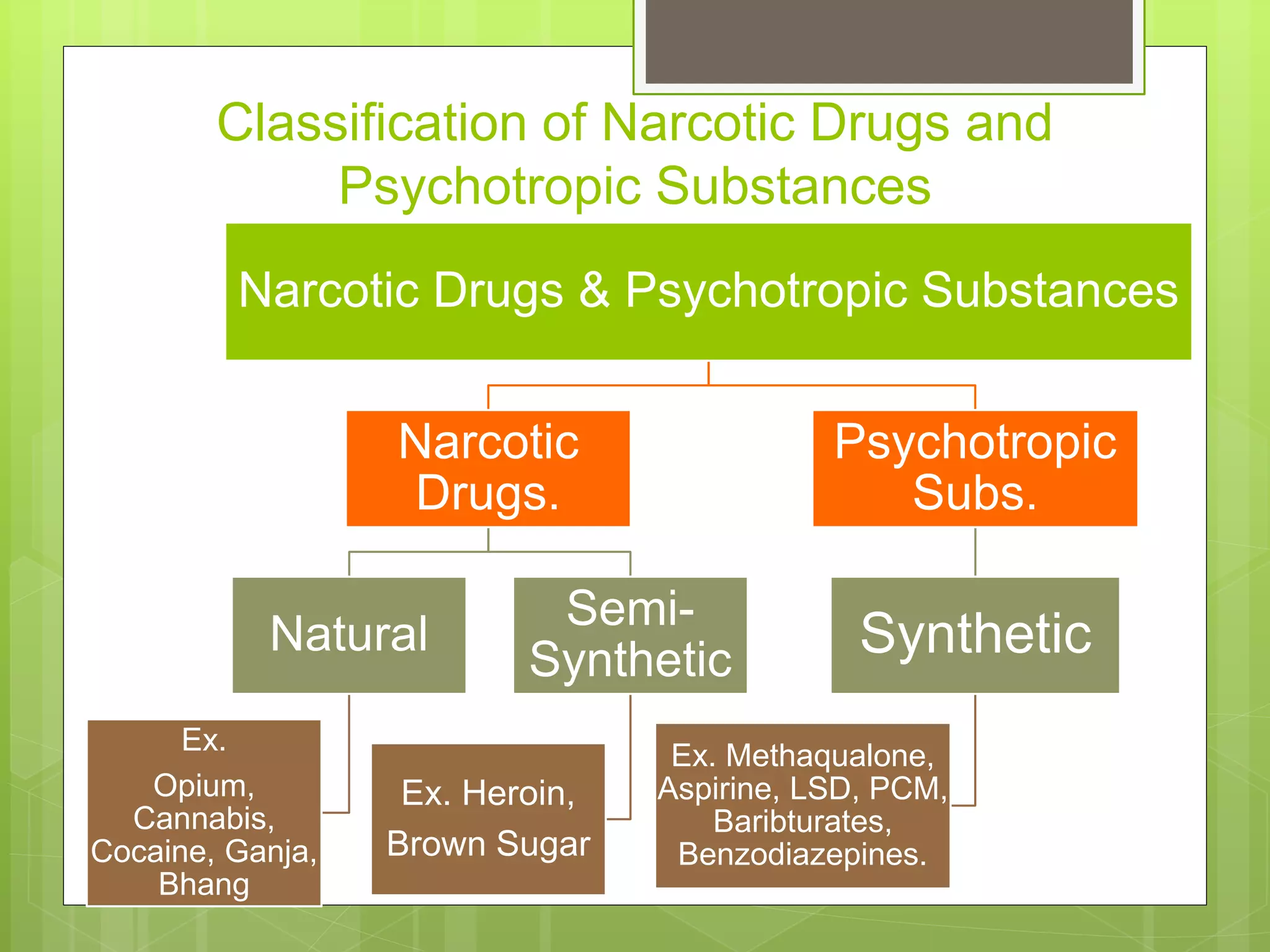
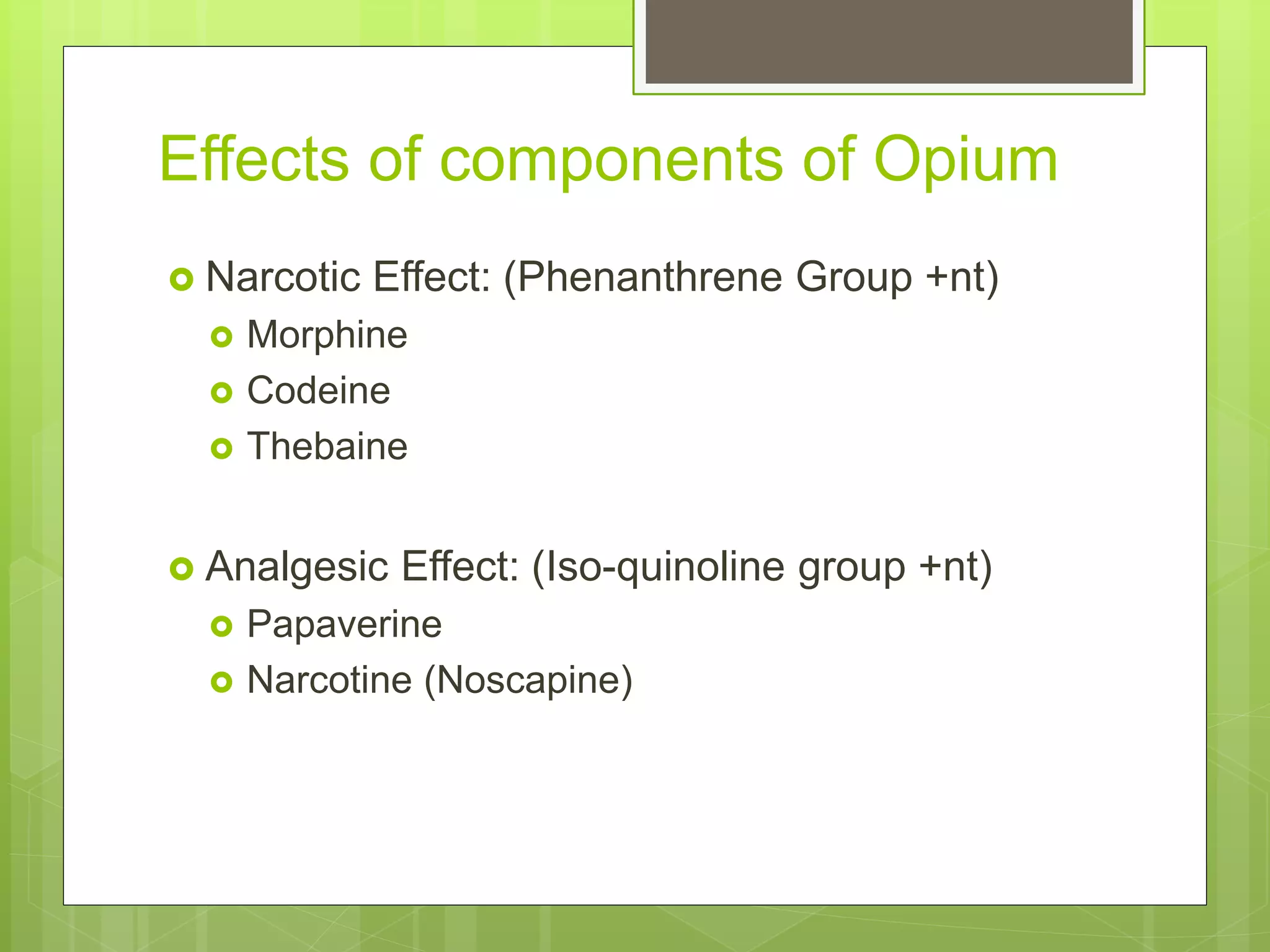
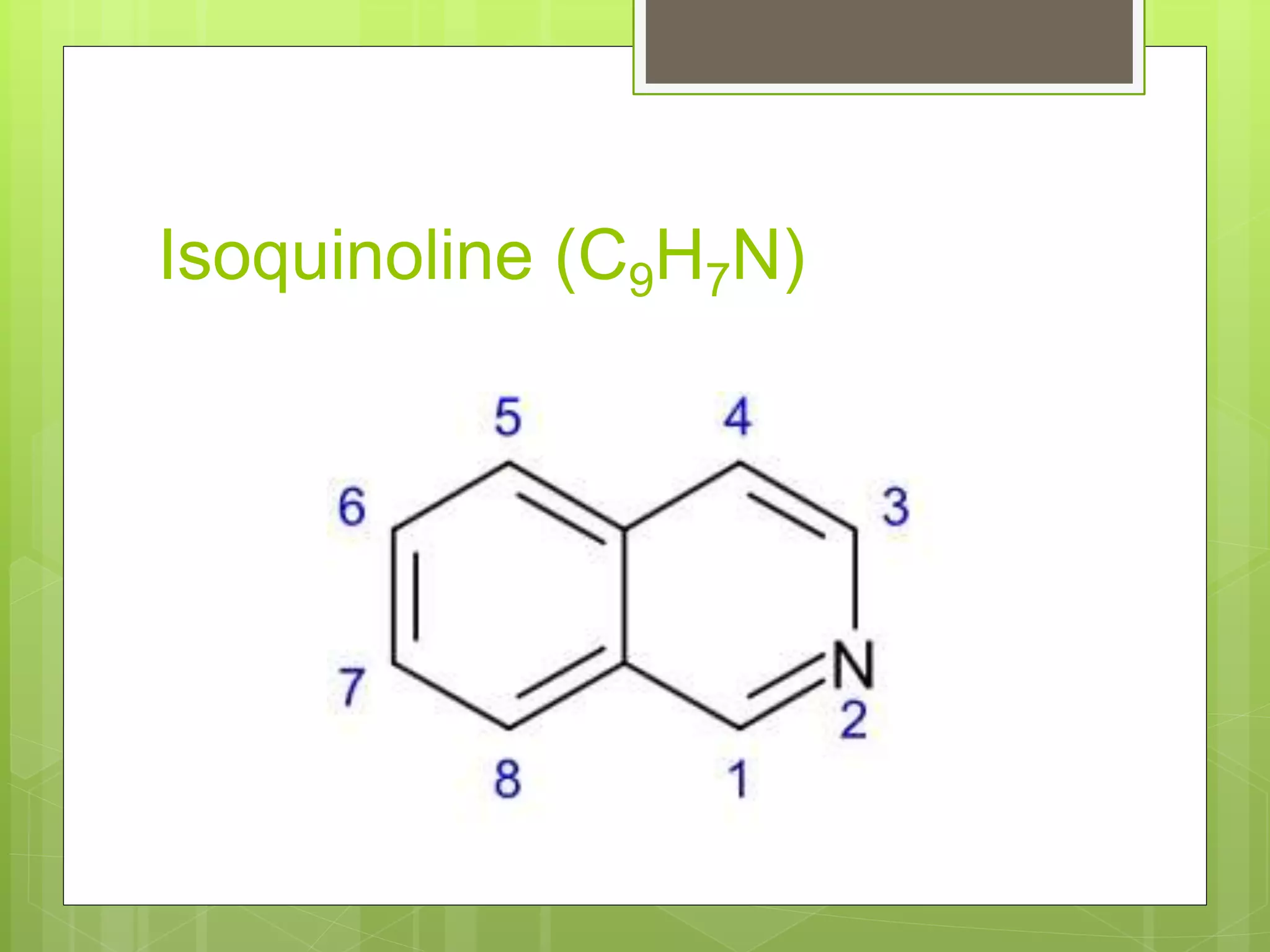
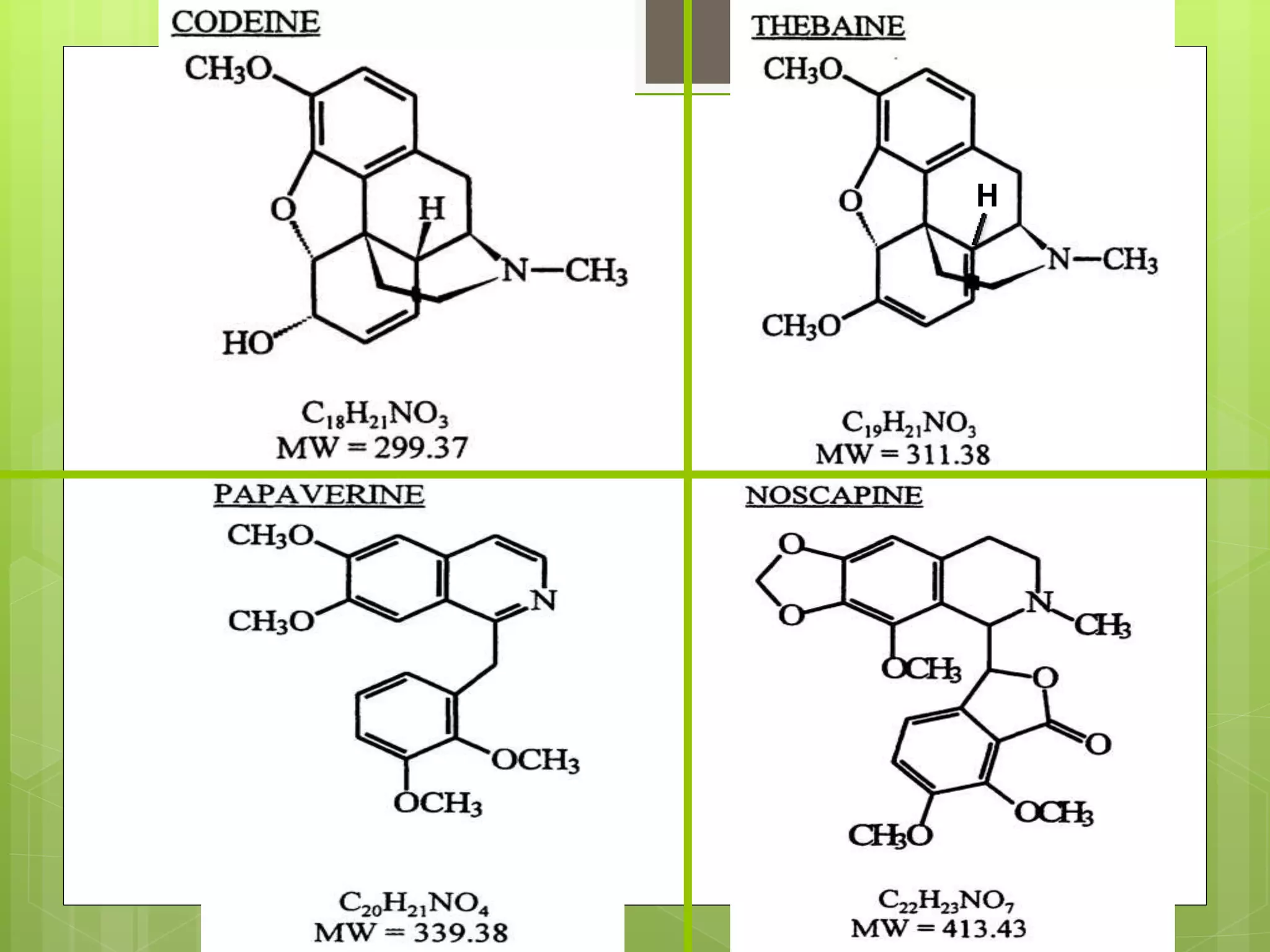
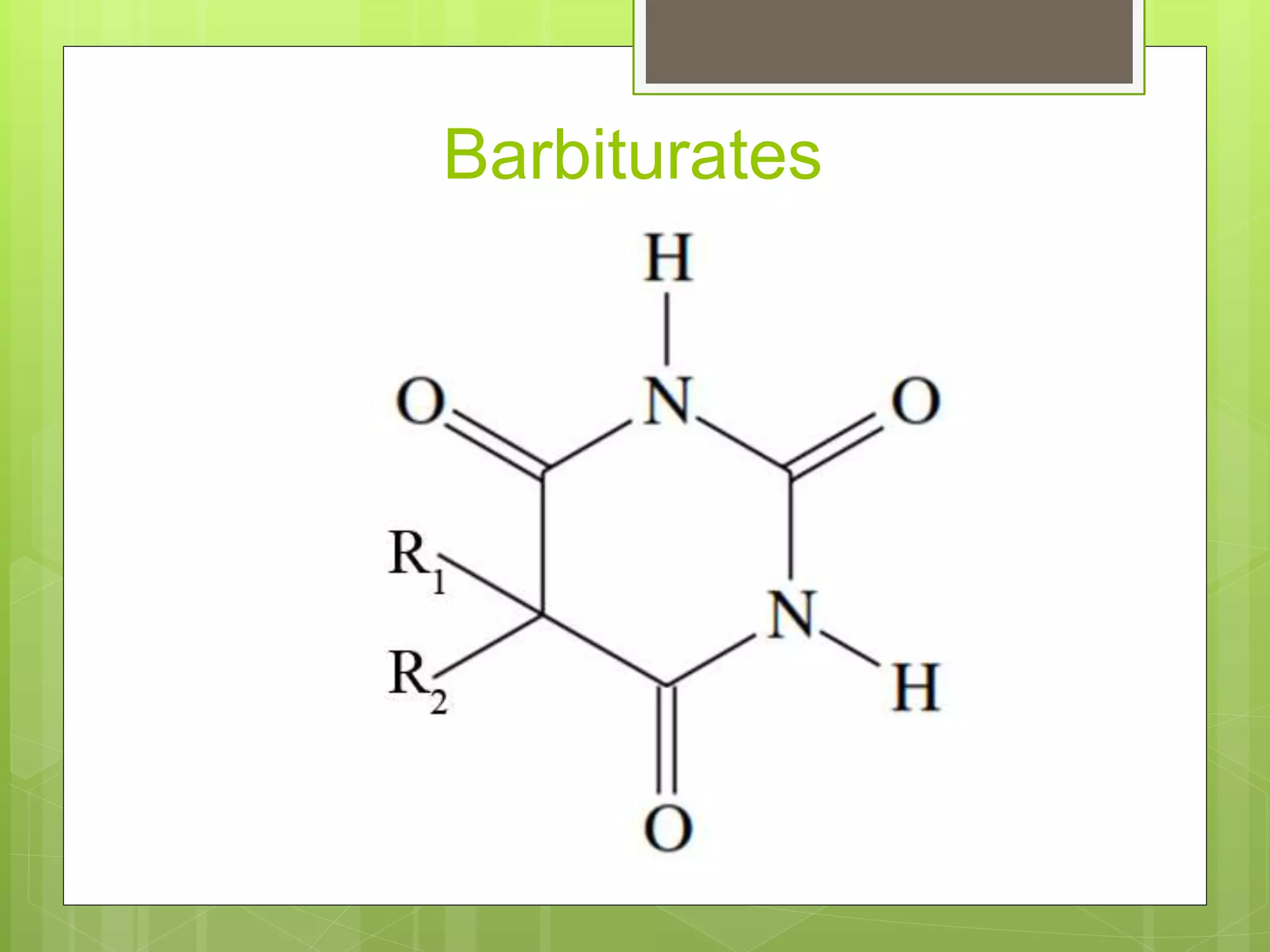
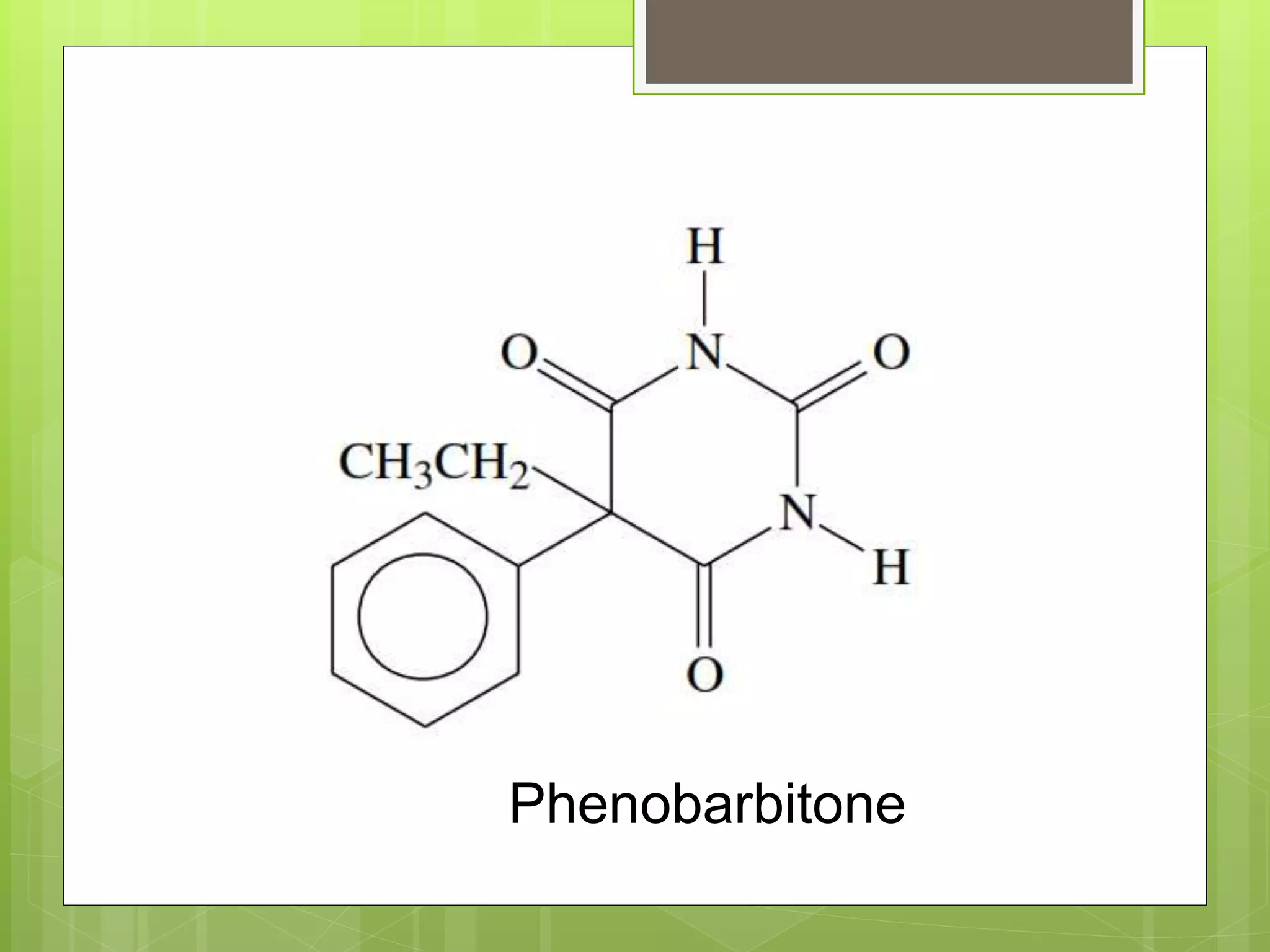
The document provides definitions and information about narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances. It discusses various types of narcotics including natural narcotics like opium, cannabis, and cocaine. It also covers semi-synthetic narcotics derived from natural drugs like heroin, as well as synthetic narcotics made wholly through chemical processes. Psychotropic substances are also defined and examples provided like methaqualone, amphetamines, and LSD. The effects and methods of analysis and extraction for key narcotics like opium, cannabis, cocaine are summarized.