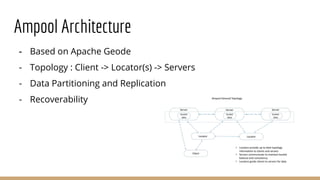
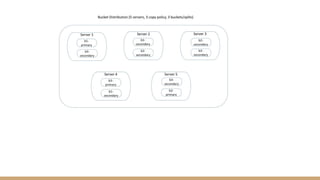
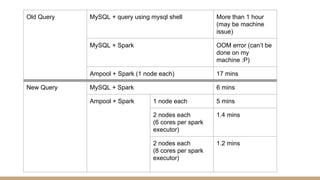
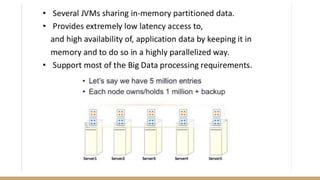
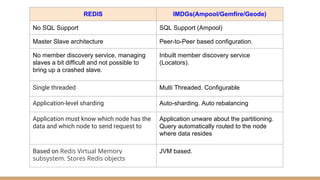
The document discusses in-memory data grids and Ampool. It describes that in-memory data grids like Ampool are sophisticated in-memory data stores that provide low latency reads and writes through data partitioning and replication across a scalable cluster. The document then provides details on Ampool's architecture based on Apache Geode, how it compares favorably to other in-memory solutions in providing both low-latency and analytics capabilities, and demonstrates its performance through examples.