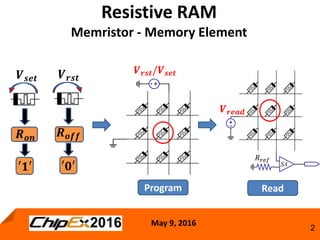
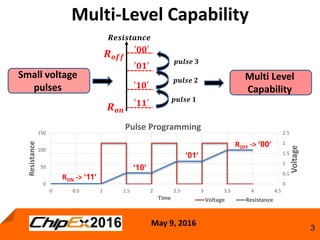
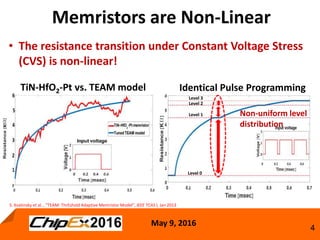
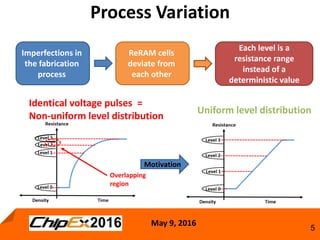
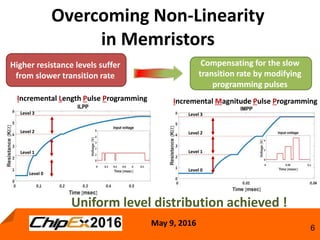
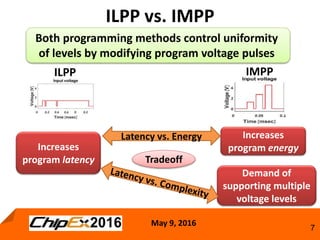
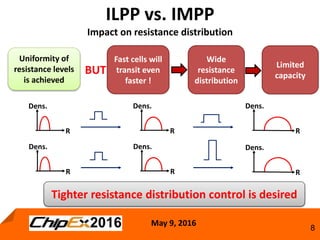
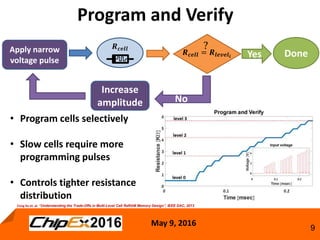
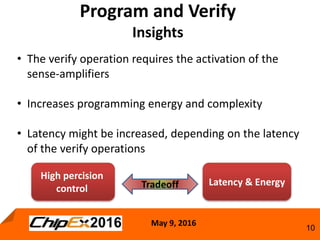
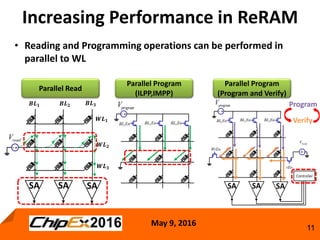
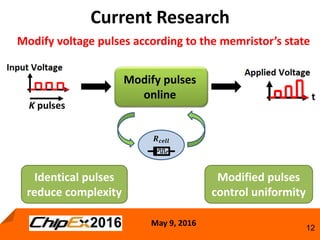
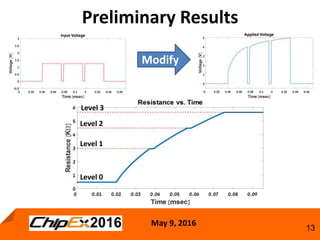
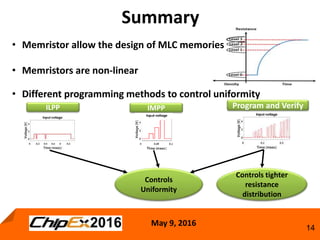
This document discusses techniques for programming and controlling uniformity in multi-level cell resistive random access memory (ReRAM). It summarizes that memristors are non-linear, leading to non-uniform resistance levels with identical programming pulses. Two methods, incremental length pulse programming and incremental magnitude pulse programming, modify the programming pulses to achieve uniform resistance distributions across levels. Program and verify methods apply narrow pulses and verify the resistance, allowing tighter control but increasing latency and energy usage. Overall, modified programming techniques are needed to overcome non-linearities and variation in memristors for multi-level cell ReRAM.