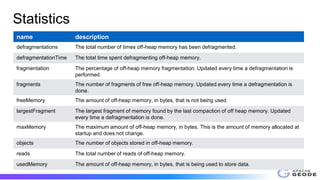
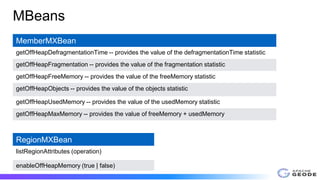
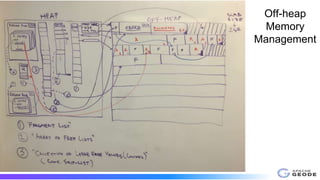
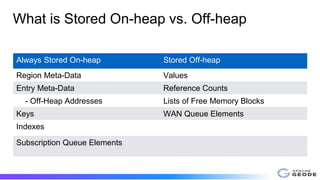
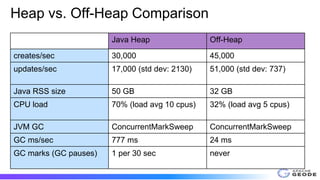
The document outlines the implementation and benefits of off-heap storage in Apache Geode, focusing on increasing data density and reducing memory overhead while maintaining throughput performance. It details usage features, startup options, resource management, monitoring, and benchmarks comparing off-heap and heap performance. Best practices and future considerations for off-heap storage are also discussed, highlighting its advantages in specific usage patterns and emphasizing the importance of minimizing fragmentation.