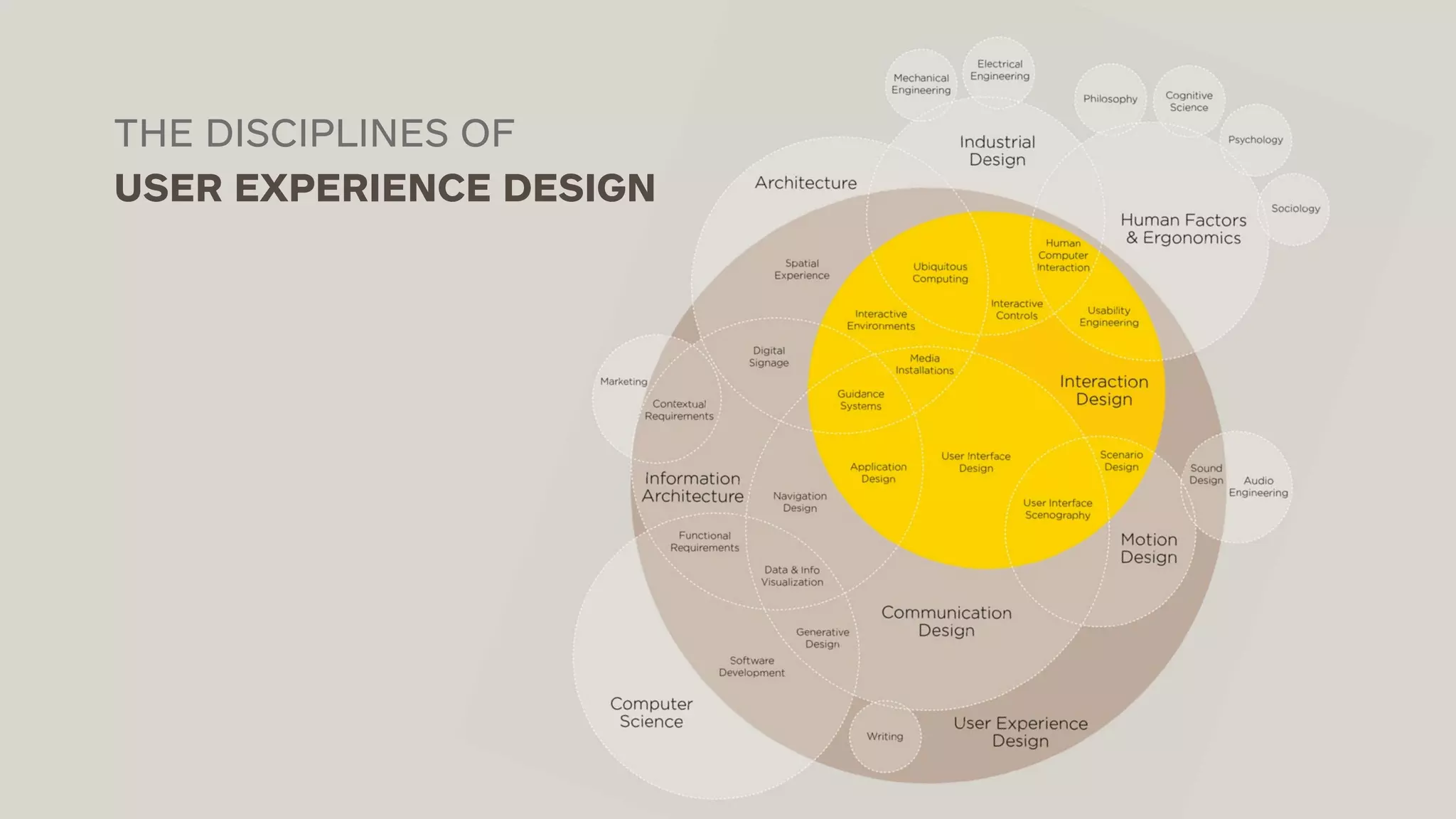
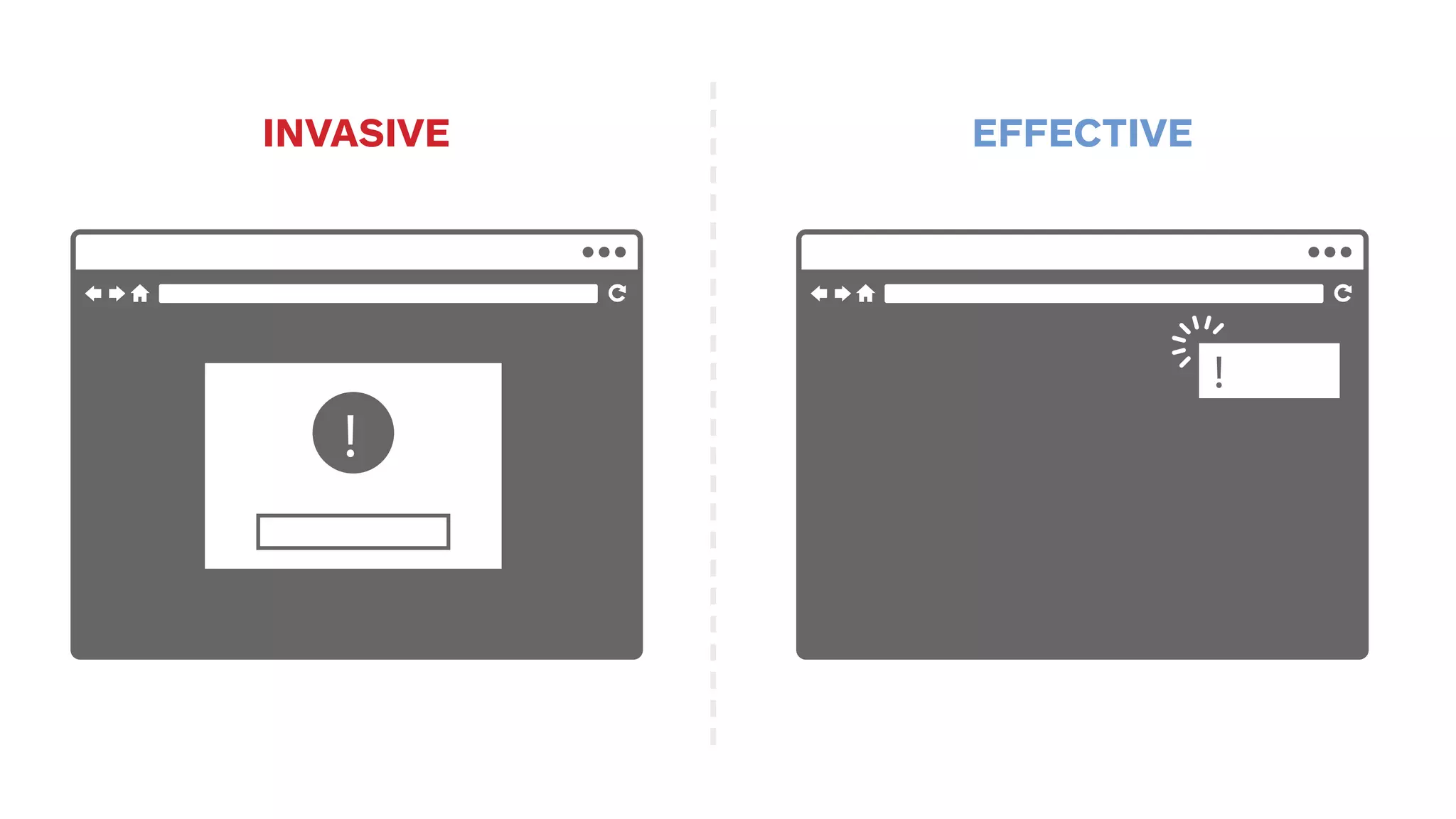
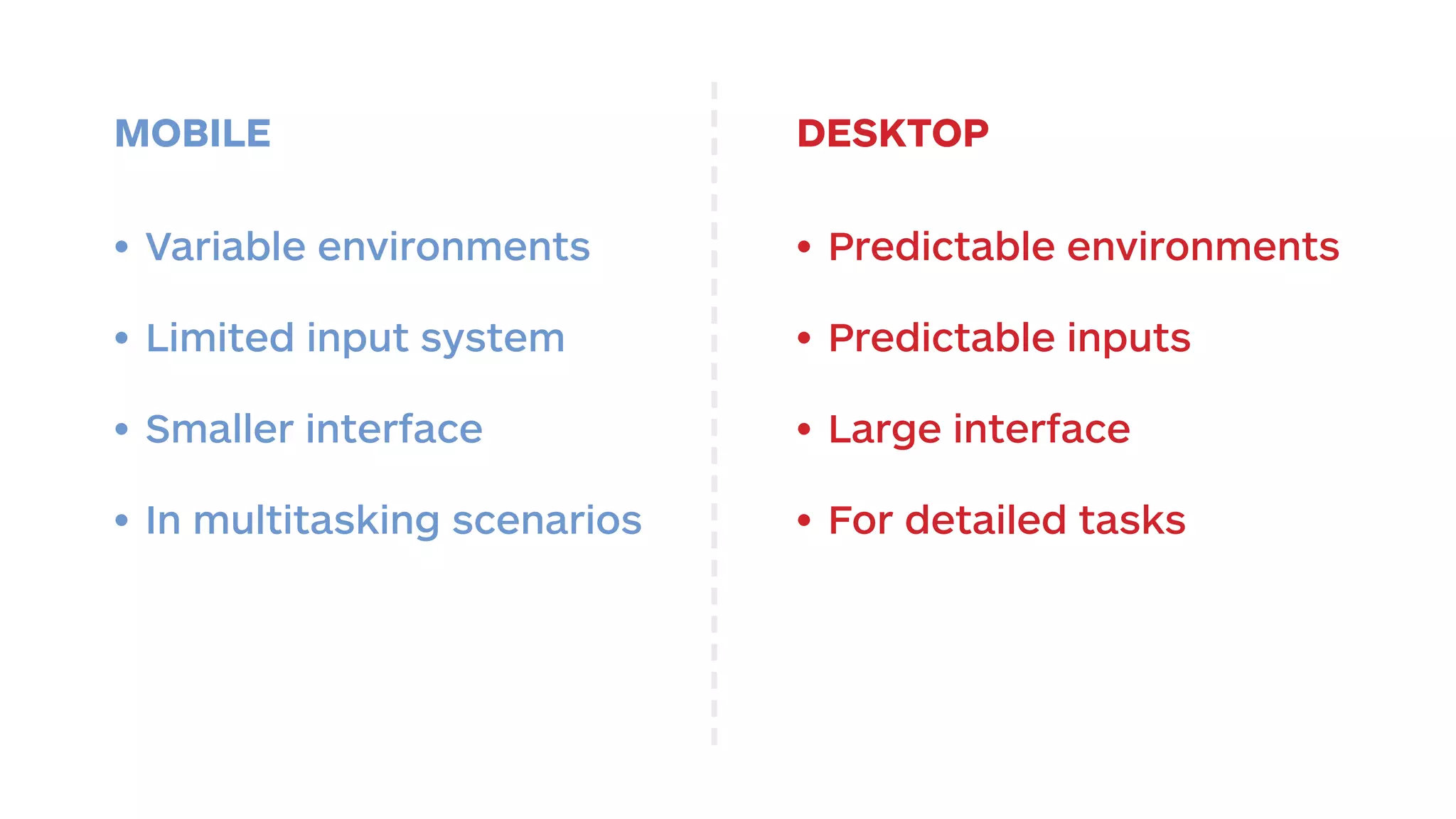
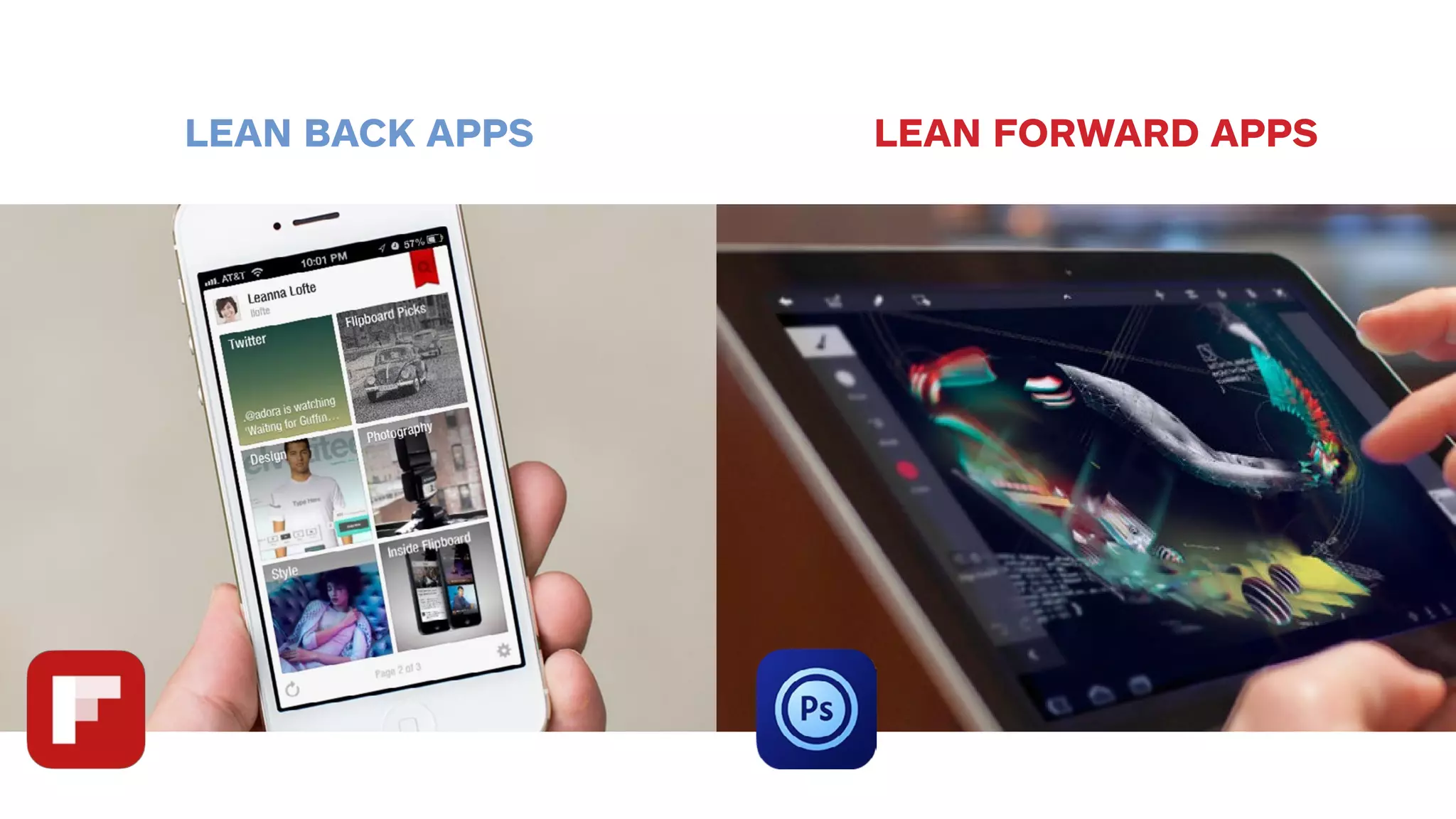
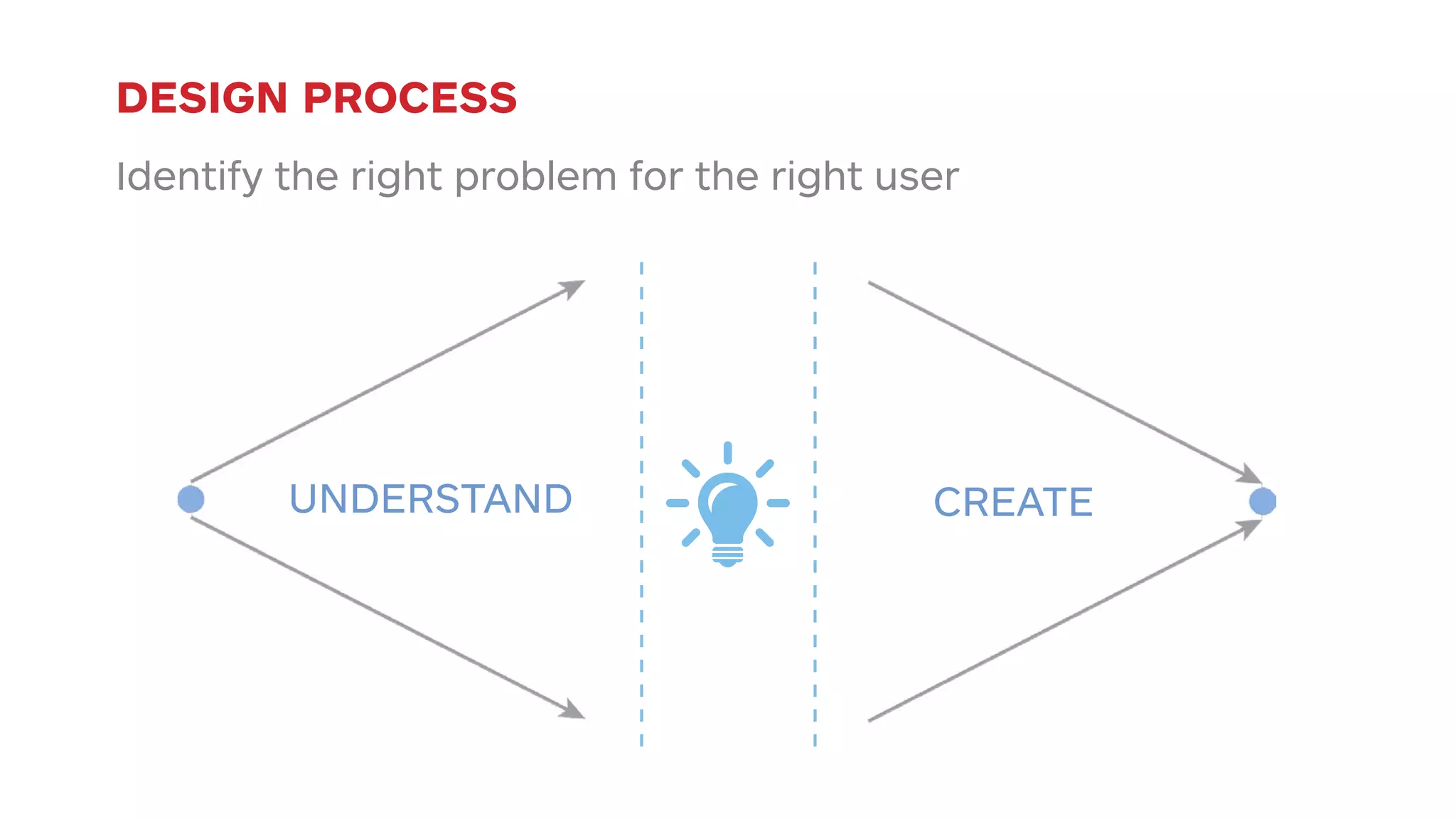
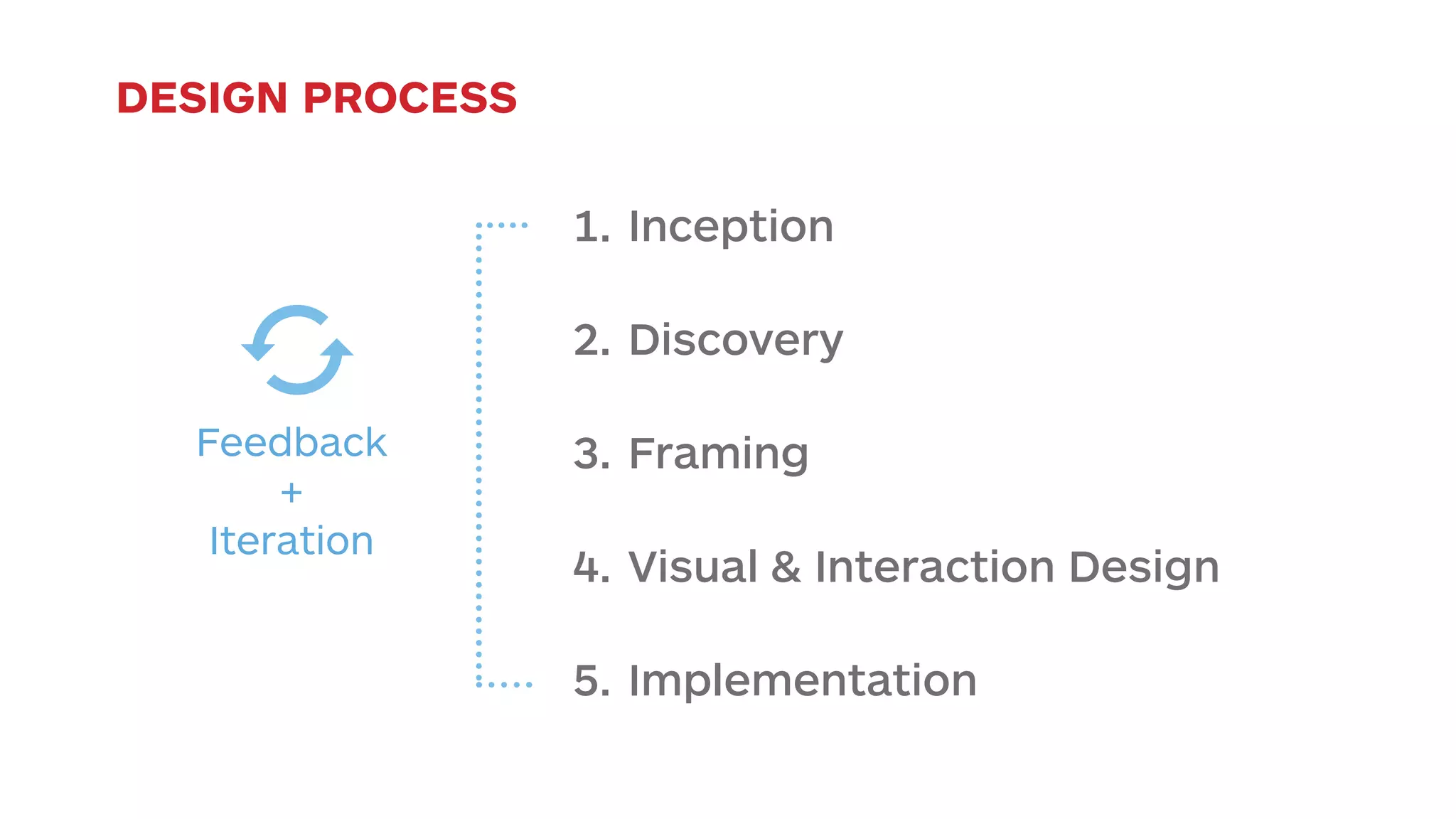
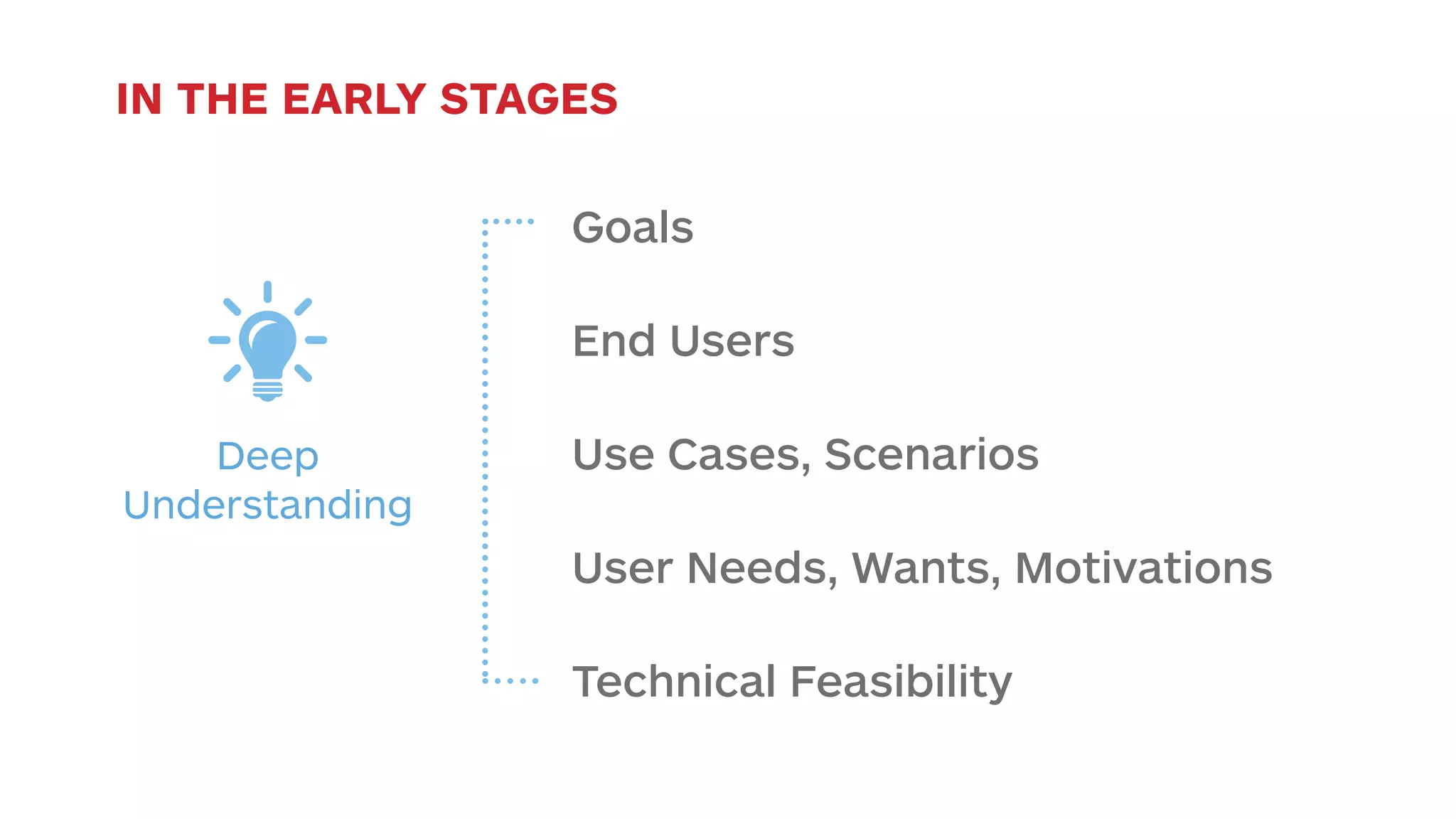
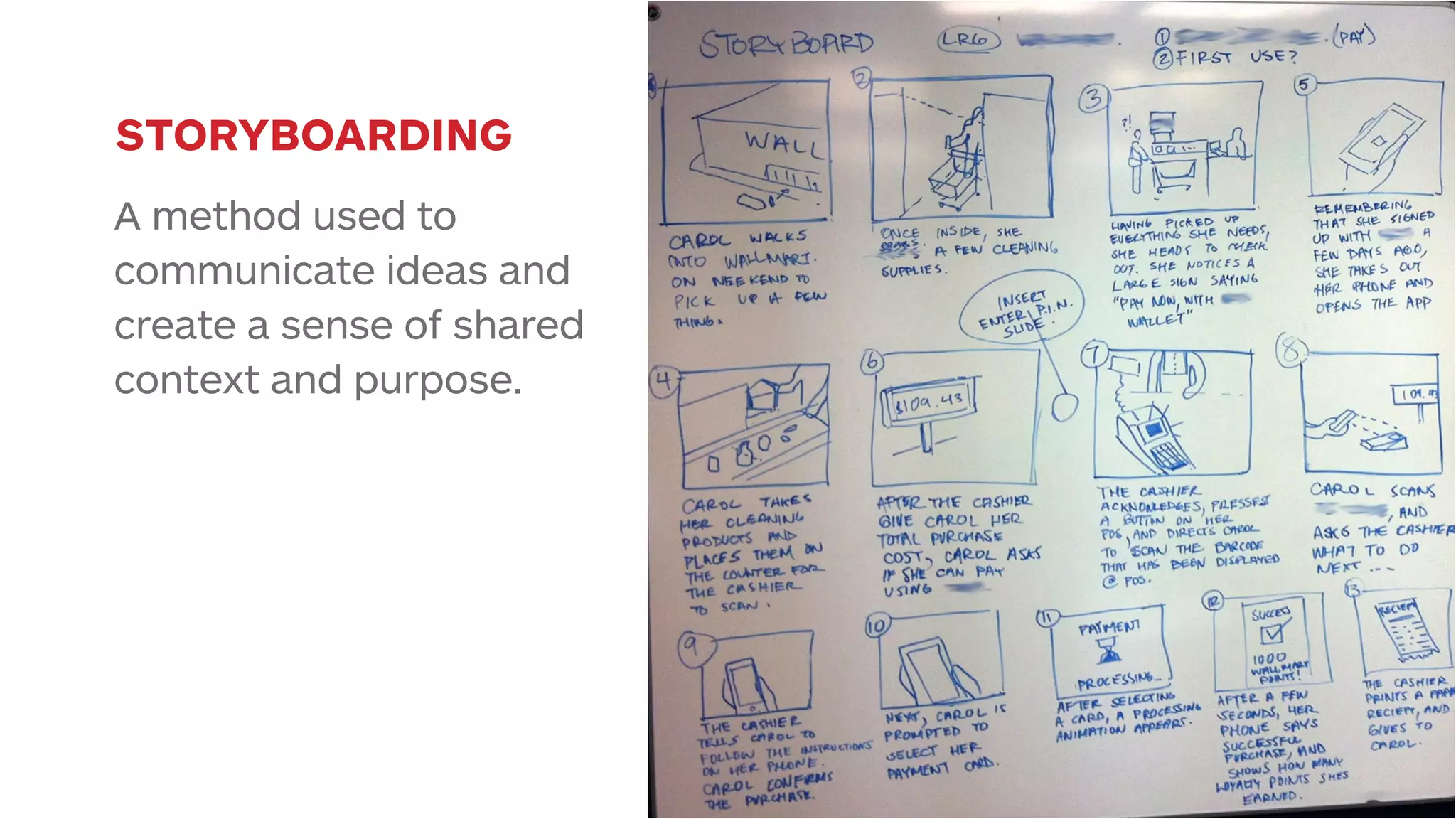
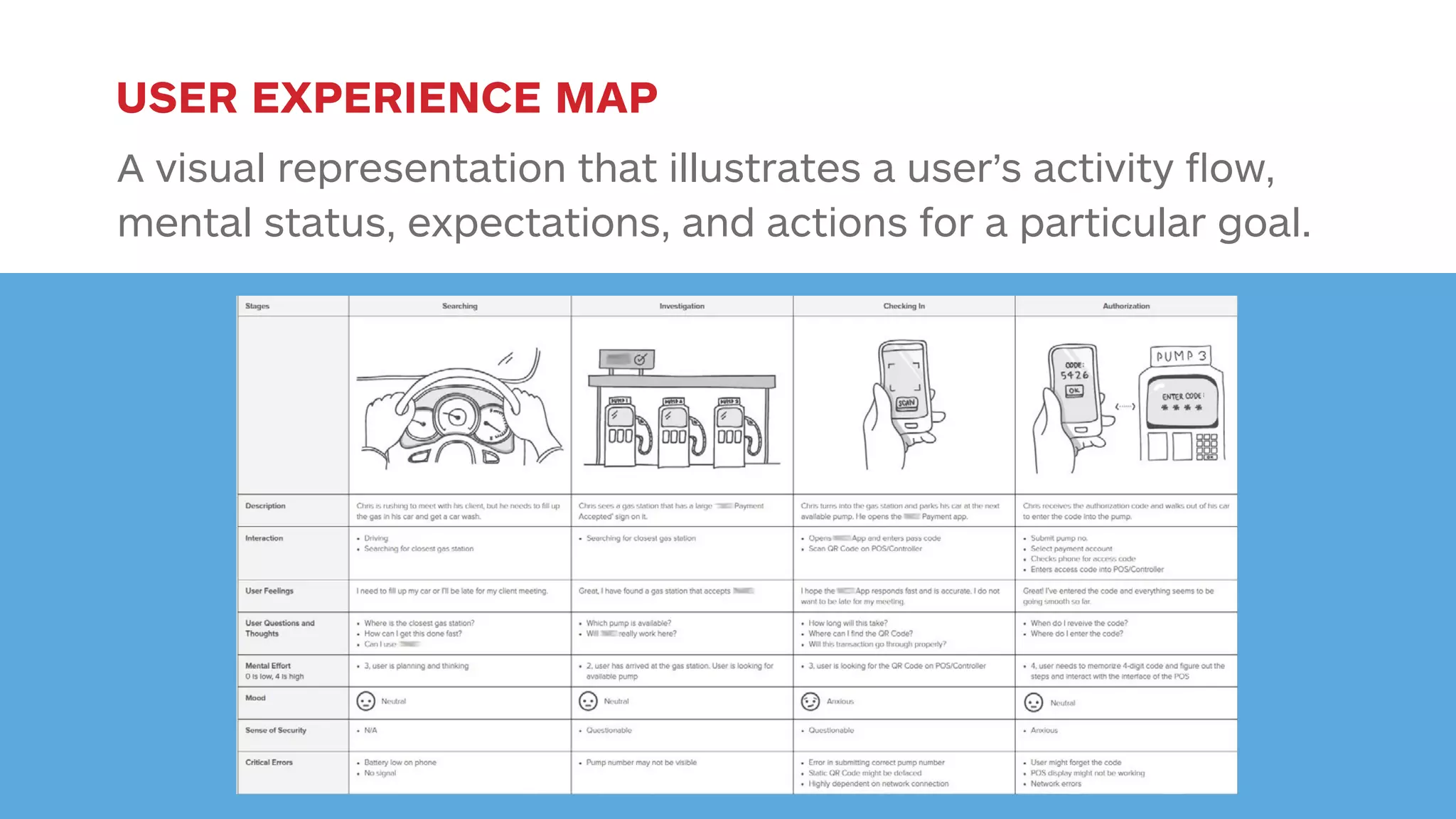
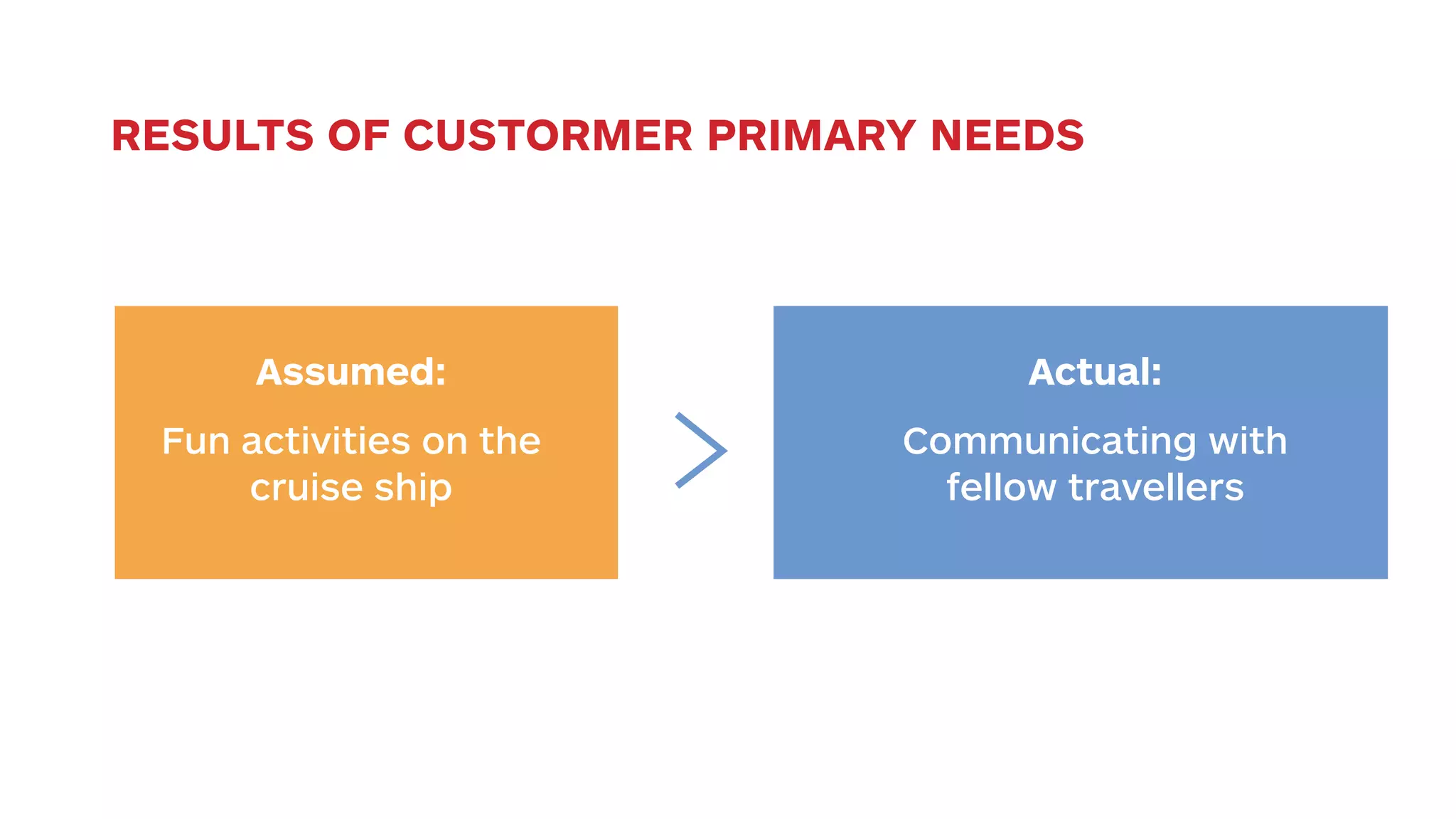
The document outlines the early-stage UX design process for mobile applications, emphasizing the importance of user experience (UX) and usability defined by the 5 E's: ease of learning, engagement, efficiency, effectiveness, and error tolerance. It contrasts mobile and desktop environments, detailing the design process from inception to implementation while highlighting the necessity of understanding end user needs through research, feedback, and iteration. Use cases and example projects, such as a universal mobile payment app, demonstrate the application of these principles in real-world scenarios.