Embed presentation








![Page 10
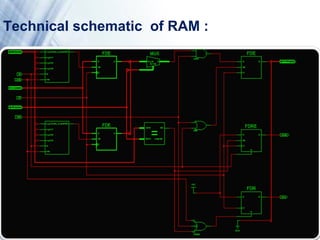
If value of read pointer and write pointer is same then it is
defined to be empty.
If write location is 31 locations next to read [3:0] then it is
defined to be full.
Program Logic:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mnr-130613014218-phpapp01/85/Mnr-10-320.jpg)



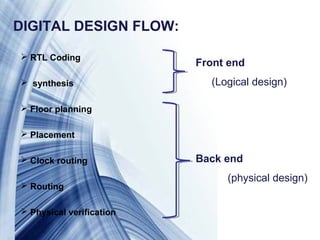
This document discusses features of VLSI chips including compactness, speed, ease of maintenance, and cost effectiveness. It describes Moore's Law, which states that the number of transistors on chips doubles every two years, causing computer performance to double every 18 months. The digital design flow includes RTL coding, synthesis, floorplanning, placement, routing, and verification. Programming languages for digital design include VHDL and Verilog HDL. RAM is used as working memory and has faster access times than hard disks, measured in nanoseconds versus milliseconds. The document outlines program logic for reading from and writing to RAM and detecting when it is empty or full.









![Page 10
If value of read pointer and write pointer is same then it is
defined to be empty.
If write location is 31 locations next to read [3:0] then it is
defined to be full.
Program Logic:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mnr-130613014218-phpapp01/85/Mnr-10-320.jpg)


