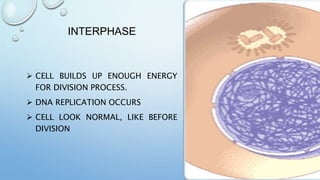
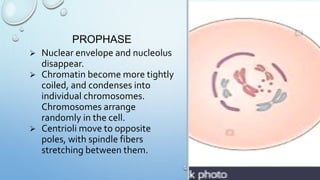
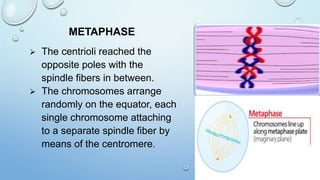
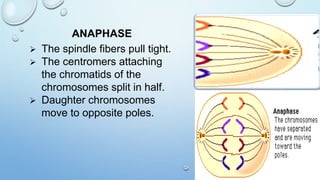
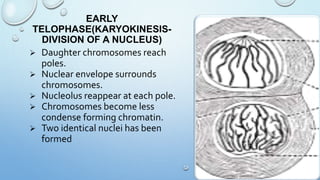
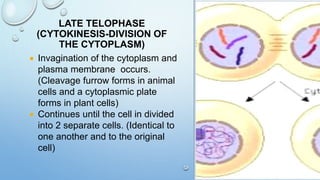
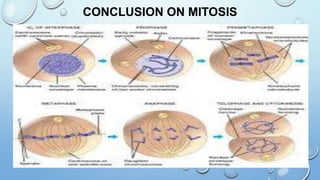
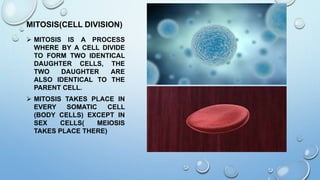
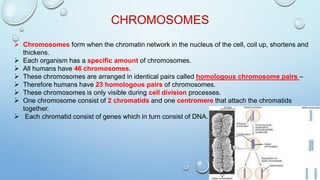
Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides to form two identical daughter cells, occurring in somatic cells but not in sex cells. It involves several phases: interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, culminating in cytokinesis, and is essential for growth, repair, and reproduction in organisms. Each human cell contains 46 chromosomes organized in 23 homologous pairs, with genetic information stored in DNA within chromatids.
![THE PHASES OF THE CELL DIVISION CYCLE
INTERPHASE (INCLUDE G1- , S- [DNA SYNTHESIS] AND G2 PHASE)
MITOSIS
CYTOKINESIS
GROWTH
THE RESULTS IS TWO NEW IDENTICAL DAUGHTER CELLS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mitosis-180827141801/85/Mitosis-3-320.jpg)