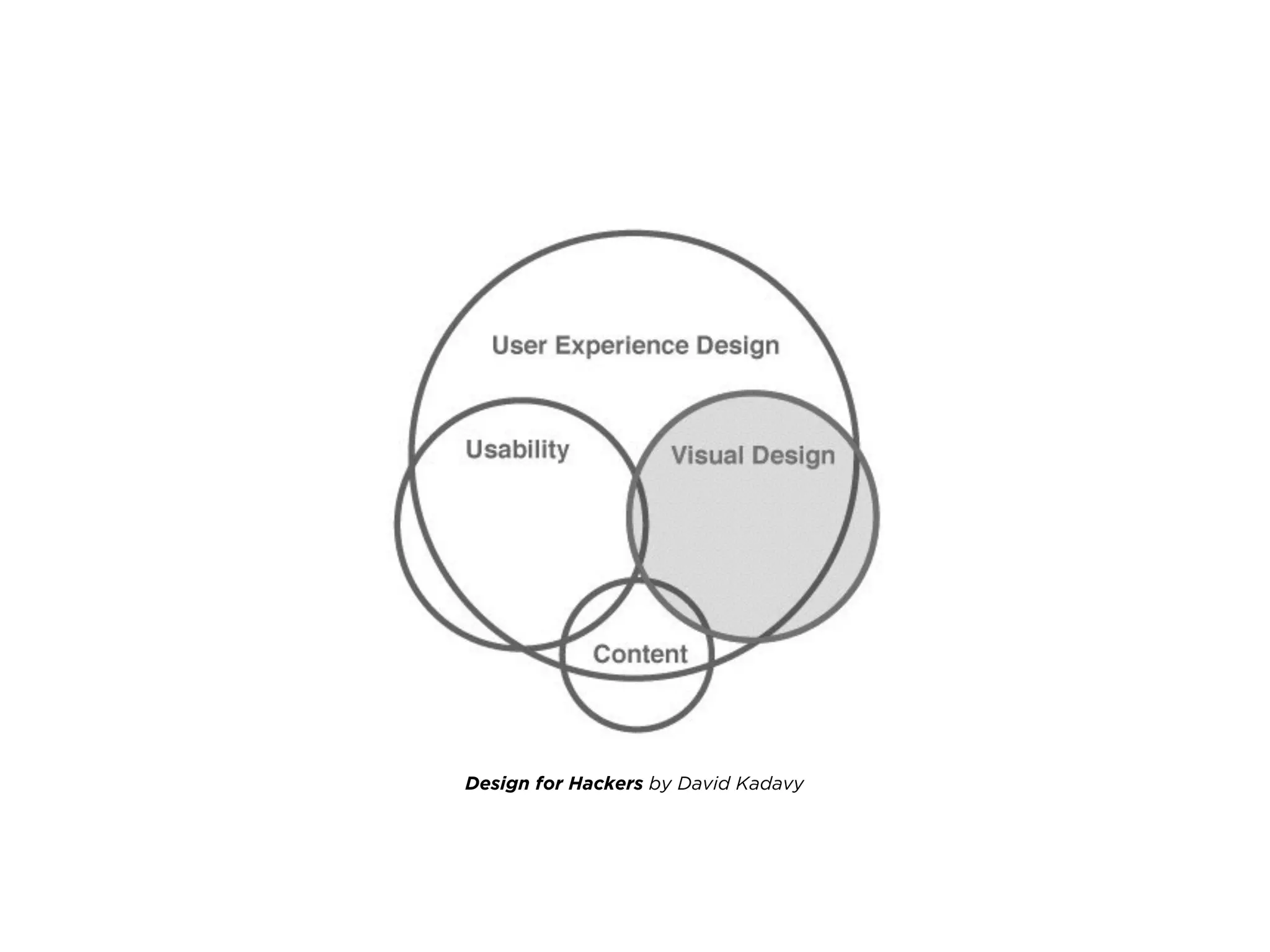
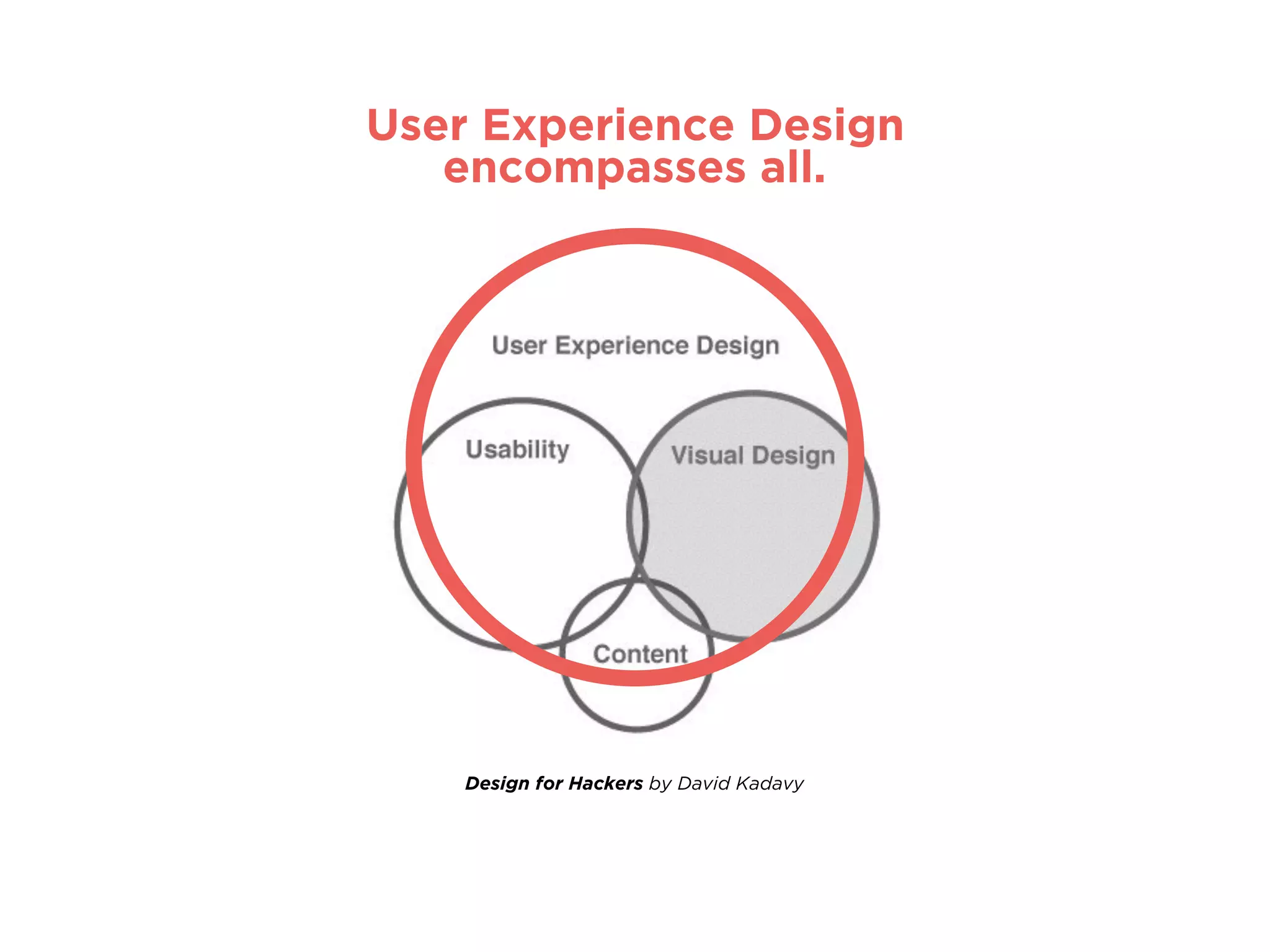
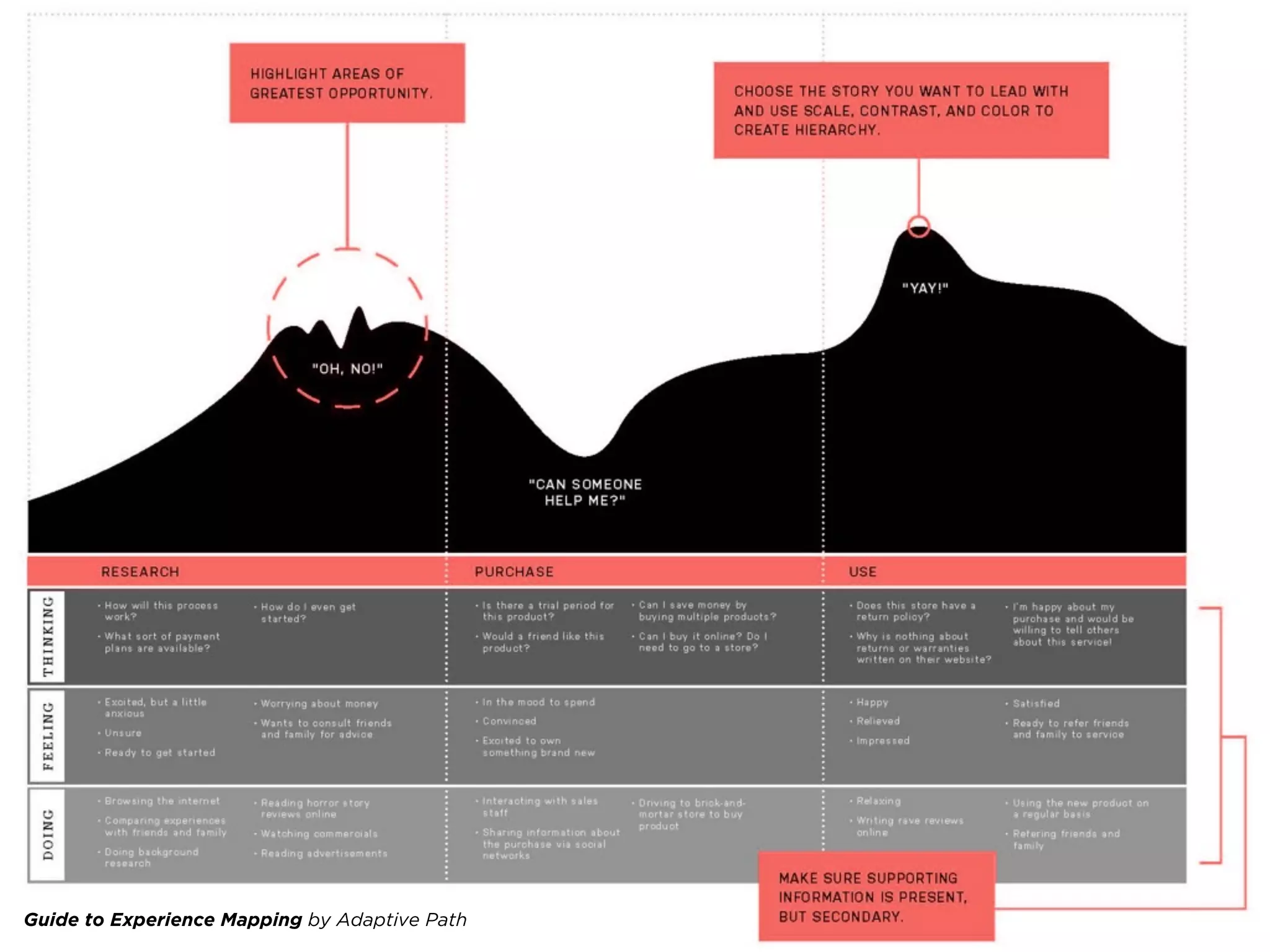
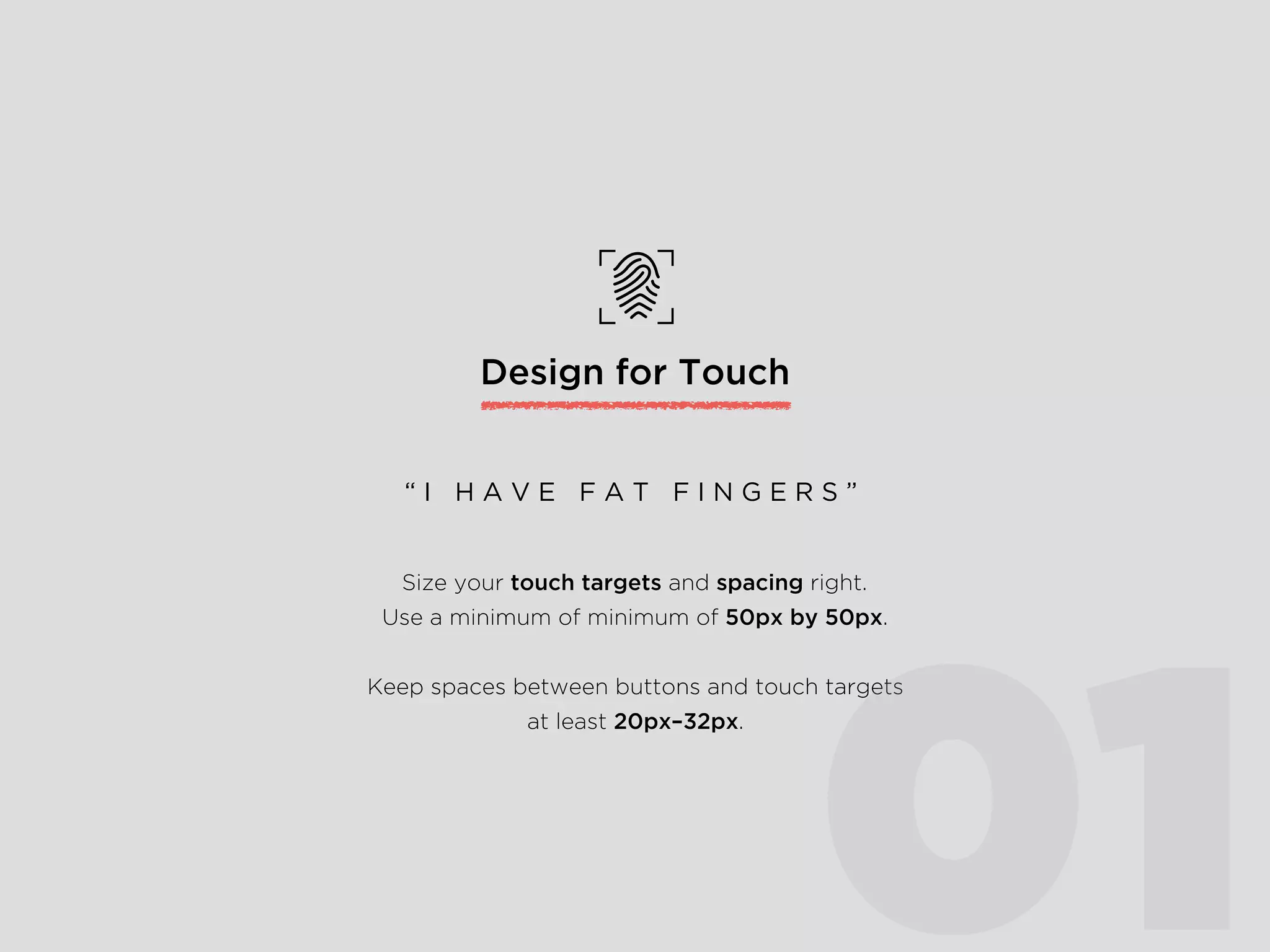
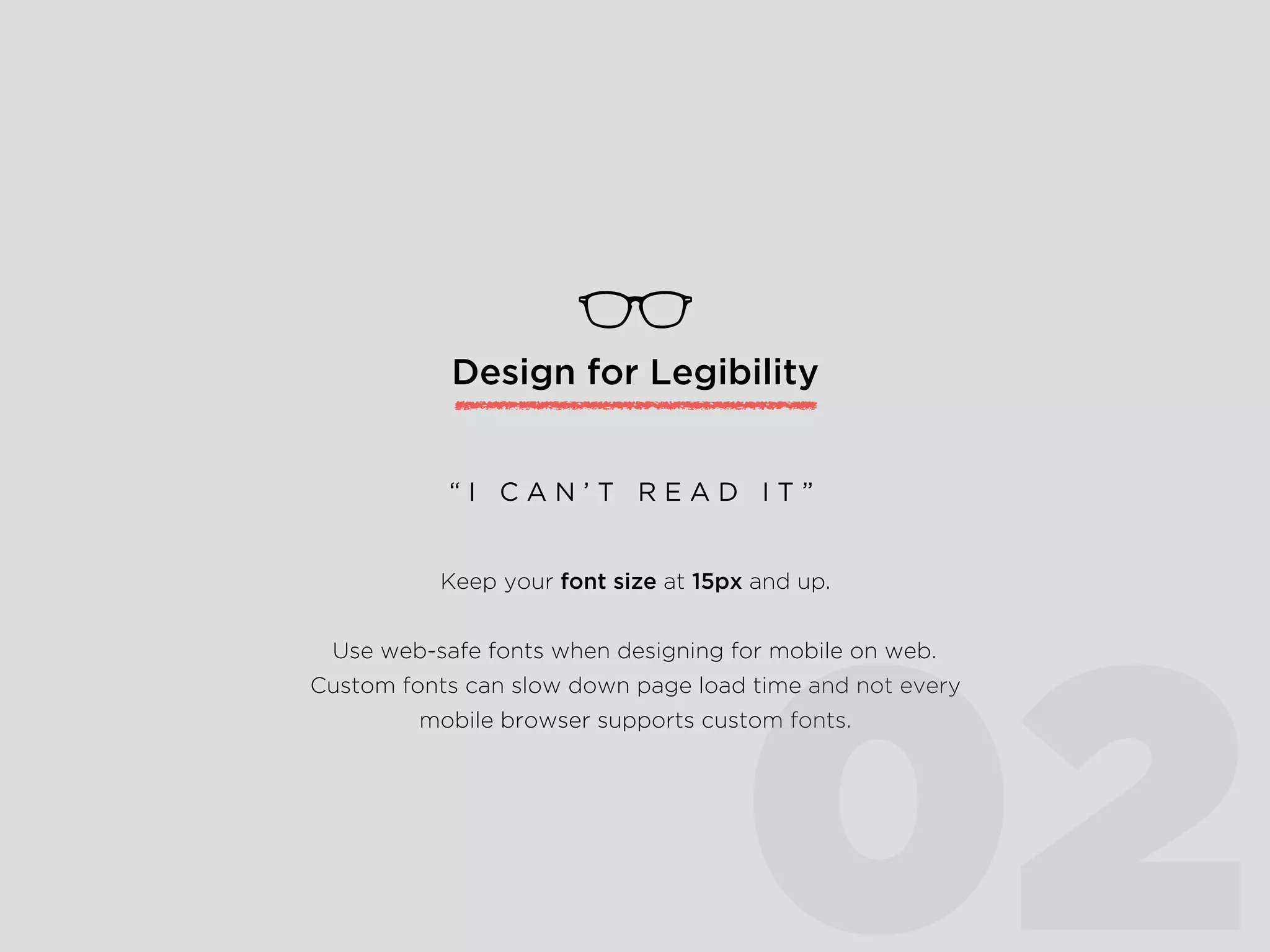
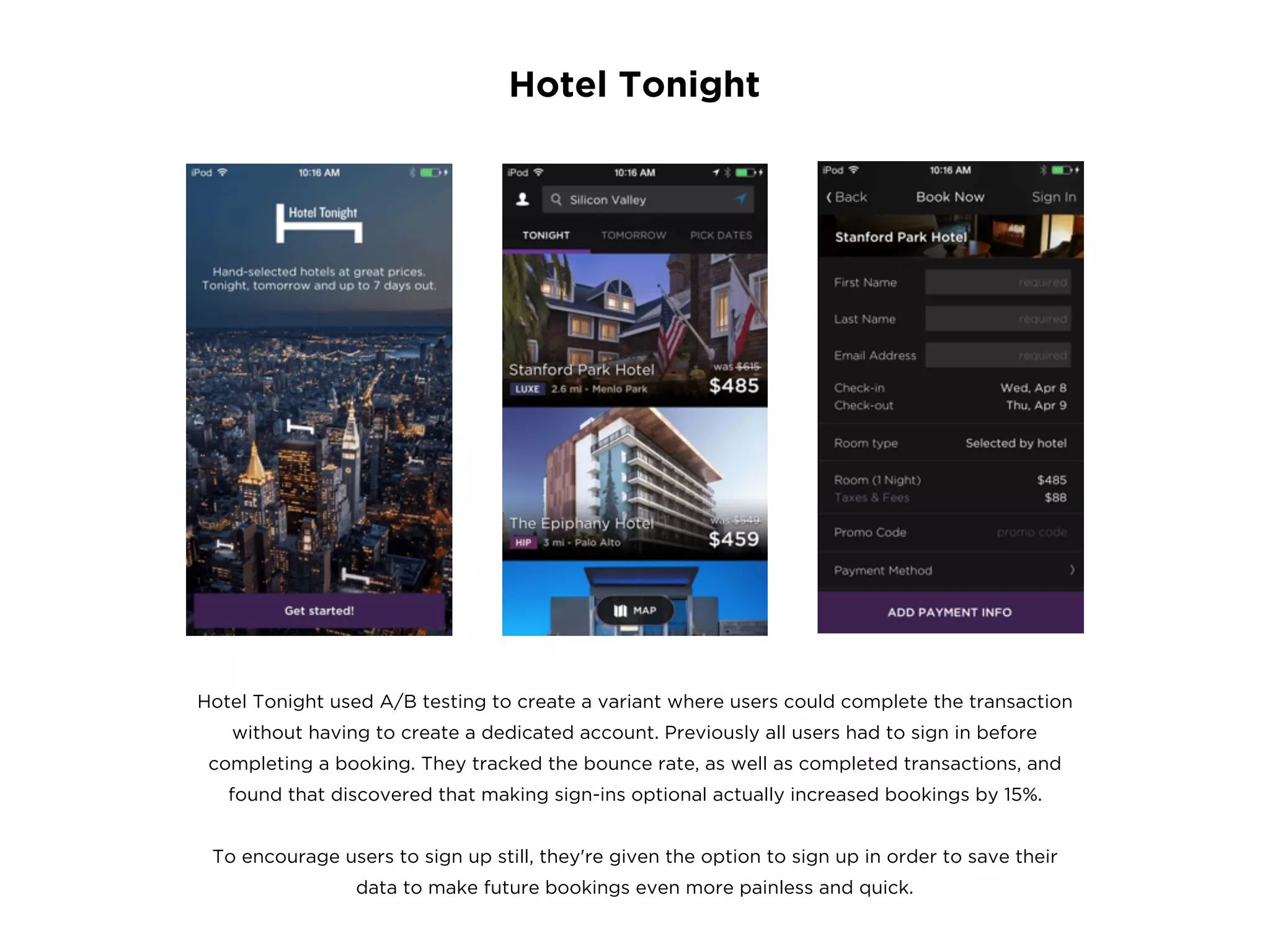
The document provides an overview of Lean UX, designing for mobile, and why enterprise UX is awesome. It discusses Lean UX methodology and practices like defining goals, designing, and testing and refining. It also covers principles of mobile design like designing for touch, legibility, and speed. Finally, it notes that while enterprise software is often seen as dull, startups are shifting perceptions by making enterprise tools easy to use, adopt, and roll out.