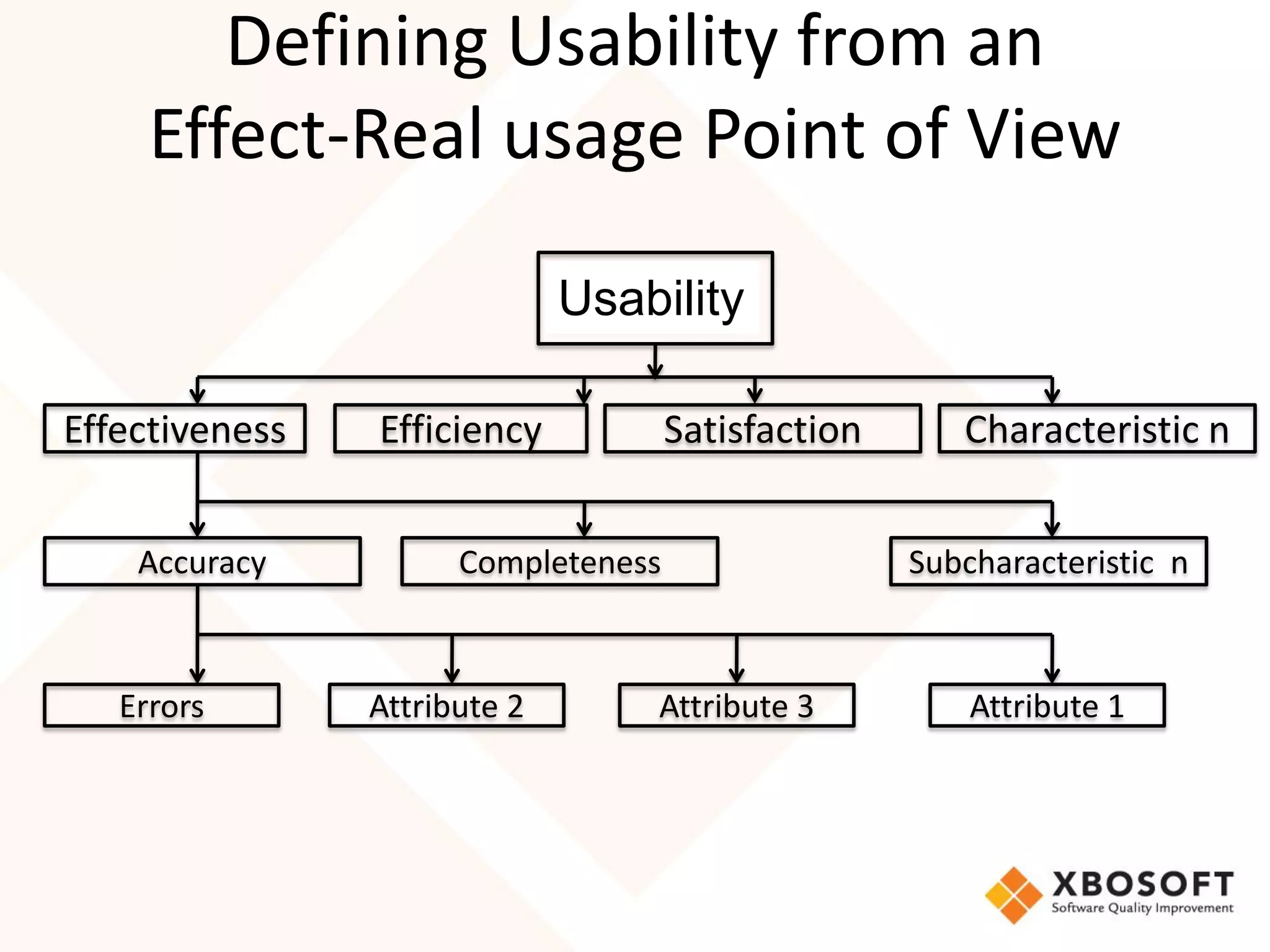
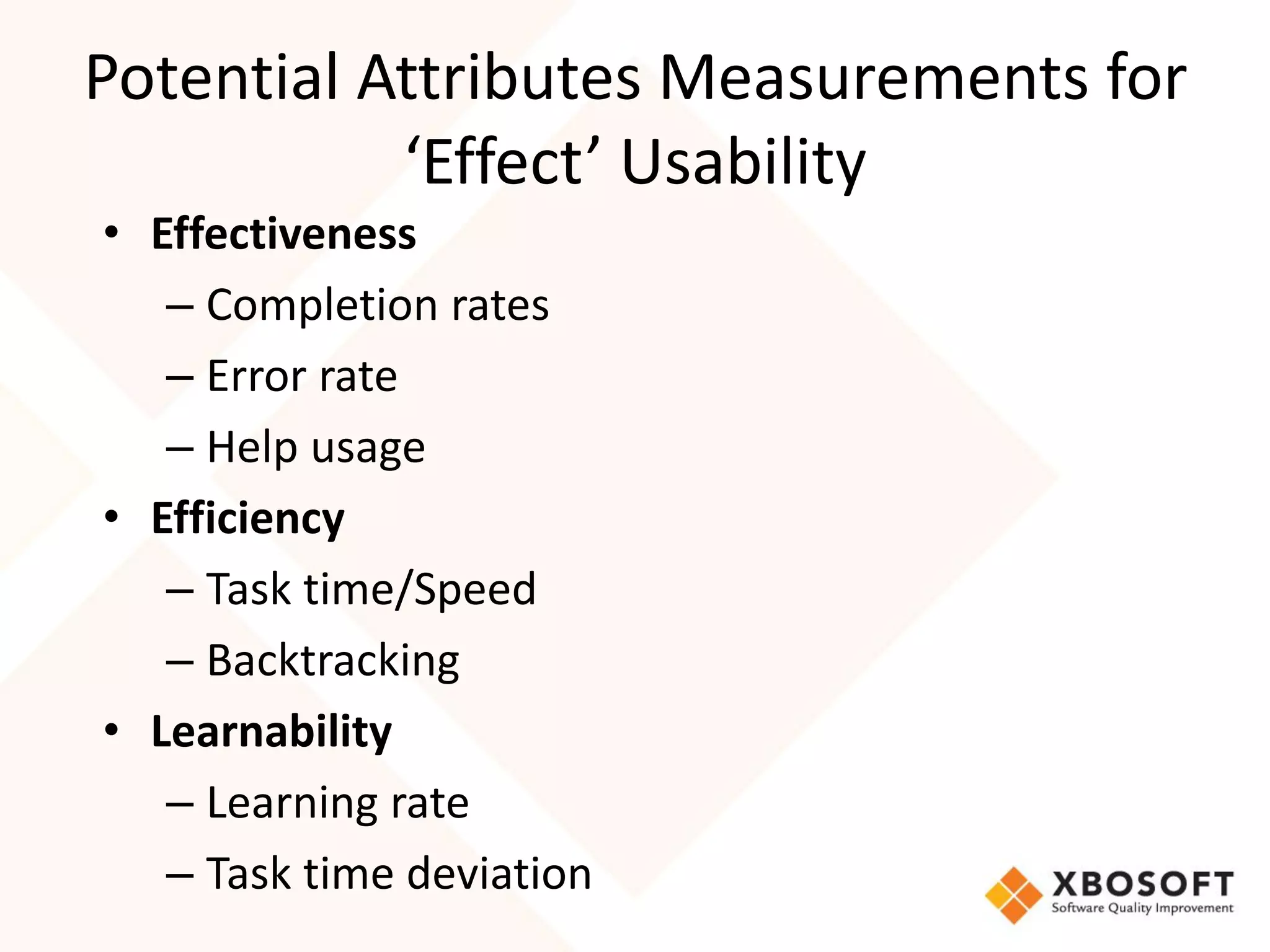
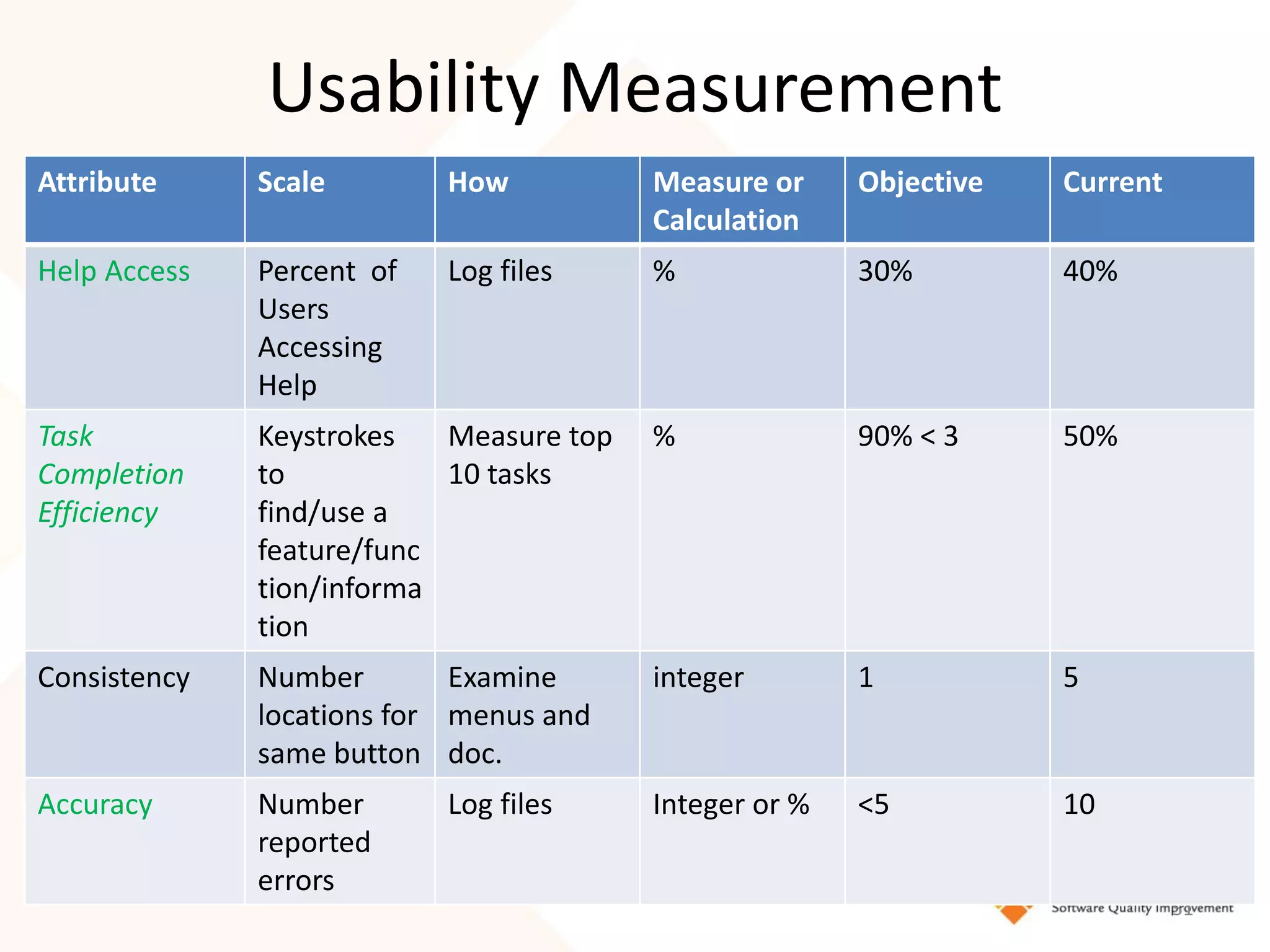
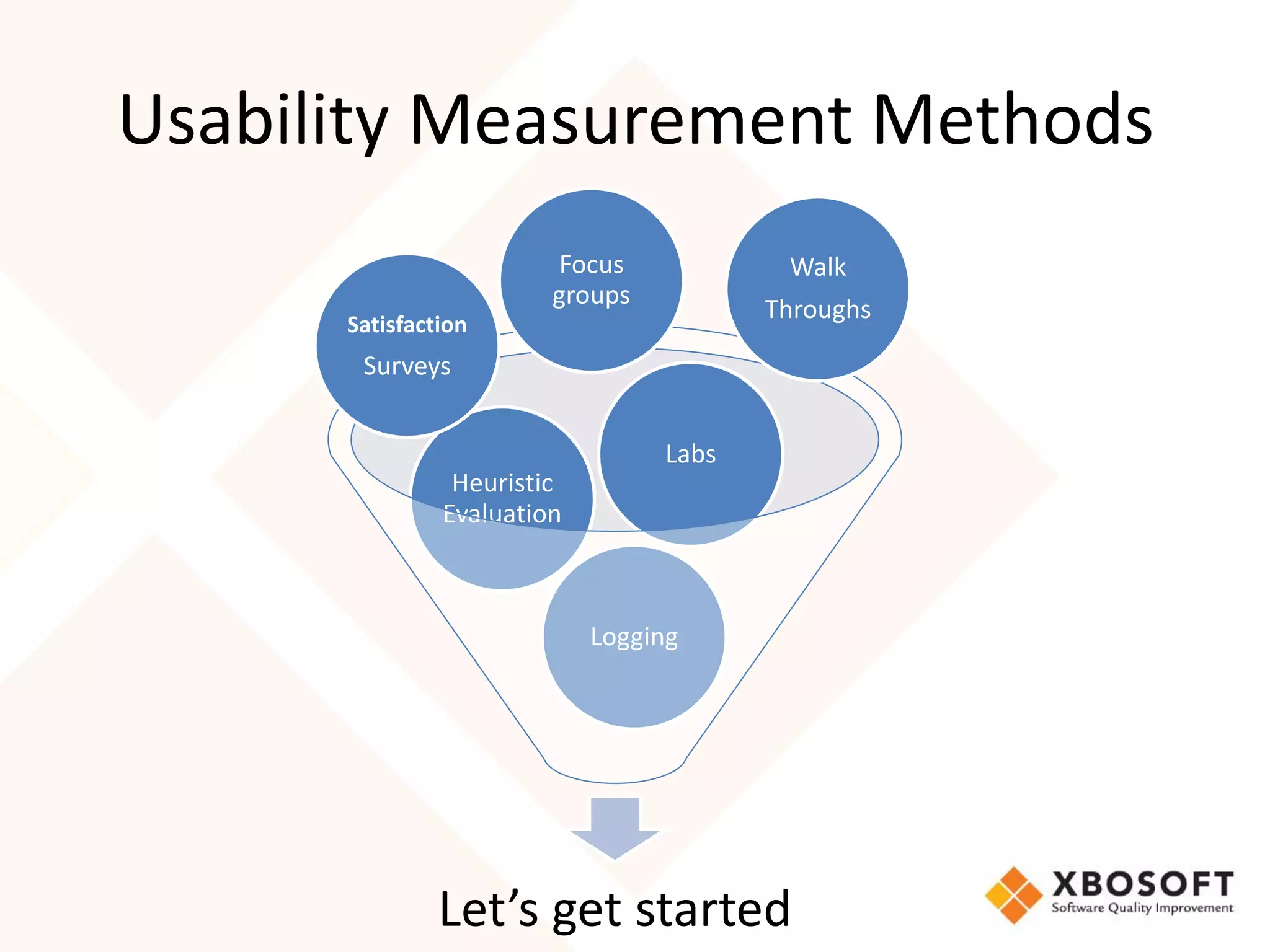
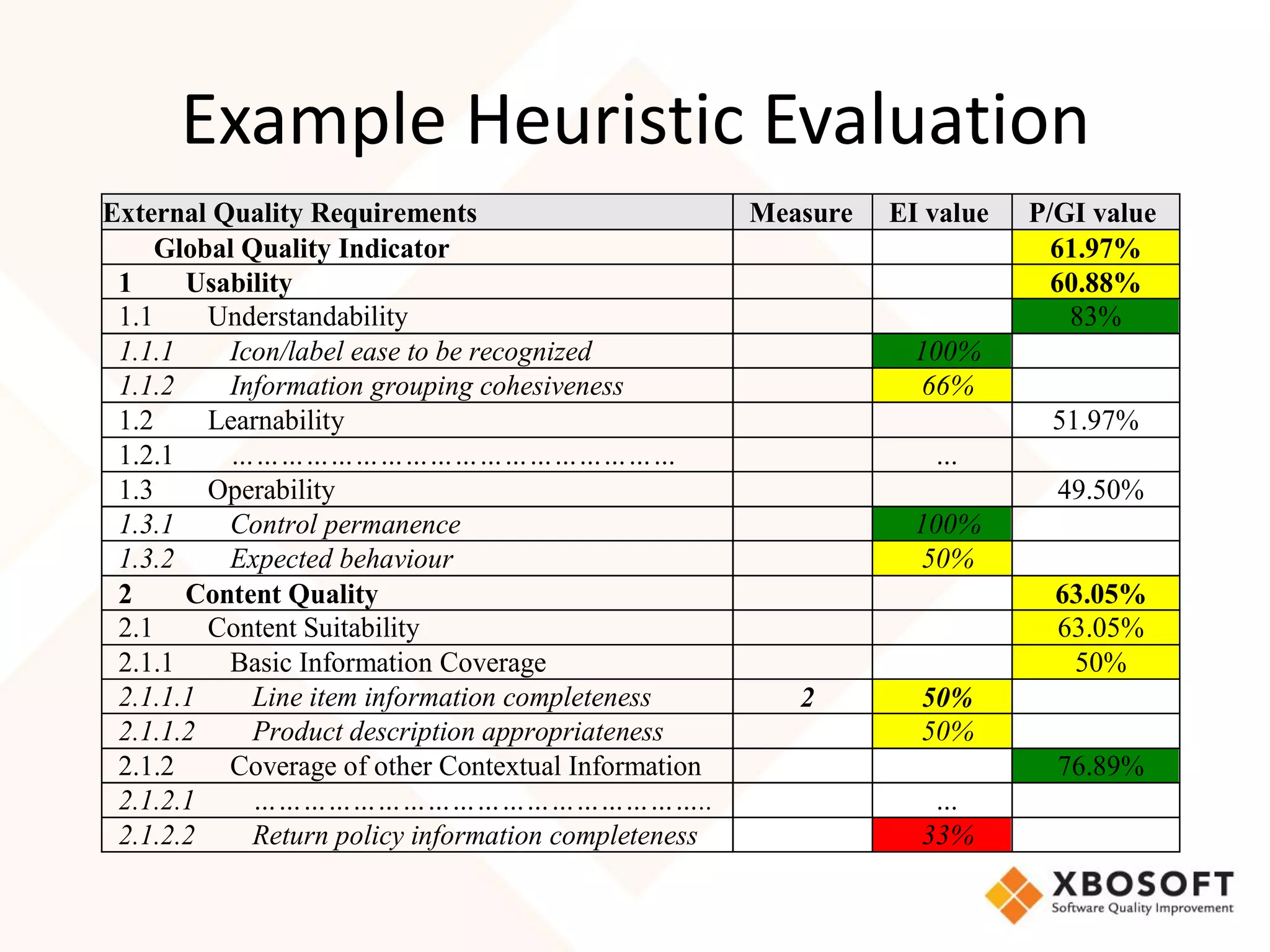
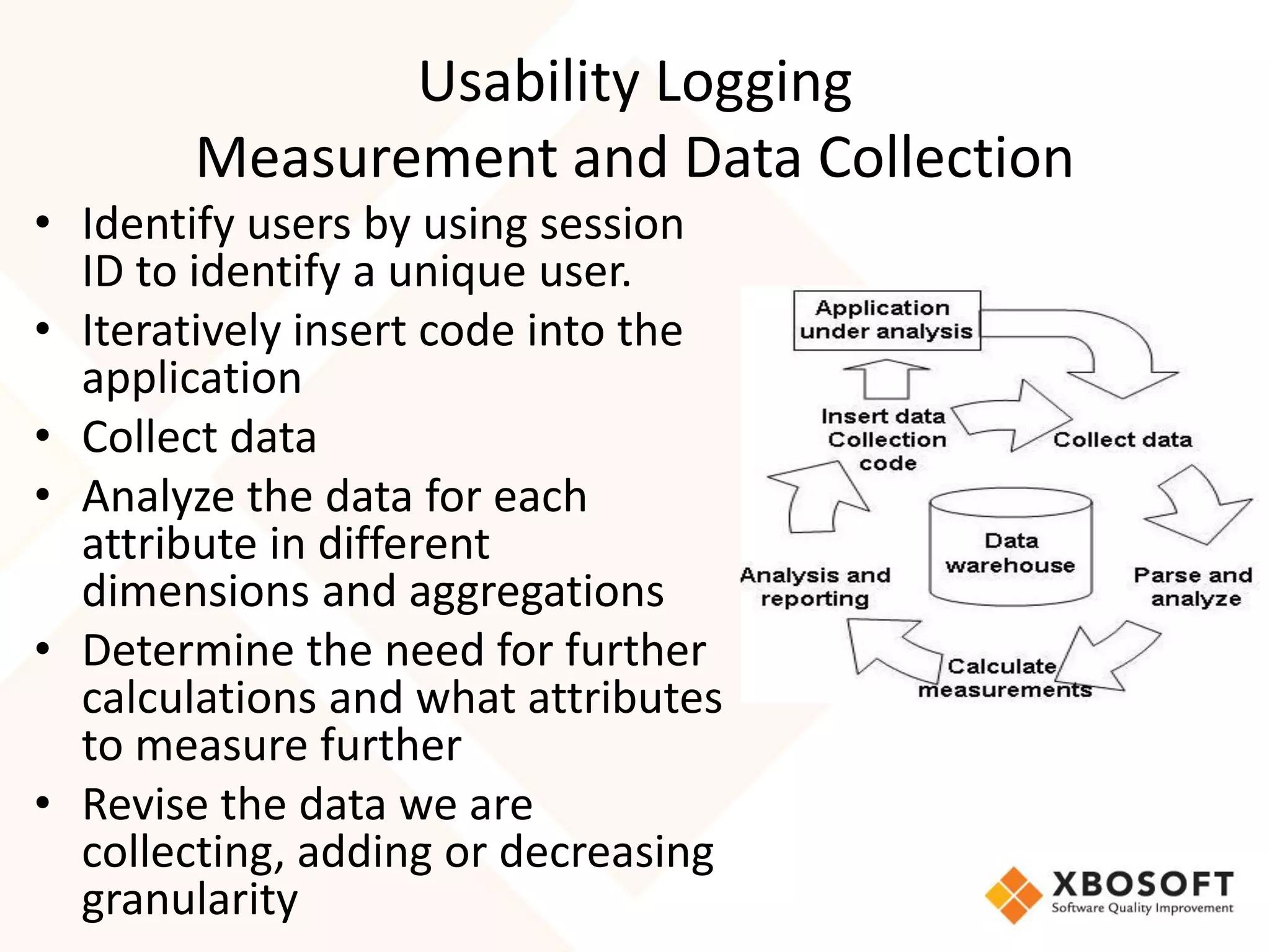
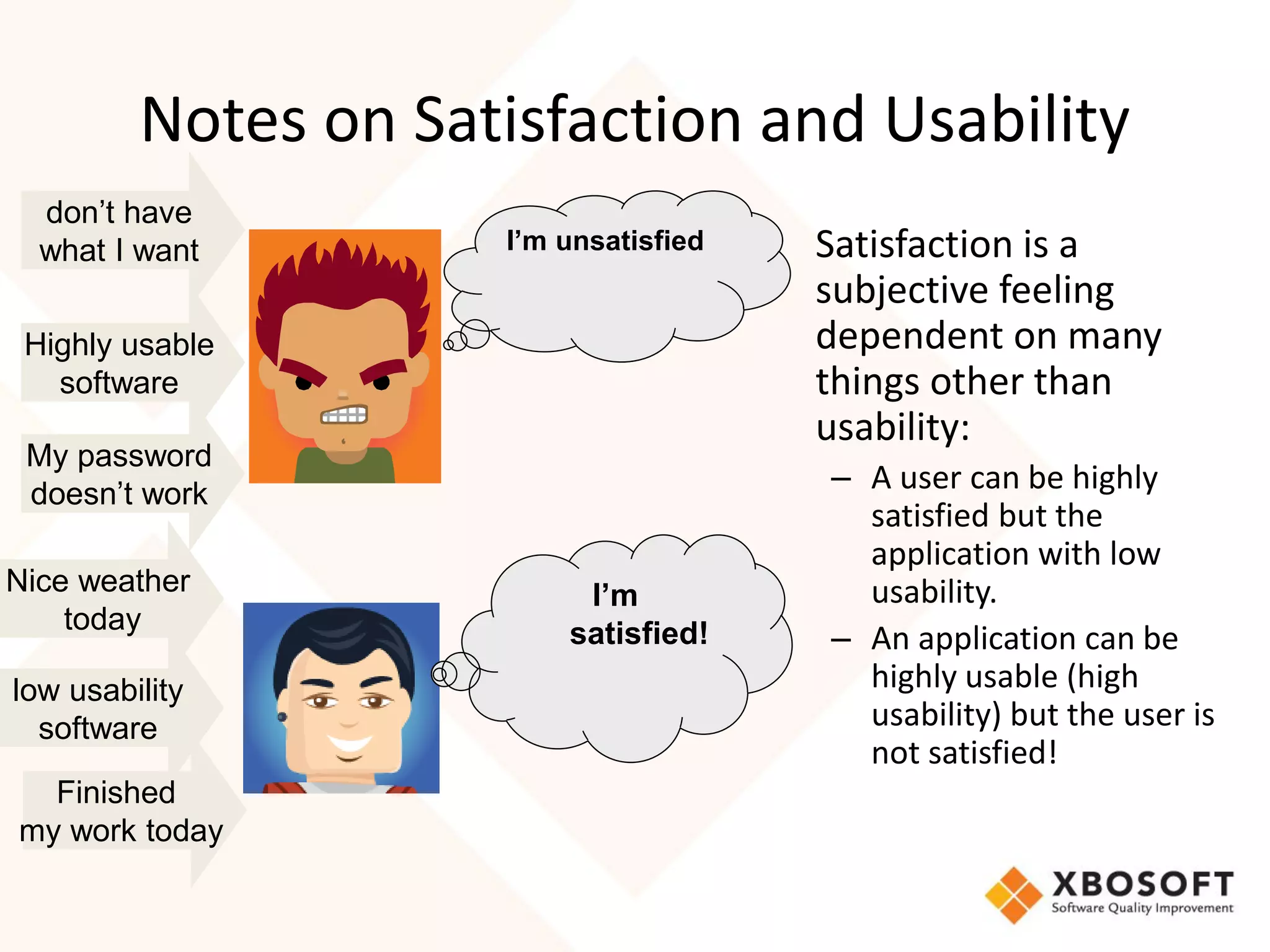
The document discusses the importance of usability and user experience (UX) measurements for mobile healthcare applications, emphasizing the need to adapt usability principles to meet evolving user expectations. It outlines key concepts such as usability characteristics, measurement methods, and the impact of design elements like color and size on user engagement. Additionally, it introduces the imedtablet technology designed for patient care coordination and stresses the importance of establishing a usability model tailored to organizational needs.